Container network accesses the public network via NAT gateway
1. Overview
In some scenarios, the users should enable the nodes and pods in the K8S cluster CCE to access the public network. To access the external source address to download and install software and containers through the yum install and other commands, some services, etc. in the public network should be accessed. We provide the following two plans to enable the cluster to access the public network. The users can select by themselves according to specific requirements.
This document primarily introduces how containers access the Internet under two network modes: VPC-ENI and VPC Route.
1.1 Related concepts
- EIP, or Elastic IP, is a service provided by Baidu AI Cloud that can be attached to CCE nodes, BLB, NAT gateways, and other services, enabling those resources to access the public network.
- NAT gateway: The NAT gateway of Baidu AI Cloud supports the connection of BCC, DCC and other instances in the user VPC subnet to the public network, and realizes the conversion of the intranet IP into the public IP address by the NAT gateway. Node subnet: The users can select the VPC subnet where the node is located when creating the CCE work node. The subnet type is general-purpose subnet. Nodes in the general-purpose subnet can mount EIP directly to access the public network, and can also access the public network through NAT gateway.
2. Prerequisites
To configure pod Internet access, ensure the required products are purchased and properly set up.
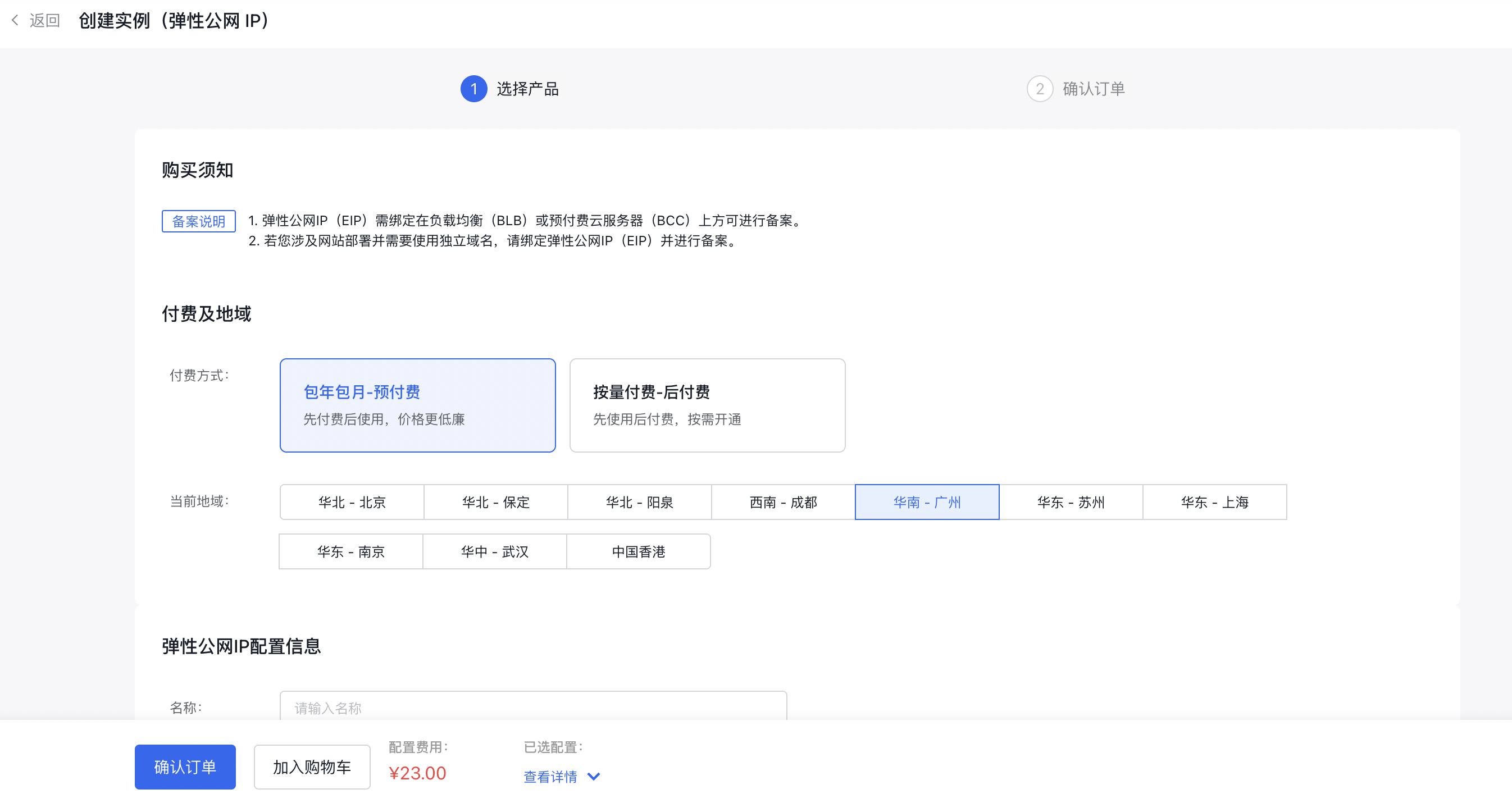
2.1 Create EIP
Go to the EIP console, select "Create Instance," and acquire a new EIP.
