Create TensorFlow Task
Updated at:2025-10-27
You can create a new task specifically of the TensorFlow type.
Prerequisites
- You have successfully installed the CCE AI Job Scheduler and CCE Deep Learning Frameworks Operator components; without these, the cloud-native AI features will be unavailable.
- As an IAM user, you can only use a queue to create new tasks if you are part of the users linked to that queue.
- Installing the CCE Deep Learning Frameworks Operator component will also install the TensorFlow deep learning framework.
Operation steps
- Sign in to the Baidu AI Cloud official website and enter the management console.
- Go to Product Services - Cloud Native - Cloud Container Engine (CCE) to access the CCE management console.
- Click Cluster Management - Cluster List in the left navigation pane.
- Click on the target cluster name in the Cluster List page to navigate to the cluster management page.
- On the Cluster Management page, click Cloud-Native AI - Task Management.
- Click Create Task on the Task Management page.
- On the Create Task page, configure basic task information:
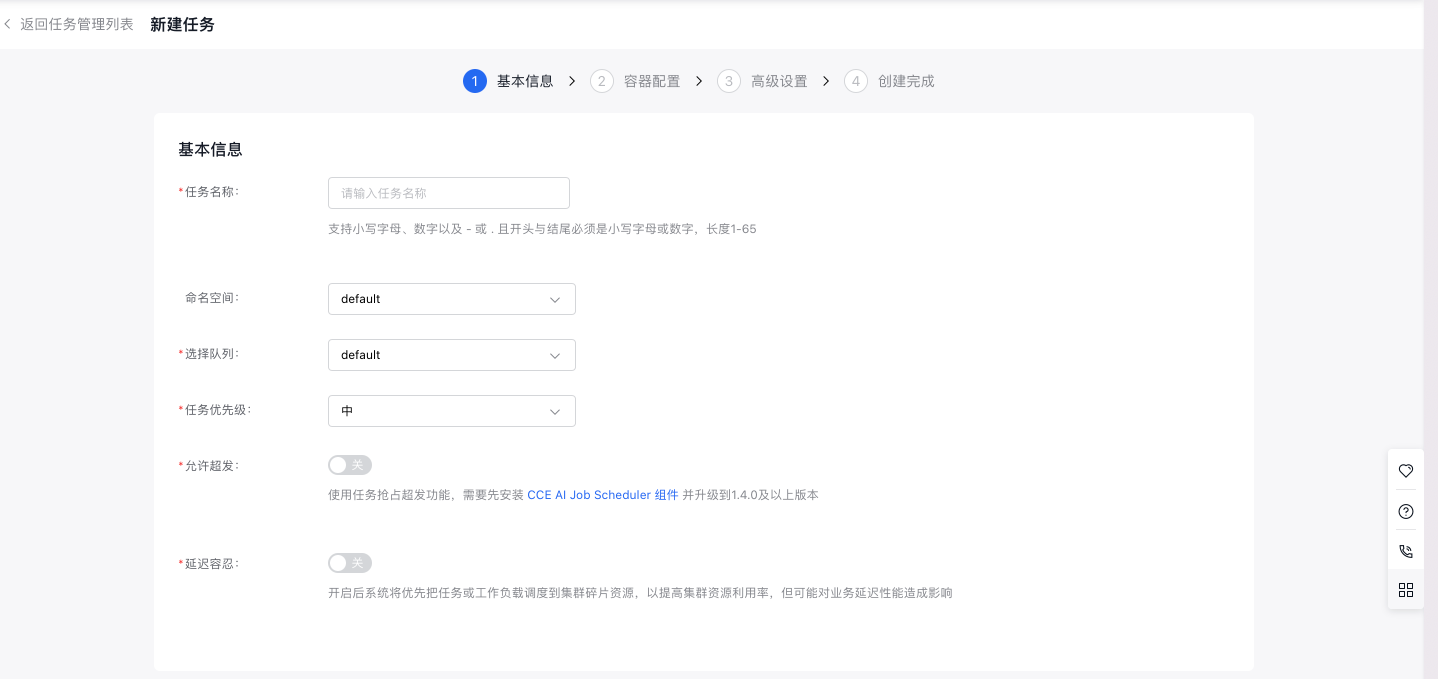
- Specify a custom task name using lowercase letters, numbers, “-”, or “.”. The name must start and end with a lowercase letter or number and be 1-65 characters long.
