Typical Practice for Setting Up Access VPN
Overview
By utilizing a VPN dial-up, a secure connection between internet terminals and internal cloud platform resources is established, allowing users to securely access the intelligent cloud remotely from any location.
Requirement scenarios
Requirement scenario 1: For enterprise IT personnel to enhance the management and maintenance of cloud resources
It simplifies cloud resource operations and maintenance while eliminating the differences between managing cloud and on-premises resources.
Requirement scenario 2: For ordinary enterprise employees to provide a mobile office solution under a hybrid cloud
It accelerates the digital transformation of enterprise IT infrastructures, facilitates true mobile office experiences, and enables employees to seamlessly access the enterprise IT system as if they were on the company's intranet, anytime and anywhere.
Solution overview
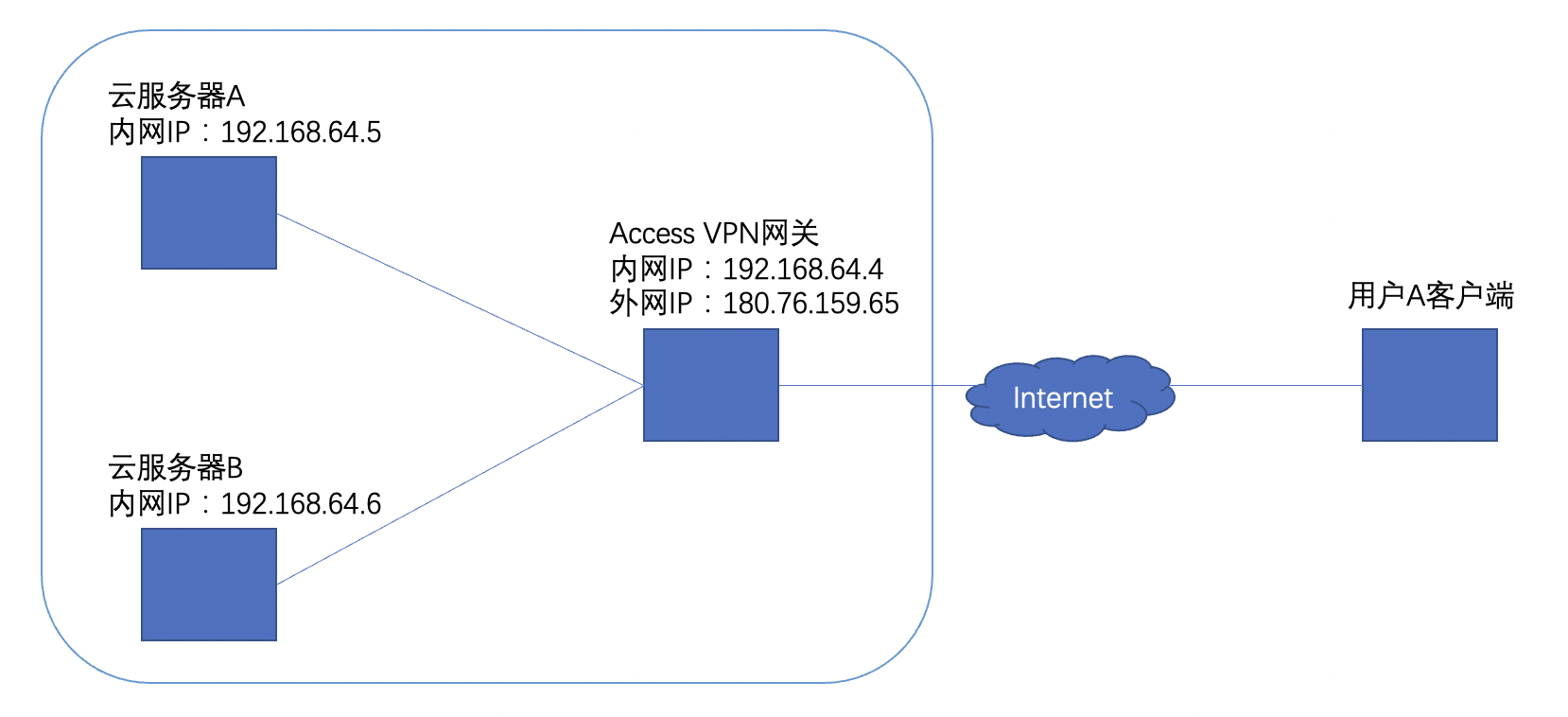
As illustrated below, users can leverage the Baidu Cloud Compute (BCC) product to configure an Access VPN server as a VPN gateway, enabling client devices to connect remotely to intelligent cloud resources. The cloud platform provides a service-integrated image embedded with the open-source OpenVPN Access Server, enabling users to quickly deploy an Access VPN service when creating a BCC using this image.
