System Optimization Operations (Linux)
Modify the fstab file disk identification method to UUID
Run the command: blkid on your system. The returned result is shown in the following figure:

In the cat /etc/fstab file, check the line corresponding to the root directory ("/") of the mount point. As shown in the following figure, no changes are necessary.

If the first column lists a disk partition name, as shown in the figure below, you need to edit the /etc/fstab file and replace the disk partition name /dev/vda1 with the format [UUID=xxxxxxx].

Modify the grub file disk identification method to UUID
When creating an instance from an imported image, it is highly recommended to use the UUID in the grub configuration file to identify the boot disk and ensure the system boots successfully.
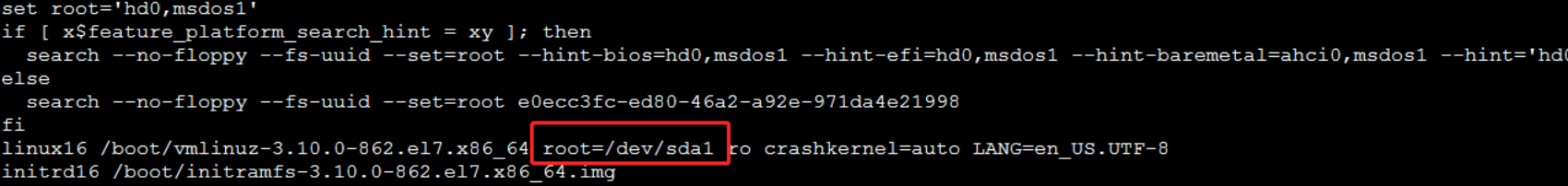
Using CentOS 7 as an example, check the /boot/grub2/grub.conf file. If it displays root=UUID=ID, no changes are necessary.
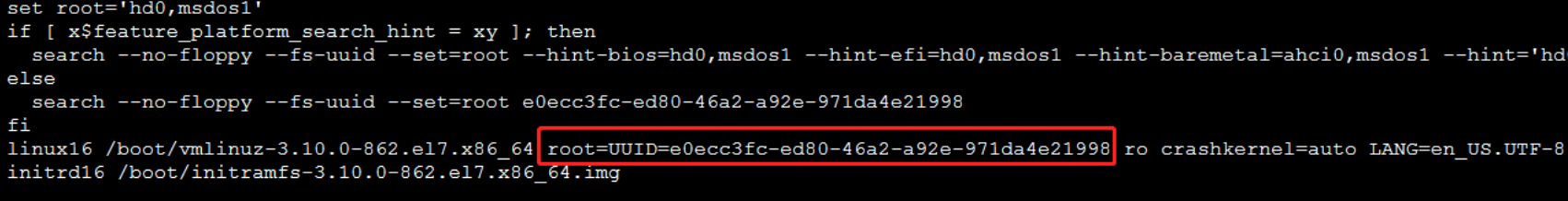
If it displays root=/dev/, you need to use the blkid command to find the UUID of the corresponding disk partition and then update it to the root=UUID=ID format in the /boot/grub2/grub.conf file.
Check grub startup parameters
Before importing the image to Baidu AI Cloud Platform, you need to check the startup parameters in the grub configuration file:
Taking CentOS7 as an example, view/boot/grub2/grub.cfg
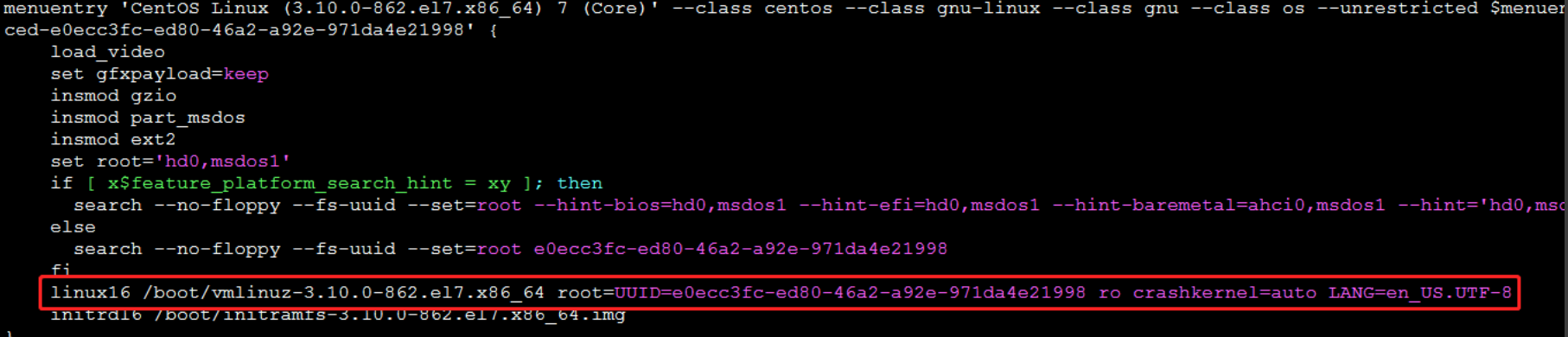
As shown in the figure, verify in the menuentry section whether the parameter "console=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200" is present in the red box.
If the parameter is missing, edit the /boot/grub2/grub.cfg file and add "console=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200" after the ro parameter.
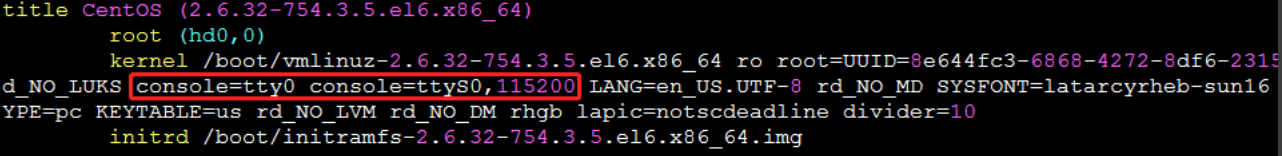
Note: For CentOS6 systems, console=tty0 console=ttyS0,115200 also needs to be placed after the root parameter, as shown in the following figure:
Note: The grub startup parameters for ubuntu systems are console=tty1 console=ttyS0,115200n8
Configure DNS
You must configure DNS settings to ensure normal network connectivity after importing your image.
- CentOS/RHEL
Taking the network interface card eth0 as an example, edit /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 and add the following settings:
RES_OPTIONS="rotate timeout:1"
- Debian/Ubuntu
Edit the /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/tail file and add the following content to the end of the file:
options rotate timeout:1
- openSUSE
Edit /etc/sysconfig/network/config and find "NETCONFIG_DNS_RESOLVER_OPTIONS" and modify it to:
NETCONFIG_DNS_RESOLVER_OPTIONS="timeout:1 rotate"
Clear network rule file
Before importing your server system to Baidu AI Cloud, make sure the /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules file is empty.
Run the following code in the command line: cat /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules. If the returned information contains the following content:
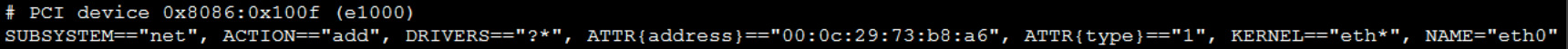
Delete all similar entries or completely remove the /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules file.
Disable the firewall
Using a CentOS system as an example.
For CentOS6 system, run the following command in the terminal:
chkconfig iptables off
For CentOS7 system, run the following command in the terminal:
systemctl disable firewalld
Disable SELinux on CentOS system
Edit the /etc/selinux/config file and change SELINUX=enforcing to SELINUX=disabled.