- Namespace: Choose the namespace for the new task.
- Queue: Choose the corresponding queue for the new task.
- Task priority: Set the priority level for the task.
- Allow overcommitment: Enable this option to use task preemption for overcommitment. The CCE AI Job Scheduler component must be installed and updated to version 1.4.0 or higher.
- Tolerance for delay: The system will prioritize scheduling tasks or workloads to fragmented cluster resources to enhance cluster resource utilization, though this might impact business latency performance.
- Configure basic code information:
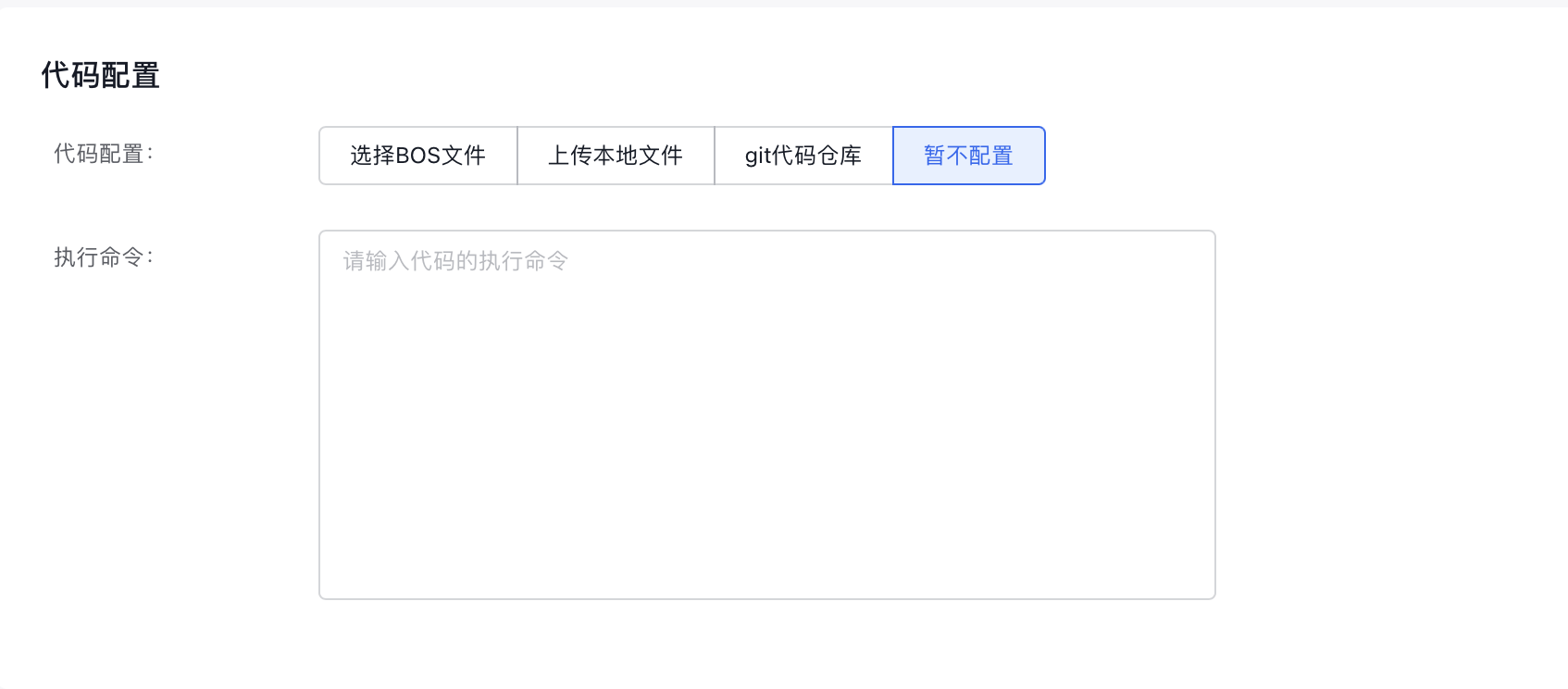
- Code Configuration Type: Choose the method for code configuration, currently supporting "BOS File," "Local File Upload," "Git Code Repository," and "Not Configured Temporarily."