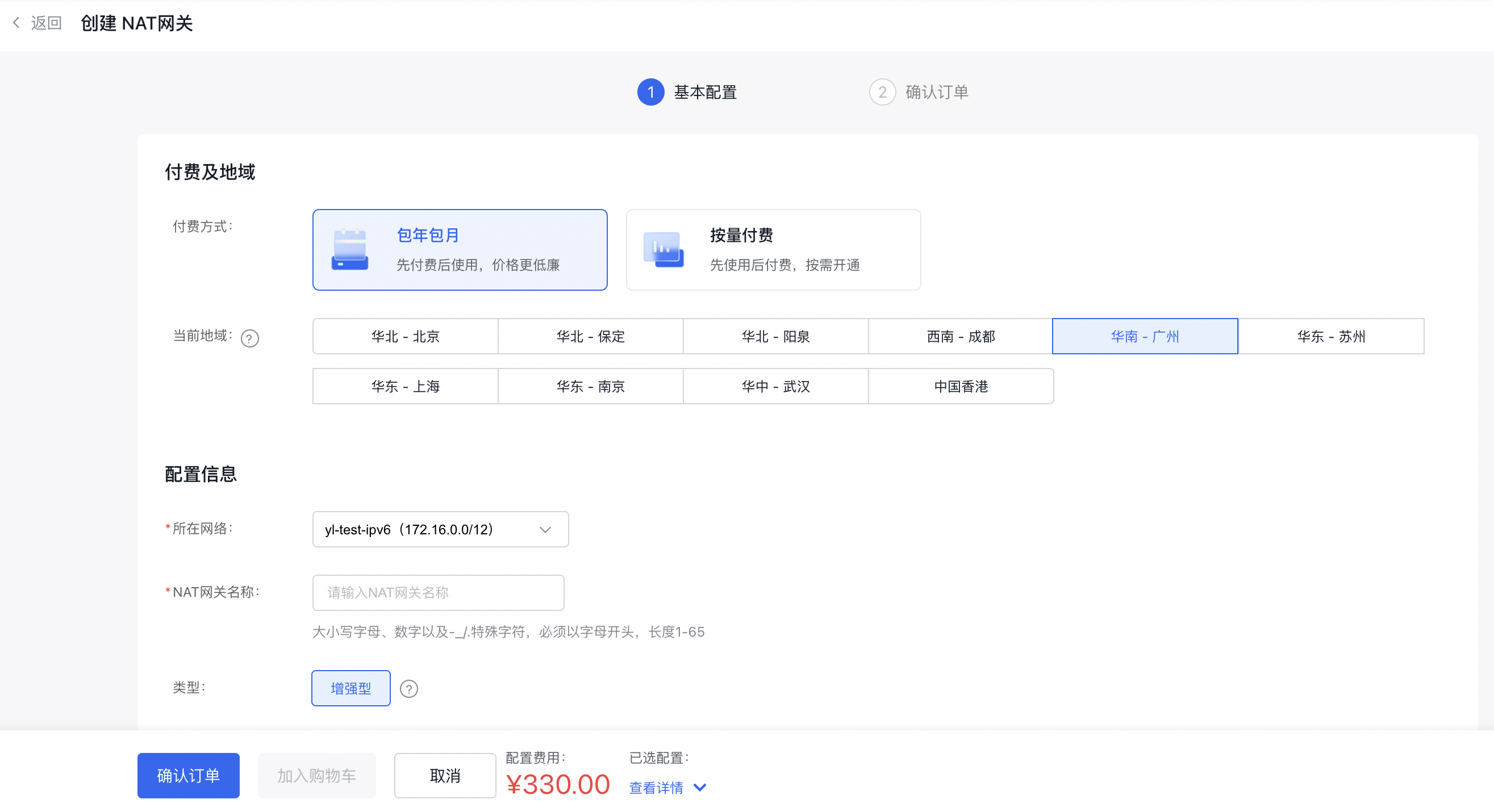
2.2 Create NAT gateway
Access the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) console, choose the appropriate VPC, create a NAT gateway instance, and assign the newly created EIP to the SNAT configuration of the NAT gateway.