Once the service is configured, users can connect to the VPN from a PC equipped with a VPN client, achieving remote access to cloud server resources (e.g., cloud server A and cloud server B shown in the following diagram).
Configuration steps
Environment preparation
- Client: A PC or laptop that can connect to the Internet
- Server: A BCC with a bound public IP, serving as the Access VPN gateway
- Server configuration recommendation: For a concurrent connection scale of 500 users, it is recommended to use the bcc.g3.c4m16 model (Intel Xeon(Skylake) Gold 6148, 4-core CPU, 16GB memory) to support it. If only a few operation and maintenance personnel are signing in, a lower-configuration server (such as bcc.g3.c1m4) can be used
Note: The EIP bandwidth can be adjusted flexibly based on the user’s actual usage requirements.
Server (Access VPN gateway) configuration example
- The cloud platform offers users a service image equipped with the open-source OpenVPN Access Server, streamlining the process of setting up a VPN gateway. Users can purchase a BCC within the Baidu AI Cloud Console and select "Service Integration Image > Access VPN CentOS 6.5 (64-bit)" from the available image options.
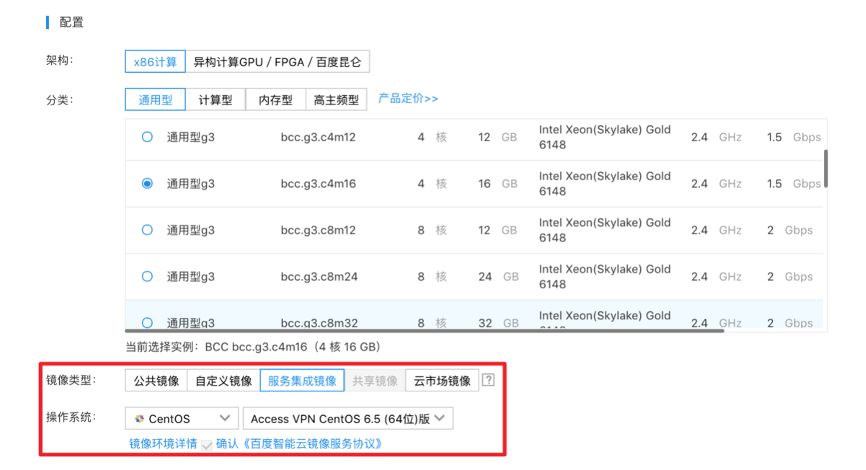
Note: Users also have the option to select an appropriate public image and manually download the VPN Server installation package to set up a VPN gateway.
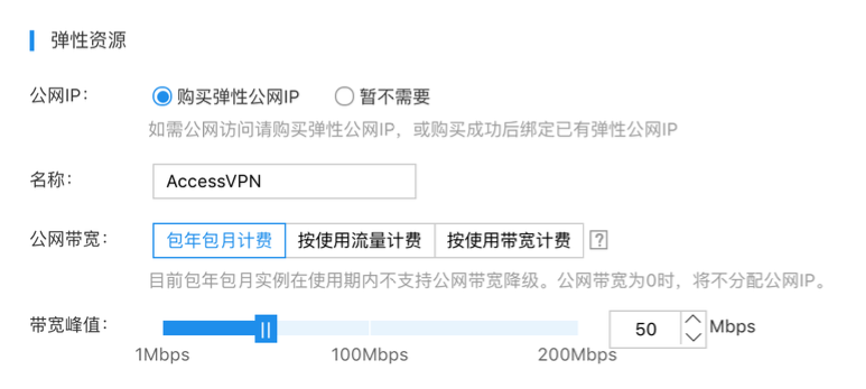
- On the purchase page, users should also select "Purchase EIP" and determine the charge type and desired bandwidth peak based on their requirements.