- Execution command: Define the command to execute the code.
- Configure data-related information:
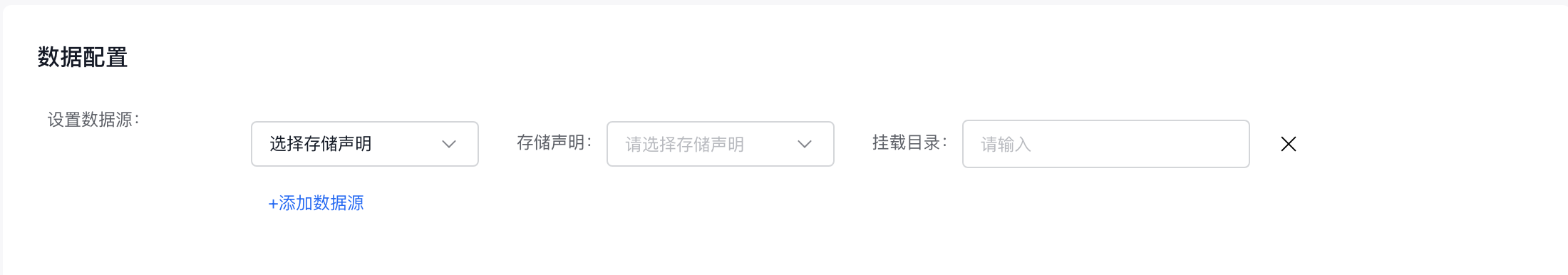
- Set data source: Currently supports datasets, persistent volume claims, temporary paths, and host paths. For datasets: All available datasets are listed; selecting a dataset automatically matches the PVC with the same name. For persistent volume claims: Choose the persistent volume claim directly.
- Click "Next" to proceed to container-related configurations.
