CCE - Public Network Access Practice
Overview
In some scenarios, the users should enable the nodes and pods in the K83S Cluster CCE to access the public network. To access the external source address to download and install software and containers through the yum install and other commands, some services, etc. in the public network should be accessed. We provide the following two plans to enable the cluster to access the public network. The users can select by themselves according to specific requirements.
Related concepts
EIP, or Elastic IP, is a service provided by Baidu AI Cloud that can be attached to CCE nodes, BLB, NAT gateways, and other services, enabling those resources to access the public network.
NAT Gateway: Baidu AI Cloud's NAT gateway allows instances like BCC, DCC, and others in the user VPC subnet to connect to the public network. It facilitates the conversion of private IP addresses to public IP addresses via the NAT gateway.
Node Subnet: When creating a CCE worker node, users can select the VPC subnet where the node resides. The subnet type is a general-purpose subnet. Nodes within this subnet can either directly mount an EIP to access the public network or utilize the NAT gateway for public network access.
(Note: Baidu AI Cloud's Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) no longer supports the creation of NAT-dedicated subnets. If using Plan 2 for public network access, select a general-purpose subnet as the node subnet. Existing NAT-dedicated subnets will remain unaffected and can continue to be used normally.)
Plan 1: General-purpose subnet + EIP
Select the general-purpose subnet for nodes when creating and adding CCE nodes:
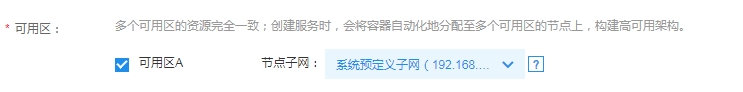
If failing to confirm the general-purpose subnets in the subnet list, you can view the device type of the subnet in the VPC console:
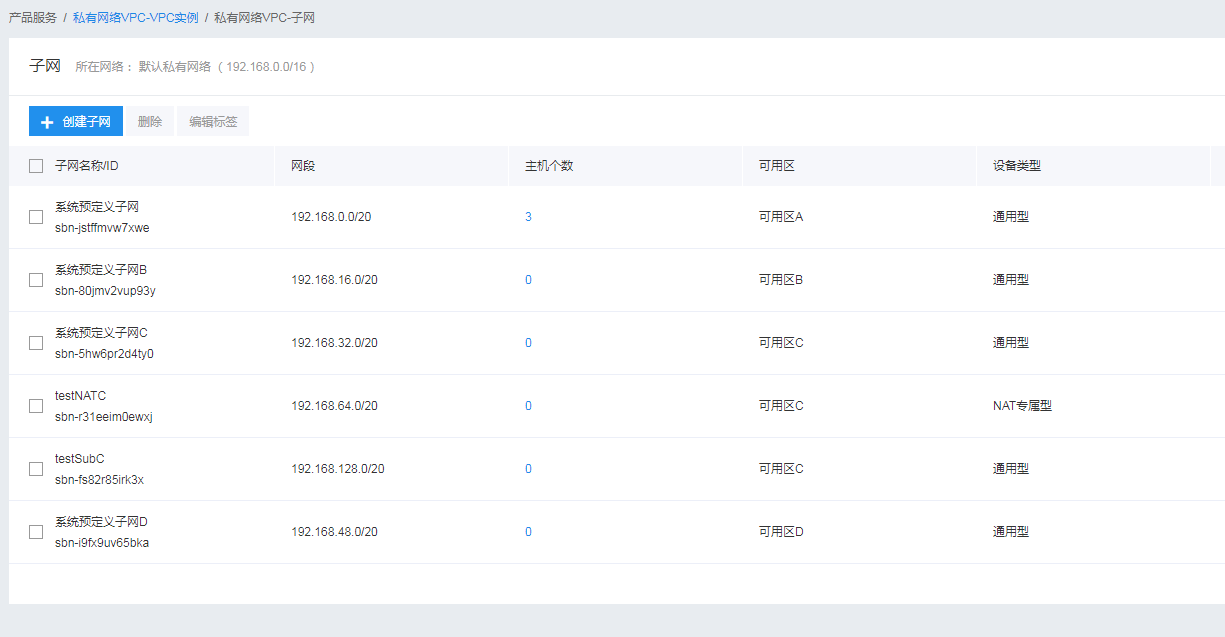
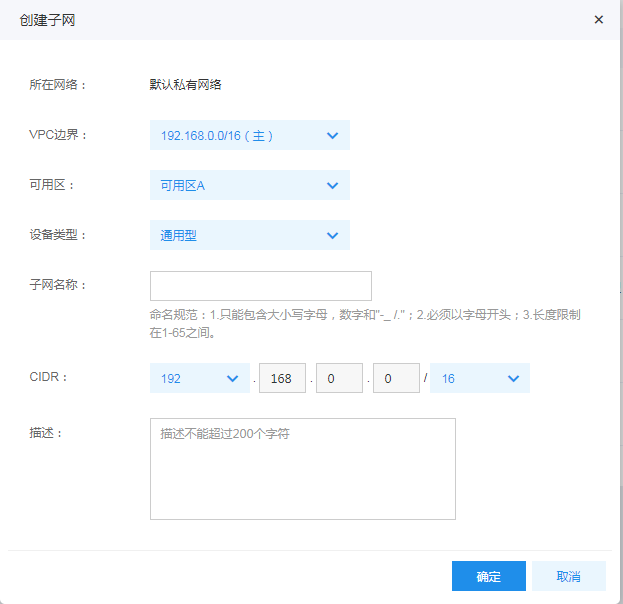
If the VPC contains no suitable general-purpose subnet, you can create a general-purpose subnet and select the general-purpose type of the device.