3. Enable the capability of container accessing public network
3.1 Enable the capability of node accessing public network
If a node requires direct access to the public network, you need to configure both SNAT rules and custom route settings.
3.1.1 SNAT rule configuration
In the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) -> NAT Gateway Console, select the NAT gateway instance, configure SNAT, and add the subnet containing nodes that need public network access to the new SNAT entry.
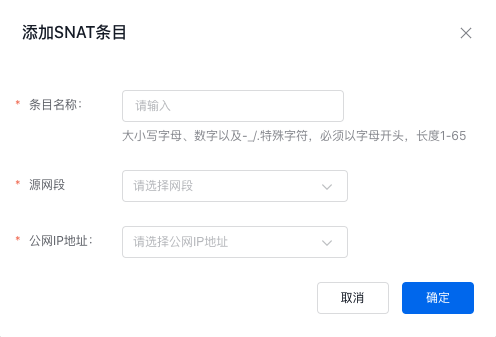
- Select the subnet where the node allowed to access public network resides as the source network segment
- Select the corresponding EIP instance for the public IP address
3.1.2 Custom route rule configuration
In the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) -> Route Table console, navigate to the target VPC's route table and create a new route entry.
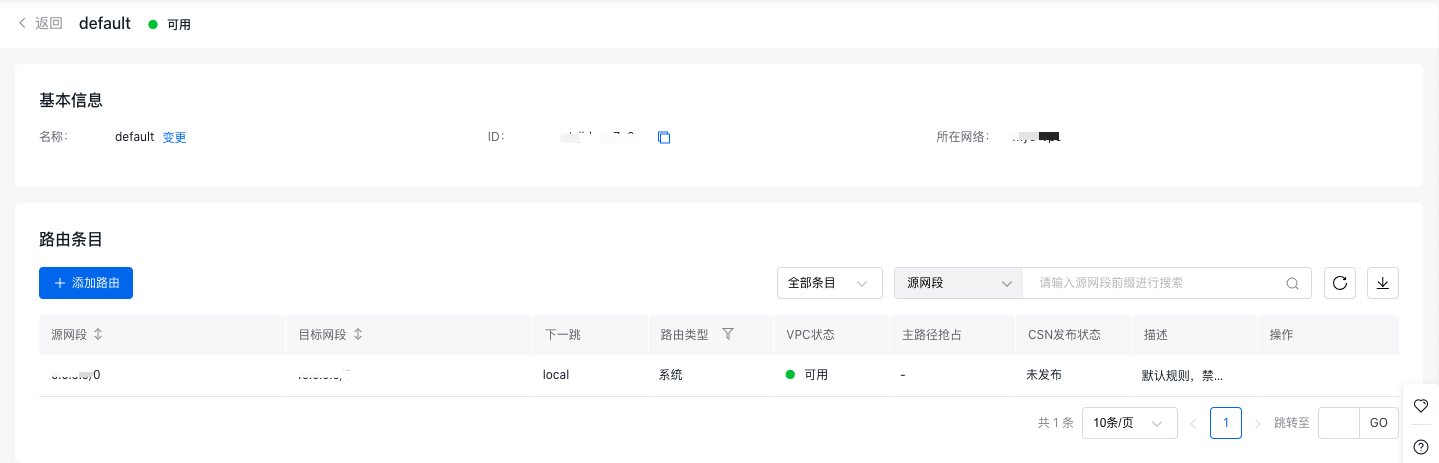
- Choose the subnet hosting the node that requires public network access as the source network segment.
- For the destination network segment, set it to 0.0.0.0/0 or the CIDR of the Internet service you wish to reach.
- Select NAT gateway as the route type
- For the next instance, select the NAT gateway with pre-configured SNAT rules
Once these configurations are completed, you can verify the node's network connectivity to ensure it can access the public network.
