Snapshot Overview
Overview
A snapshot is a file representing the data state of a Cloud Disk Service (CDS) at a specific point in time. By creating a snapshot at that moment, you can save CDS data, enabling disk data backup, recovery, and disk image creation.
Description:
- Currently, Baidu AI Cloud snapshots do not occupy the storage space purchased by users;
- CDS snapshot services began charging on March 13, 2020. For details, please refer to the Snapshot Billing help document;
- Baidu AI Cloud snapshots utilize multi-copy redundant storage, ensuring exceptionally high reliability of snapshot data.
Application scenarios
Snapshots provide a highly reliable data backup method and can be used for the Cloud Disk Server (CDS) in various scenarios.
- Disk backup: You can regularly back up the Cloud Disk Server (CDS) with snapshots to prevent the loss of important data on the disk;
- Disaster recovery backup: If you plan to switch OS for a BCC instance or perform major updates on the server, it is strongly recommended to take a snapshot of the disk to avoid accidentally deleting important data;
- Disk resizing: If you plan to expand the disk size or change the disk type, it is strongly recommended to take a snapshot of the disk first to prevent accidental deletion of important data on the disk;
- Disk detaching: If you plan to [detach](CDS/Disk Operation Guide/Basic Operations/Unmount Cloud Disk Server.md) or [release](CDS/Disk Operation Guide/Basic Operations/Release cloud disks.md) the disk, it is recommended to take a snapshot of the disk first to prevent the loss of important data;
- Disk rollback: If you want to rollback the data on the disk to a status at a certain point in the past, you can use snapshots to perform [disk rollback operation](BCC/Operation guide/Snapshot/Rollback snapshot.md);
- Custom image: If you want to set up a system disk environment identical to an existing one, you can create a [custom image](BCC/Operation guide/Image/Create a custom image.md) by using a snapshot to create a new system disk.
Snapshot principle
Cloud Disk Server (CDS) uses distributed storage technology. Once you create and format a cloud disk server, its logical disk is divided into multiple data blocks. When data is written, it is saved to these data blocks. Any changes to a block (like writing or deleting data) affect only that specific block.
Similarly, the industry's advanced incremental snapshot technology is utilized in the snapshot service. When creating snapshots following data changes, only the portions related to modified data blocks are updated in the snapshot. Meanwhile, unchanged data blocks remain as they were. Incremental snapshot technology greatly reduces redundancy in snapshot data, helping to lower snapshot costs.
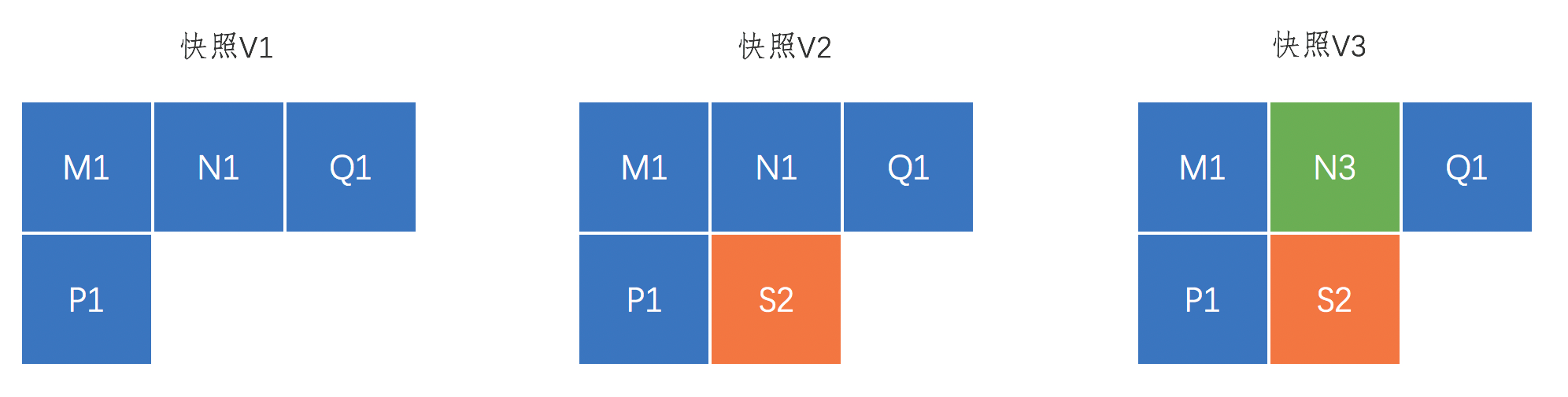
As illustrated above: Snapshots V1, V2, and V3 represent the first, second, and third snapshots taken for the disk, respectively.
Create the first snapshot
Snapshot V1 is the initial snapshot created for the disk. Its data consists of four data blocks: M1, N1, Q1, and P1.
Description:
- For most disks created before October 2017, the first snapshot is a full snapshot. This means the snapshot captures the entire disk size rather than just the data that has been written. For instance, if the purchased cloud disk is 50 GB and only 10 GB of data has been written, the first snapshot will still occupy 50 GB.
- For disks created after October 2017, the first snapshot is incremental. In the example above, the initial snapshot for the disk will occupy 10 GB, corresponding to the data written to the disk.
Create a new snapshot
Starting from the second snapshot, all snapshots for cloud disks are incremental. In the diagram above, Snapshot V2 is the second snapshot for the disk, adding one data block (S2) to the original four data blocks. All other data blocks still point to the four blocks in V1, avoiding duplicate data.
Snapshot V3 represents the third snapshot created for a disk. Compared to V2, Snapshot V3 changes only the N3 data block, while the M1, Q1, and P1 data blocks continue to reference the corresponding blocks in V1, and S2 still references the S2 block in V2. N3 represents the newly updated data block.
Delete snapshot
If the user deletes Snapshot V3, only data block N3 is removed, while other blocks with existing pointers remain intact. Deleting Snapshot V3 alone does not affect the availability of V1 or V2.
Rollback snapshot
When rolling back a disk to the state of Snapshot V3, data blocks M1, N3, Q1, P1, and S2 will all be restored to the disk, ensuring an accurate rollback of data.
Data volume in the snapshot chain
For the snapshot chain corresponding to this disk, the total capacity is 4 + 1 + 1 = 6 blocks, not 4 + 5 + 5 = 14.
Snapshot methods
Snapshots can be created manually or by configuring automatic snapshot settings.
- Manual snapshot: Manual snapshots require you to initiate them actively. For detailed operations, please refer to [Create Disk Snapshot](BCC/Operation guide/Snapshot/Create disk snapshot.md).
- Automatic snapshot: For automatic snapshots, you can add an automatic snapshot policy when creating them. For detailed operations, please refer to [Automatic Snapshot](BCC/Operation guide/Snapshot/Automatic snapshot.md).
Snapshot limit
Each cloud account can create up to 512 snapshots, consisting of 256 manual snapshots and 256 automatic snapshots.
- If the maximum automatic snapshot quota for a disk is reached, the earliest-generated automatic snapshot will be deleted automatically to make room, ensuring that new automatic snapshots are unaffected.
- If the manual snapshot quota for a disk is reached, the creation of new manual snapshots will be blocked. Please promptly delete unnecessary manual snapshots. When a disk reaches its manual snapshot limit, a small red alarm clock icon will appear next to the name of the CDS disk in the disk list on the CDS console as a warning.
Effective time of snapshot
The time required to create a CDS snapshot (manual or automatic) depends on its size, typically taking anywhere from a few seconds to a few minutes.