- Configure task type information:
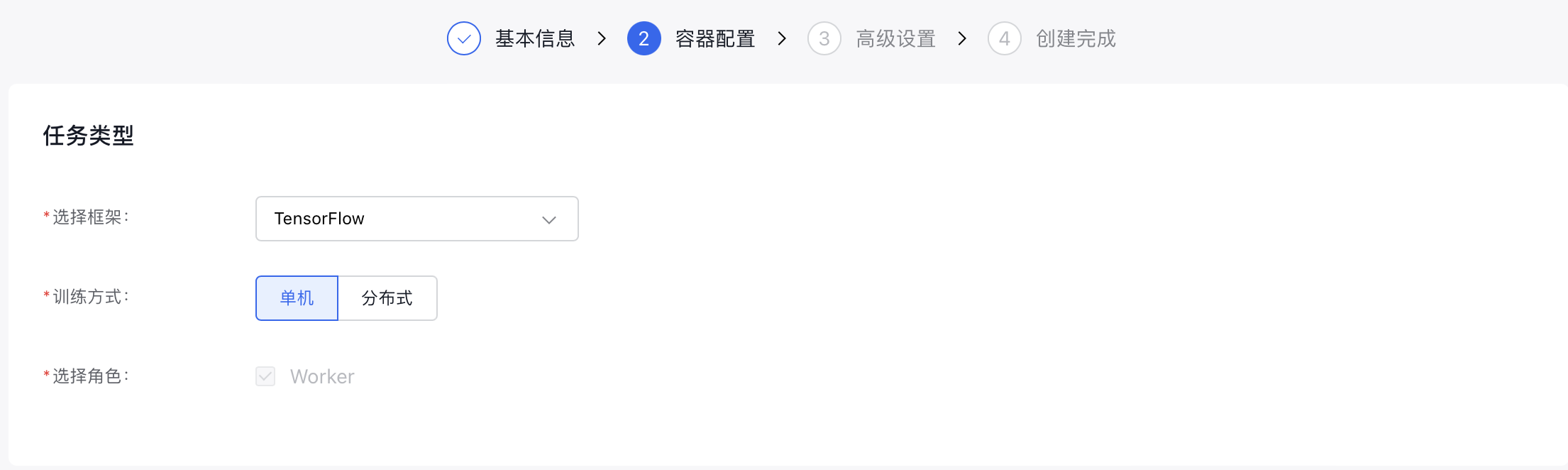
- Select framework: Choose TensorFlow.
- Training method: Select either Single-Machine or Distributed training.
- Select Role: For "Single-machine" training, only "Worker" can be chosen. For "Distributed" training, additional roles such as "PS," "Chief," and "Evaluator" can be selected.
- Configure pod information (advanced settings are optional).
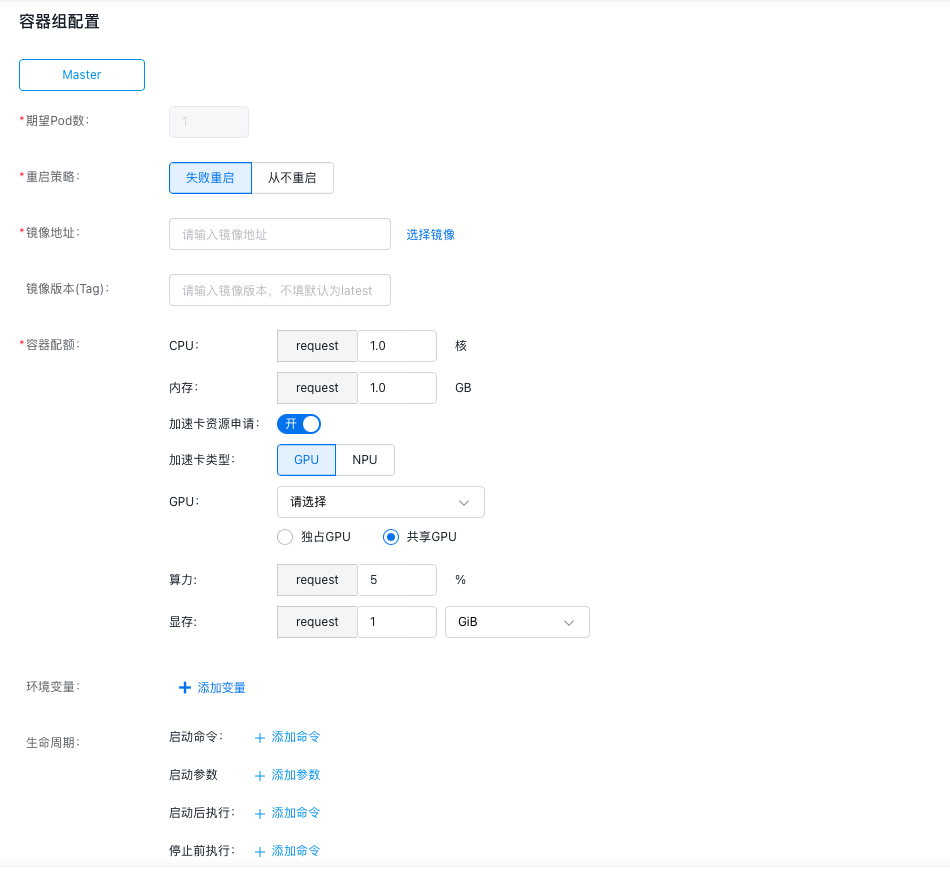
- Specify the number of pods desired in the pod.