3.2 Container accessing public network in VPC-ENI mode (optional)
3.2.1 Confirm the container network mode information
When creating a cluster, the container network mode must be selected. Navigate to CCE, select an existing cluster, go to the Cluster Details page, and verify the container network mode and pod subnet settings. In this example, the cluster uses a VPC-ENI container network with two subnets configured.
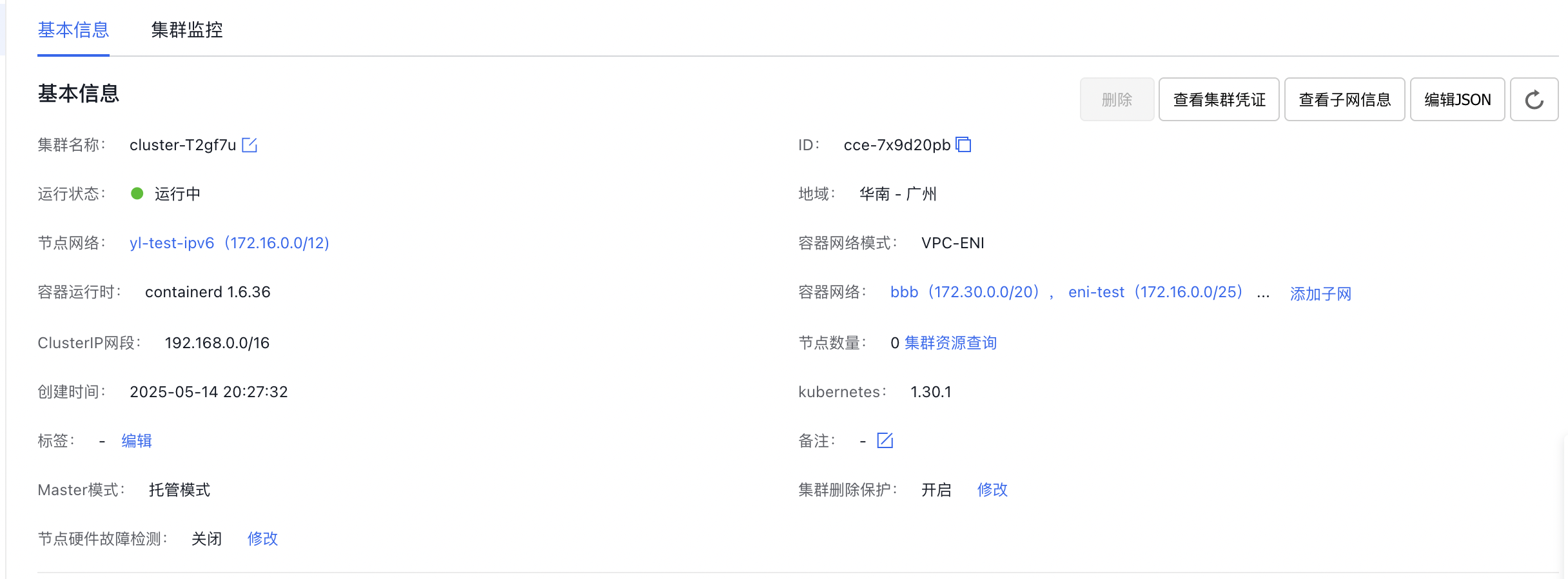
3.2.2 SNAT rule configuration
In the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) -> NAT Gateway console, choose the NAT gateway instance, configure SNAT, and add the subnet containing nodes that need to access the public network to the new SNAT entry.

- Select the subnet where the container allowed to access public network resides as the source network segment
- Select the corresponding EIP instance for the public IP address
Note
For each subnet containing containers that need public network access, proactively add SNAT rules.
3.2.2 Custom route rule configuration
In the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) -> Route Table console, navigate to the route table of the target VPC, and add a new route entry. Configure a route pointing to the NAT gateway for all container subnets that require public network access.
