CCE Fluid Description
Updated at:2025-10-27
Component introduction
CCE Fluid is an open-source, Kubernetes-native orchestration and acceleration engine for distributed datasets, designed primarily for data-intensive applications in cloud-native scenarios like big data and AI workloads.
Component function
- Dataset abstraction
- Data pre-load and acceleration
- Collaborative orchestration of data applications
- Multi-namespace support
- Heterogeneous data source management
Application scenarios
Accelerate machine learning training by improving data access speed through using datasets to create AI training tasks
Limitations
- Supports only Kubernetes clusters version v1.16 and above.
Install component
- Sign in to the Baidu AI Cloud official website and enter the management console.
- Go to Product Services - Cloud Native - Cloud Container Engine (CCE) to access the CCE management console.
- Click Cluster Management - Cluster List in the left navigation pane.
- Click on the target cluster name in the Cluster List page to navigate to the cluster management page.
- On the Cluster Management page, click Component Management.
- From the component management list, choose the Fluid component and click Install to complete the component installation.
Basic concepts of components
- Dataset: Used to define datasets and specify the configuration of original data sources.
-
Runtime: The implementation of specific dataset storage engines. Currently, CCE supports the following two runtime:
- RapidFSRuntime: Baidu’s self-developed storage engine
- AlluxioRuntime: Open-source Storage Engine
Component usage - Accelerate BOS data access with RapidFS
- Create a BOS Bucket: First, create a BOS Bucket for storing original data and upload your training data to this bucket. To ensure optimal access speed, it is recommended to create the BOS in the same region as the compute nodes.
- Create dataset: Data source configuration
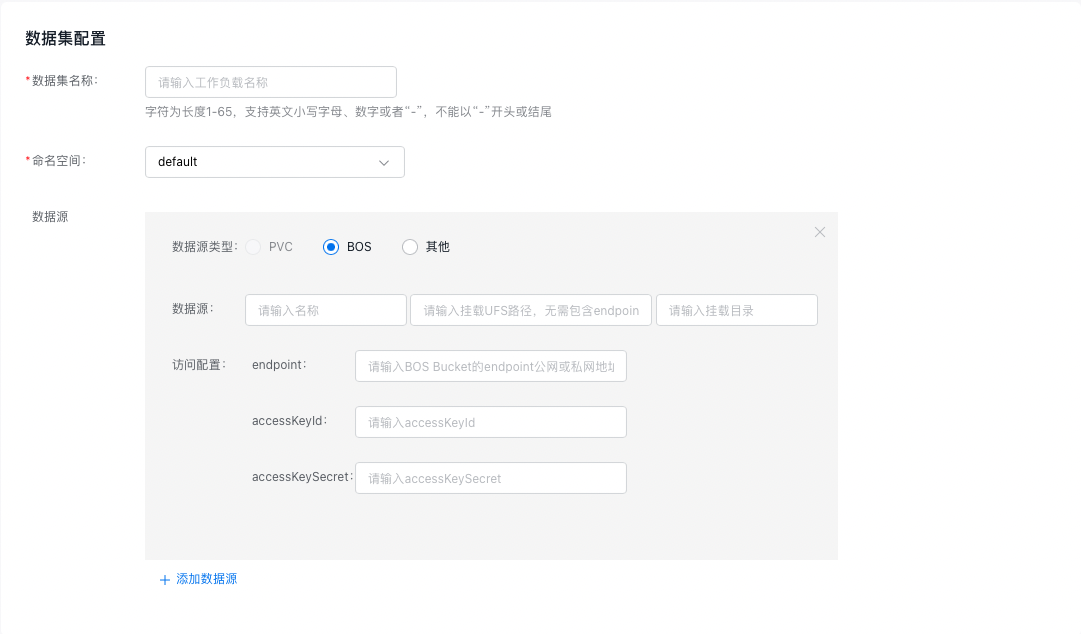
| Configuration field | Description |
|---|---|
| Data source name | Used to identify the unique name of this data source in the dataset, which is required and cannot be null |
| Data source mounting UFS path | |
| Data source mounting path | Specifies the subpath of the data source within this dataset, such as /subpath. This field is optional; if left empty, the data source name will automatically be used as the subpath. |
| Access configuration: endpoint | BOS access endpoint, such as bj.bcebos.com. Please refer to Obtain the Access Domain Name |
| Access configuration: accessKeyId | accessKeyId used for BOS access |
| Access configuration: accessKeySecret | accessKeySeret used for BOS access |
- Create dataset: Scheduling configuration (optional)
When creating a dataset, you can additionally set tolerance and affinity policies to allocate data to specific compute nodes. Optimal access speed is achieved when the dataset and the training task are assigned to the same node.