- Define the restart policy for the pod. Options: “Restart on Failure” or “Never Restart”.
- Provide the address for pulling the container image. Alternatively, click Select Image to choose the desired image.
- Enter the image version. If left unspecified, the latest version will be used by default.
- Container Quota: Specify the CPU, memory, and GPU/NPU resource allocation for the container.
- Environment Variables: Enter the variable names and their corresponding values.
- Lifecycle: Includes start commands, parameters, actions after startup, and actions before stopping, all of which can be customized as needed.
- Configure the advanced task settings.
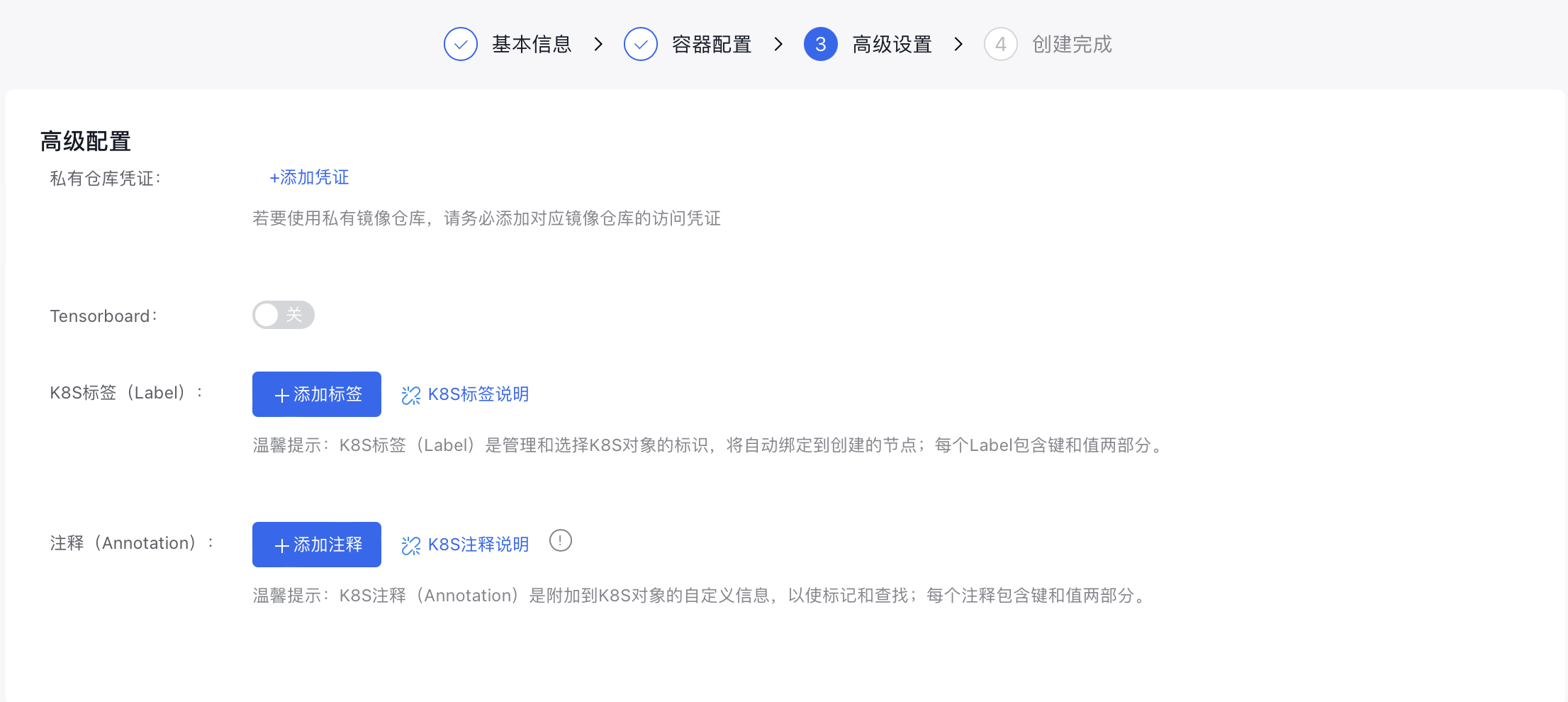
- Add credentials to access the private image registry if using a private image.