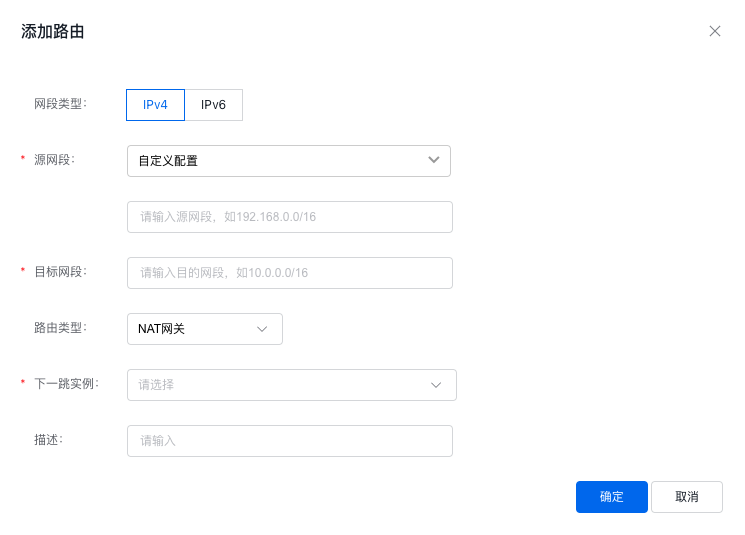
- Select the subnet where the Pod permitted to access the public network is located as the source network segment.
- For the destination network segment, set it to 0.0.0.0/0 or the CIDR of the Internet service you wish to reach.
- Select NAT gateway as the route type
- For the next instance, select the NAT gateway with pre-configured SNAT rules
At this stage, the configuration for pods accessing the public network under the VPC-ENI container network is complete, and you can verify network connectivity within the container.
3.3 Container accessing public network in VPC route mode (optional)
3.3.1 Confirm the container network mode information
The container network mode is determined during cluster creation. Go to CCE -> select an existing cluster, enter the Cluster Details page, and reconfirm the container network mode and pod subnet information. In this example, the cluster uses VPC route container networking with the container network segment set to 172.21.0.0/16.
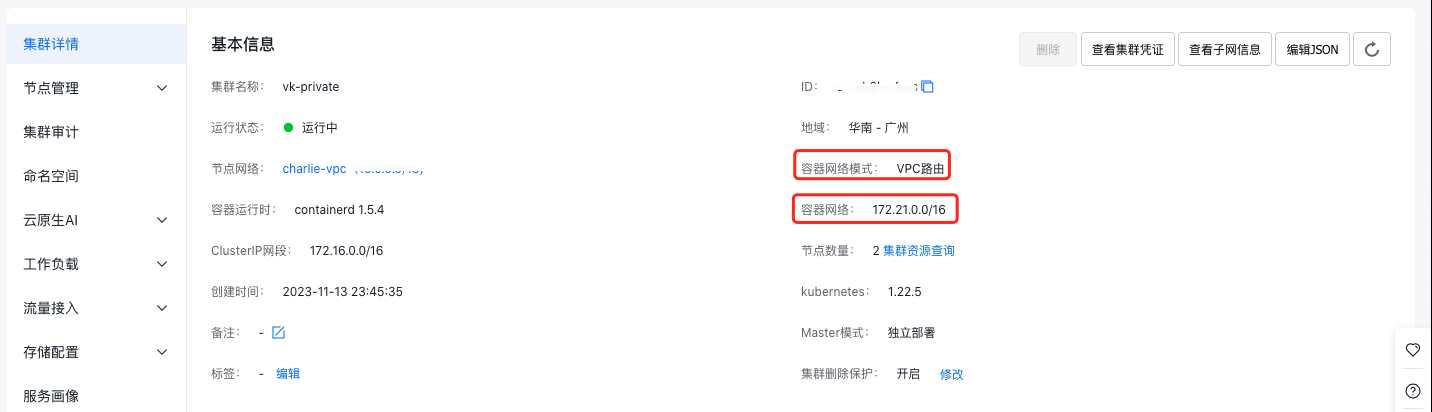
3.3.2 SNAT rule configuration
In the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) -> NAT Gateway console, choose the NAT gateway instance, configure SNAT, and add the subnet containing nodes that need to access the public network to the new SNAT entry.

- Choose custom configuration for the source network segment and specify the container network segment permitted to access the public network (e.g., 10.22.0.0/16).
- Select the corresponding EIP instance for the public IP address.
3.3.3 Enable route relay
In the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) console, select the target VPC instance to enable the route relay switch. In a VPC route container network, if pod IP addresses are outside the VPC address range, enabling the route relay function is necessary for adding custom routes with source network segments beyond the VPC.