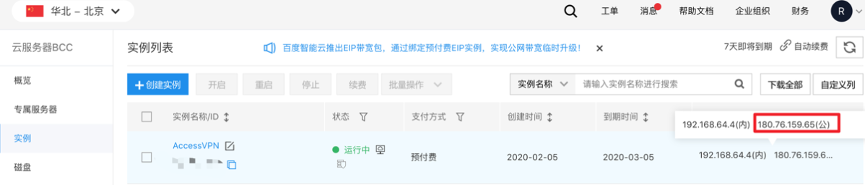
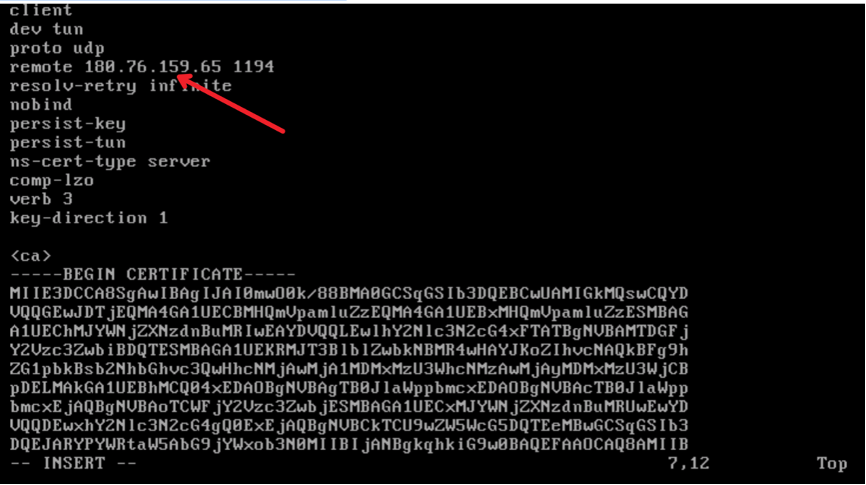
- After creating the server, copy the public IP address of the Access VPN server, which can be found on the instance list interface. For example, in the illustrated figure, the IP is 180.76.159.65.
- SSH into the Access VPN server and update the fourth line in the /root/client.ovpn file to reflect the server’s public IP address.
Taking the public IP 187.76.159.65 as an example in this example, you can use the command sed -ri "s/remote\s+\s+1194/remote 187.76.159.65 1194/g" /root/client.ovpn. The command is for reference only, and other modification methods are also acceptable.
The following figure shows the modified client.ovpn file:
- Extract the client.ovpn file from the Access VPN server and transfer it to the client machine.
- To distribute route and DNS configurations, log in to the Access VPN server, add push configuration items to /etc/openvpn/server.conf, and restart the VPN service using the command service openvpn restart.
Client (Open VPN Client) configuration example
- For Windows, Linux, or Mac systems, visit the official OpenVPN website, download, and install the client corresponding to your operating system.
- Import the client.ovpn configuration file replicated from the server into the client configuration.
- Launch the OpenVPN Client, select the imported configuration file, connect, and log in successfully.
Testing and verification
On User A's PC or laptop, where all configurations are complete, perform a Ping test to connect to the intranet IP of the cloud server BCC (the intranet IP of cloud server A is 192.168.64.5, and that of cloud server B is 192.168.64.6). A successful Ping indicates that the VPN is set up properly.
At this point, User A has successfully accessed the BCC resources within the cloud platform via the Access VPN method.