If the nodes are in the general-purpose subnet, you can directly bind EIP to the nodes, link and purchase EIP when creating and adding nodes, or bind EIP after the nodes are added to the cluster.
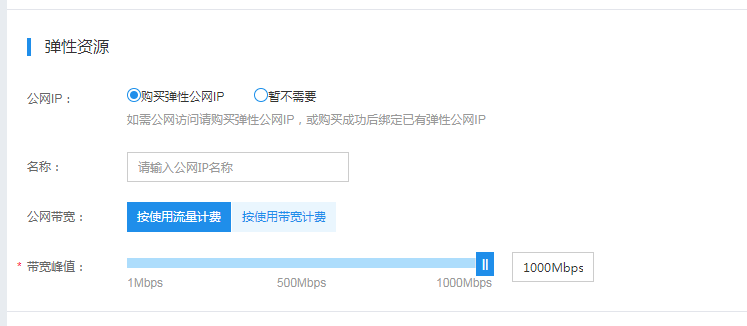
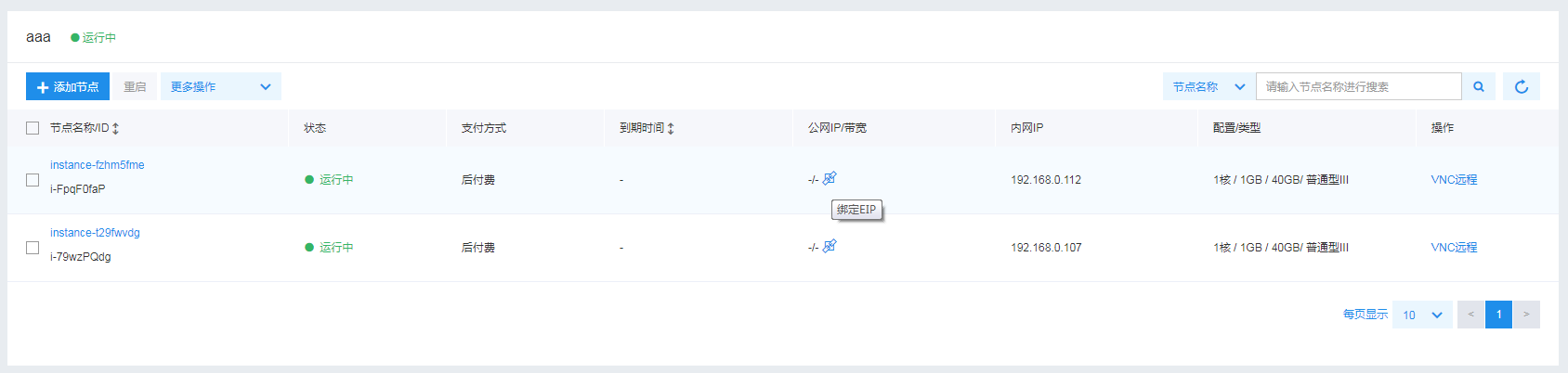
Once an EIP is bound to the nodes, they can access the public network directly.
Plan 2: NAT-dedicated subnet + NAT gateway
(Note: Baidu AI Cloud's Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) no longer supports the creation of NAT-dedicated subnets. If using Plan 2 for public network access, select a general-purpose subnet as the node subnet. Existing NAT-dedicated subnets will remain unaffected and can continue to be used normally.)
If you prefer not to expose the node's public IP while accessing the public network, you can provide private network access to public network services through the NAT gateway.
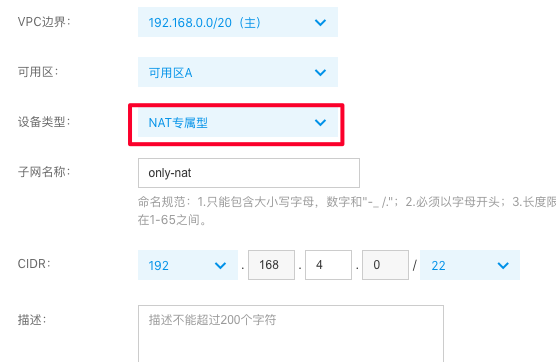
First, create a subnet in the VPC, and select the NAT-dedicated type of the device.