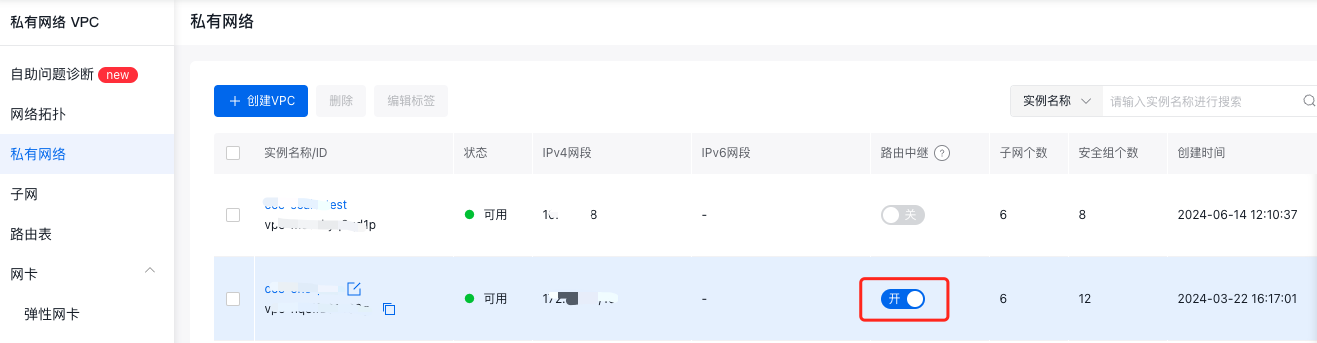
Once the route relay function is activated, the route table can forward traffic not originating from the local VPC. By default, this option is disabled, meaning the route table only forwards traffic originating from this VPC.
3.3.4 Custom route rule configuration
In the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) -> Route Table console, navigate to the route table of the target VPC, and add a new route entry. Configure a route pointing to the NAT gateway for all container subnets that require public network access.
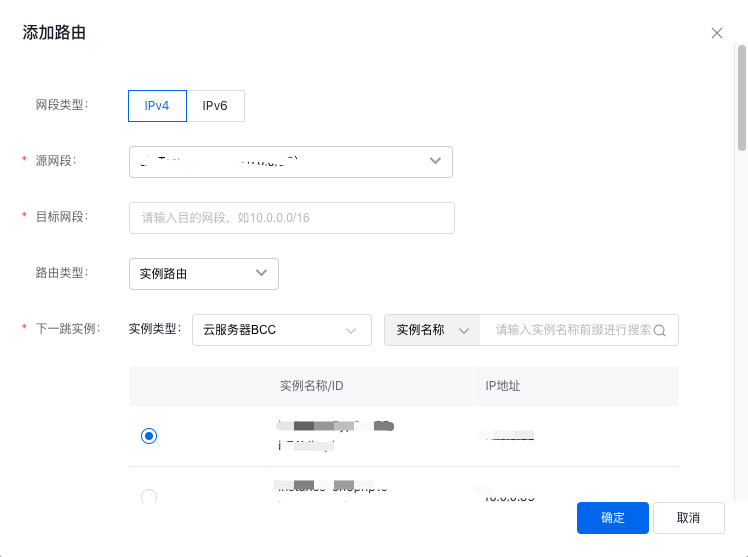
- For the source network segment, choose custom configuration and manually input the custom pod network segment, for example, 10.22.0.0/16.
- For the destination network segment, set it to 0.0.0.0/0 or the CIDR of the Internet service you wish to reach.
- Select NAT gateway as the route type.
- For the next step, select the NAT gateway with pre-configured SNAT rules.
At this point, the configuration for pods accessing the public network under the VPC route container network is complete, and you can verify network connectivity within the container.
4. Common issues
4.1 ACL rules causing container unable to access public network
4.1.1 Security group causing container unable to access public network
If Internet can still not be accessed after following the steps in this document, please check the nodes, ENI-bound security group, ACL, and other network policy rules to ensure that the traffic of container accessing the Internet is permitted in the rules. Some Internet hosts block ICMP traffic. If ping fails, consider using TCP/UDP to test the connectivity.
4.2 DNS causing container unable to access Internet
Before containers access the Internet, verify whether the target domain name can be resolved. If the domain name cannot be resolved, adjust the DNS configuration to complete the domain name resolution. For example, configure downstream DNS servers in CoreDNS to finalize domain name resolution. Use the following command to confirm if the domain name resolves successfully:
1dig a.example.com