- Create dataset: Runtime configuration
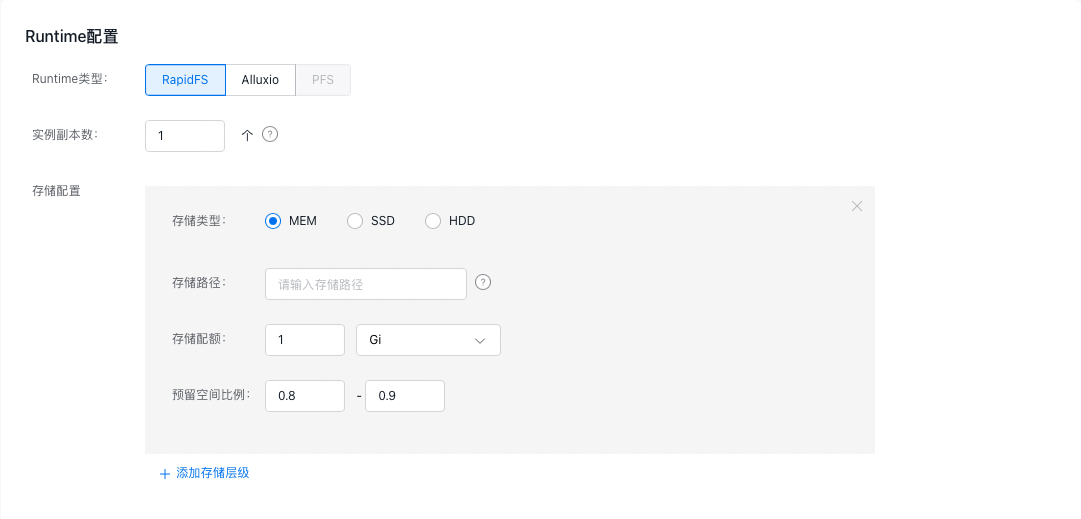
| Configuration field | Description |
|---|---|
| Runtime type | Storage engines, currently supporting self-developed RapidFS, open-source storage engine Alluxio and PFS |
| Count of instance replicas | Count of replicas for accelerated cache saved by the storage cluster |
| Storage class | Cache medium type, supporting MEM/SSD/HDD, with decreasing speed priority in sequence |
| Storage path | The path where the storage engine places the cache on the node. When selecting memory cache (MEM), you can fill in /dev/shm; when selecting SSD/HDD, you can fill in /mnt/diskx. The specific path depends on the data disk mount path of the node virtual machine and can be specified by the user |
| Storage quota | Maximum quota for the cache |
| Reserved space ratio | Upper and lower limits ratio for cache eviction. When the cache usage reaches the upper limit ratio of the quota, the storage engine will perform data eviction operations, evicting non-hotspot data based on data access |
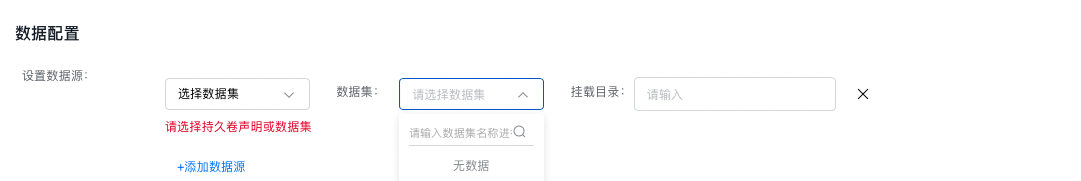
- Use the dataset: Once the dataset is successfully created, you can select it in Cloud Native AI > Task Management > Create Task > Data Configuration to mount and use it for a training task. Upon successful creation of the dataset, a PVC with the same name is automatically generated in the cluster, which you can also use directly for mounting when creating a workload.
Version records
| Version No. | Cluster version compatibility | Change time | Change content | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| v0.1.7 | CCE v1.16+ | 2023.11.17 | This upgrade will not disrupt the service. |
