CCE Cluster Node Auto-Scaling
Overview of autoscaler
CCE functions based on a cluster formed by a group of Baidu AI Cloud servers. The cluster supplies essential resources like CPU, memory, and disk for running user containers. Normally, the cluster size is defined by the user when establishing the CCE service and can be adjusted up or down at any time during use. However, if a user's services grow faster than anticipated or experience peaks, the resources provided by the cluster may fall short, potentially leading to slow service operations.
By activating the CCE auto-scaling feature, the cluster will automatically add nodes when resources are inadequate and release extra nodes when resources are excessive. This ensures sufficient resources to support business loads while minimizing costs. Users can also define the maximum and minimum number of nodes for scaling, keeping the scaling within a predefined range.
Concept explanation
| Concepts | Description |
|---|---|
| Scalability group | It refers to a collection of nodes with the same configuration, which are automatically scaled up or down based on the machine configuration of the group |
| Scalability group min | When the scalability group meets the scale-down conditions, ensure that the number of nodes in the node group after scaling down is not less than this value |
| Scalability group max | When the scalability group meets the scale-up conditions, ensure that the number of nodes in the node group after scaling up is not higher than this value |
| Scale-down threshold | When the ratio of requested resources (Request) to the resource capacity (Capacity) of a node's resources (CPU and memory) within a scalability group falls below a set threshold, the cluster may initiate automatic scale-down. |
| Scale-down trigger latency | If node resource utilization remains below the scale-down threshold during the configured scale-down trigger delay, the cluster might proceed with automatic scale-down. |
| Maximum concurrent scale-down count | This is an integer indicating the number of nodes with zero resource utilization that can be scaled down at the same time. |
| Scale-down start interval after scale-up | This is an integer in minutes. Nodes added during scale-up will undergo evaluation for potential scale-down after this duration. |
| Pods using local storage | During scale-down, you can choose to skip nodes containing pods with local storage |
| Pods in the kube-system namespace | During scale-down, you can choose to skip nodes with non-DaemonSet pods in the kube-system namespace |
| Multi-scalability group scale-up selection strategy | random: Randomly selects a scalability group from those meeting the scale-up criteria. least-waste: Chooses the scalability group with the least unused resources while fulfilling pod requirements. most-pods: Selects the scalability group that can accommodate the most pods during scale-up. |
Cluster operation guide (cluster ID starts with cce-)
Create a new node group
Sign in to Baidu AI Cloud Management Console, navigate to Product Services -> Cloud Native -> Cloud Container Engine (CCE). In the left navigation bar, click Node Management -> Node Groups to enter the Node Group page and create a new node group.
Enable auto scaling
On the Node Group Creation page, click Auto Scaling.
Cluster operation guide (cluster ID starts with cce-)
Cluster autoscaler configuration
- Sign in to Baidu AI Cloud Management Console, navigate to Product Services -> Cloud Native -> Cloud Container Engine (CCE). In the left navigation bar, click Node Management -> Node Groups to enter the Node Group page for configuration.

- Enter the Node Group page. For the first configuration of a new cluster, you need to click Authorize in the node group configuration to enable the cluster autoscaler function and perform related configurations.
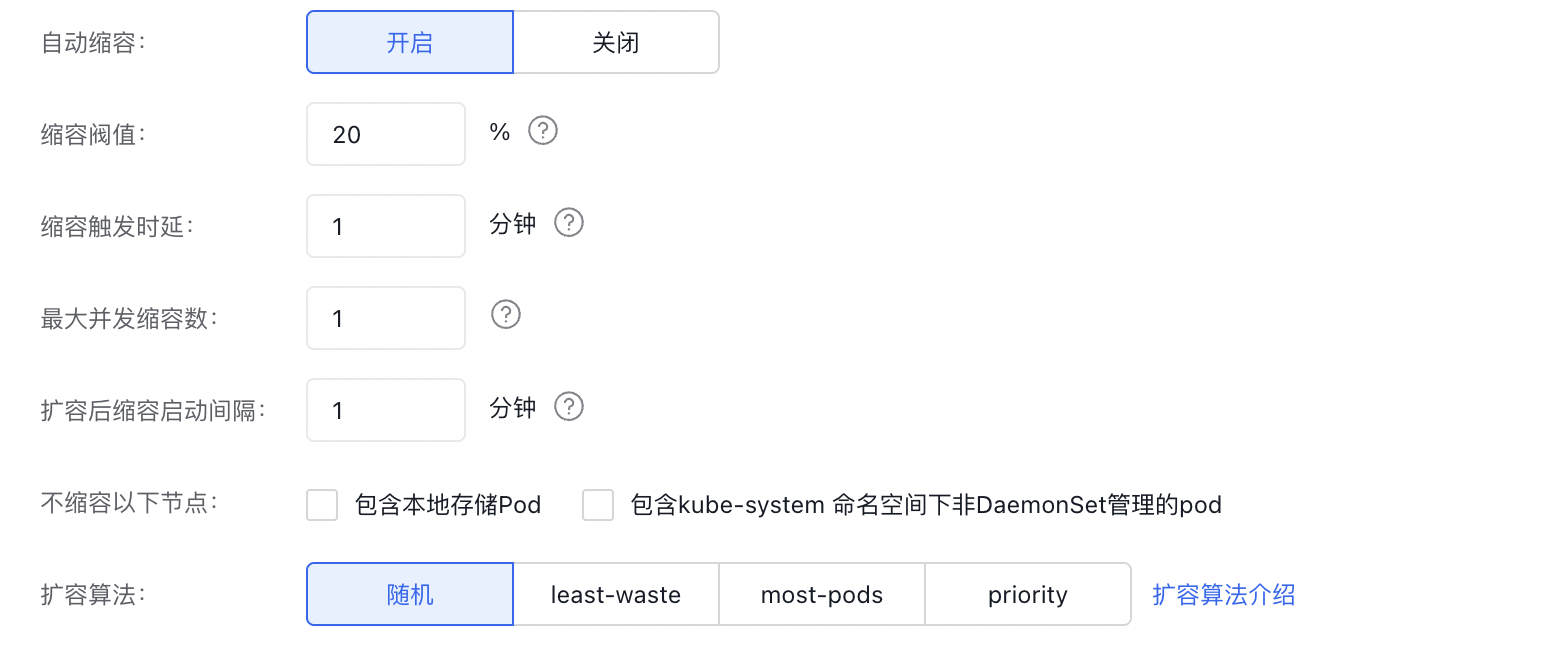
Description of scale-up algorithm options in the above figure:
- Random: When multiple scalability groups are available, randomly select one for scale-up
- least-waste: When multiple scalability groups are available, select the scalability group with the least idle CPU after deploying pending pods
- most-pods: When multiple scalability groups are available, select the scalability group that can deploy the most pods
- priority: When multiple scalability groups are available, select the scalability group with the highest priority for scale-up; the higher the priority value is, the higher the priority is