- Tensorboard: If task visualization is required, the Tensorboard function can be enabled. After enabling, you need to specify the “Service Type” and “ Training Log Reading Path”.
- Assign K8s labels to the task.
- Provide annotations for the task.
- Click the Finish button to finalize task creation.
Example of creating a task with YAML
Plain Text
1apiVersion: "kubeflow.org/v1"
2kind: "TFJob"
3metadata:
4 name: "tfjob-dist-mnist-for-e2e-test"
5spec:
6 tfReplicaSpecs:
7 PS:
8 replicas: 2
9 restartPolicy: Never
10 template:
11 metadata:
12 annotations:
13 sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
14 # if your libcuda.so.1 is in custom path, set the correct path with the following annotation
15 # kubernetes.io/baidu-cgpu.nvidia-driver-lib: /usr/lib64
16 spec:
17 schedulerName: volcano
18 containers:
19 - name: tensorflow
20 image: registry.baidubce.com/cce-public/kubeflow/tf-dist-mnist-test:1.0
21 resources:
22 requests:
23 cpu: 1
24 memory: 1Gi
25 limits:
26 baidu.com/v100_32g_cgpu: "1"
27 # for gpu core/memory isolation
28 baidu.com/v100_32g_cgpu_core: 10
29 baidu.com/v100_32g_cgpu_memory: "2"
30 # if gpu core isolation is enabled, set the following preStop hook for graceful shutdown.
31 # ${'`'}dist_mnist.py${'`'} needs to be replaced with the name of your gpu process.
32 lifecycle:
33 preStop:
34 exec:
35 command: [
36 "/bin/sh", "-c",
37 "kill -10 `ps -ef | grep dist_mnist.py | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}'` && sleep 1"
38 ]
39 Worker:
40 replicas: 4
41 restartPolicy: Never
42 template:
43 metadata:
44 annotations:
45 sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
46 # if your libcuda.so.1 is in custom path, set the correct path with the following annotation
47 # kubernetes.io/baidu-cgpu.nvidia-driver-lib: /usr/lib64
48 spec:
49 schedulerName: volcano
50 containers:
51 - name: tensorflow
52 image: registry.baidubce.com/cce-public/kubeflow/tf-dist-mnist-test:1.0
53 env:
54 # for gpu memory over request, set 0 to disable
55 - name: CGPU_MEM_ALLOCATOR_TYPE
56 value: “1”
57 resources:
58 requests:
59 cpu: 1
60 memory: 1Gi
61 limits:
62 baidu.com/v100_32g_cgpu: "1"
63 # for gpu core/memory isolation
64 baidu.com/v100_32g_cgpu_core: 20
65 baidu.com/v100_32g_cgpu_memory: "4"
66 # if gpu core isolation is enabled, set the following preStop hook for graceful shutdown.
67 # ${'`'}dist_mnist.py${'`'} needs to be replaced with the name of your gpu process.
68 lifecycle:
69 preStop:
70 exec:
71 command: [
72 "/bin/sh", "-c",
73 "kill -10 `ps -ef | grep dist_mnist.py | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}'` && sleep 1"
74 ]