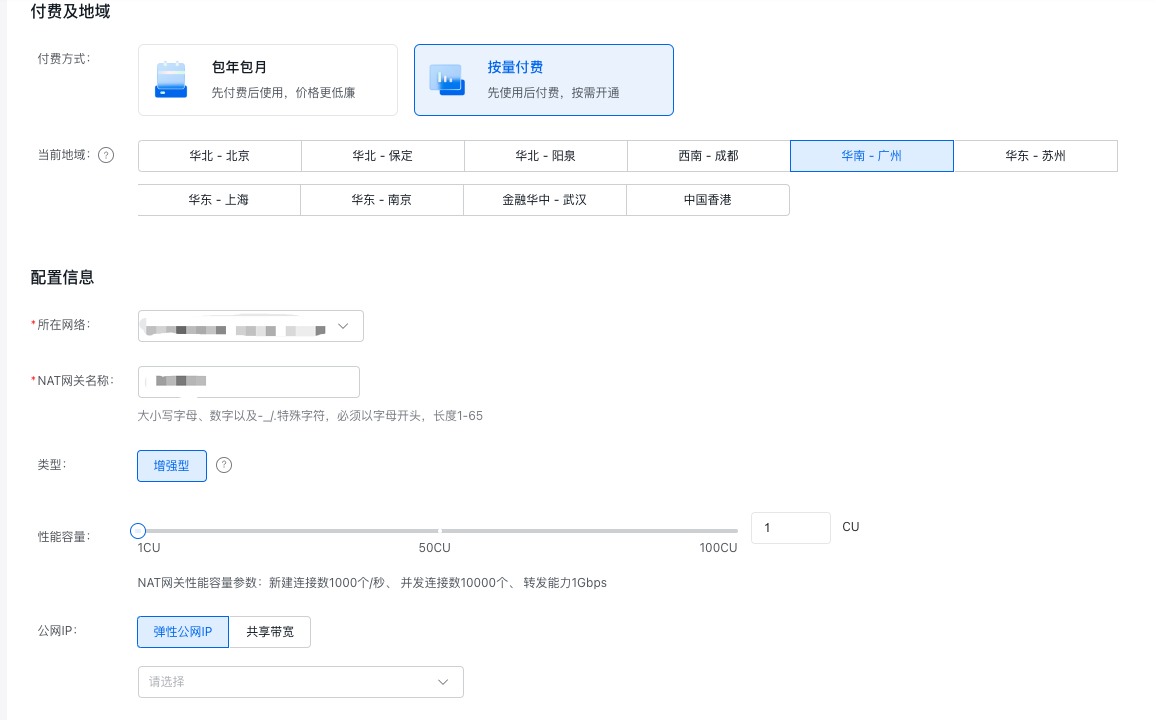
Enter the VPC Console, and select VPC Instance -- > NAT Gateway-- > Create NAT Gateway, as shown in the figure below:
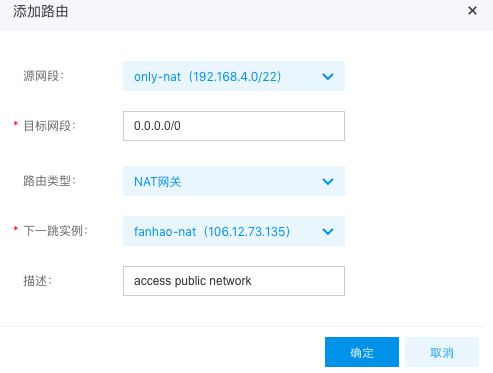
After creating the NAT gateway, configure the VPC's route table. The route's source network segment should correspond to the node's subnet, while the destination network segment should be set to all zeros. The route type should specify the NAT gateway, with the next-hop instance being the newly created NAT gateway, as illustrated in the figure below:
Upon completing the configuration, select the NAT-dedicated subnet when creating a cluster. All cluster nodes created within this setup can access the public network.
Note: Nodes in the NAT-dedicated subnet cannot have an EIP bound to them. These nodes will only be able to access the public network after the NAT gateway has been created and the route table rules are configured.
Analyze advantages and disadvantages
| Plan | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| General-purpose subnet + EIP | Simple operation No need to pay for NAT gateway |
The EIP requiring the exposure of nodes has security risks. |
| NAT-dedicated subnet + NAT gateway | No EIP for nodes, high security |
The EIP cannot be bound to the nodes, and the nodes cannot be accessed by the public network. |