For more details, refer to: https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/FAQ.md#what-are-expanders
Automatic scale-down FAQs
- When is scale-up triggered?
- There are pods in the cluster that are in the pending status due to insufficient resources (CPU and memory)
- The number of nodes in the scalability group fails to reach the max value
- Why sometimes nodes within a scalability group cannot be scaled down to 0?
- Each time a configuration is changed, the scaling component will be removed and restarted. When the scaling component is assigned to a node within a scalability group, that specific node will not undergo scale-down. (Refer to Question 5)
- Why won't the newly scaled-up machines be scaled down even if they meet the conditions?
- A newly scaled-up machine has a protection period of 10 minutes. After this time, it becomes eligible for scale-down consideration.
- Why doesn't the configuration take effect immediately after modification?
- When altering the configuration (group settings or scale-down parameters), the scaling component will restart. Existing nodes in the scalability group will then be marked as newly scaled-up and will have a fresh protection period of 10 minutes (adjustable) before meeting scale-down criteria.
- Why aren't the machines that meet the scale-down threshold and scale-down time being scaled down?
- First, check whether the number of nodes in the group has reached the set min value
- Check whether the pods on the machine can be scheduled to other nodes. If not, the machine will not be scaled down
- Check whether the node is set as non-scalable down ("cluster - autoscaler.kubernetes.io/scale-down-disabled": "true")
- Check whether the node is a newly scaled-up node (-scale-down-delay-after-add, which is set to 10 minutes by default, meaning that a newly scaled-up node will not be considered for scale-down within 10 minutes)
- Check whether the group has experienced a scale-up failure in the past 3 minutes (--scale-down-delay-after-failure, which can be set)
- Check whether the parameters --scale-down-delay-after-delete (interval between two consecutive scale-downs) and --scan-interval (scanning interval) are set
- How to view the status of scaling components within a cluster
- Check the configMap ->
kubectl get configmap cluster-autoscaler-status -n kube-system -o yaml - Check the autoscaler log ->
kubectl logs $(kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep cluster-autoscaler | awk '{print $1}') -n kube-system -f
- Why is the usage rate displayed by the scaling component different from what I calculated?
- CCE reserves certain machine resources. The CPU core count and memory calculated by the scalability component refer to the amount of resources available for users to allocate
- How to schedule pods to a specified scalability group?
- Specify the label of the scalability group when creating it. All nodes in the scalability group will have this label, and you can schedule pods through nodeSelector or node Affinity.
- How to use GPU scalability group?
- Create a GPU-based scalability group. During pod creation, specify the requests and limits nvidia.com/gpu: 1, and define the number of GPU cards required for the pod. The number of GPU cards must be a whole number.
Note
- If service interruptions cannot be tolerated, auto scaling is not recommended. During scale-down, certain pods may restart on other nodes, possibly causing brief disruptions.
- Avoid directly modifying nodes within a scalability group. All nodes in the same scalability group should have identical configurations (CPU and memory), labels, and system pods.
- Verify that the number of machine instances your account supports meets the minimum/maximum requirements for setting up the scalability group.
- When creating a pod, ensure you specify the request field.
- Limit the MEM and CPU resources used by the scalability group component: The scaling component requires 300 m memory and CPU 0.1 Core by default, with no resource limits set. To protect your machine resources, if your cluster scale is large, you can use the following formula to calculate the quota for the scaling component:
MEM = job_num*10KB + pod_num*25KB + 22MB + node_num * 200KB ;CPU = 0.5 Core ~ 1 CoreThe calculation here is the minimum requirement under ideal conditions. When the cluster has a large number of pods in pending, scale-up and scale-down statuses, additional CPU and MEM resources may be required.
