Using Parallel File System PFS L2
The Cloud Container Engine (CCE) supports the use of Baidu AI Cloud’s Parallel Filesystem Service (PFS) Extreme L2 by creating PV/PVC and mounting data volumes for workloads. This document will introduce how to dynamically and statically mount parallel filesystem service in a cluster.
Prerequisites
- The cluster has installed parallel filesystem service components. For more information, please refer to CCE CSI PFS L2 Plugin Description.
Usage restrictions
- Only the CCE CSI PFS L2 Plugin component is supported for associating PFS instances bound to mount services.
- When adding CCE nodes, ensure that the installed OS version is supported. The following are the OS versions compatible with both CCE and PFS Extreme L2.
| OS type | Distribution version | Kernel version |
|---|---|---|
| CentOS | 8 | 4.18.0-348.7.1.el8_5.x86_64 |
| Ubuntu | 20.04 | 5.4.0-135-generic |
| Ubuntu | 20.04 | 5.4.0-139-generic |
| Ubuntu | 22.04 | 5.15.0-72-generic |
Operation steps
Dynamically mount the parallel filesystem service
1. Create a StorageClass
Cluster administrators can define different storage classes for the cluster using StorageClass. By combining StorageClass with PVC, necessary storage resources can be dynamically created.
This document explains how to create a PFS L2-type StorageClass for the parallel filesystem service using Kubectl and how to customize the required template for the service.
You need to create a PFS instance first. For operation steps, refer to Create Parallel File System Extreme L2.
1kind: StorageClass
2apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
3metadata:
4 name: pfsl2-sc
5provisioner: spectrumscale.csi.ibm.com
6parameters:
7 mountTargetId: <mountTarget Id> # Required, <mountTargetId> is the mount service ID
8 pfsId: <pfsId> #Required, <pfsID> is the Parallel Filesystem Service PFS L2 instance ID to be mounted
9 #volDirBasePath: <volDirBasePath> #Optional, <volDirBasePath> is a subpath within the PFS system to be mounted. The dynamically created volume will create PVC based on this path, which needs to already exist in the system; otherwise, PVC creation will fail.
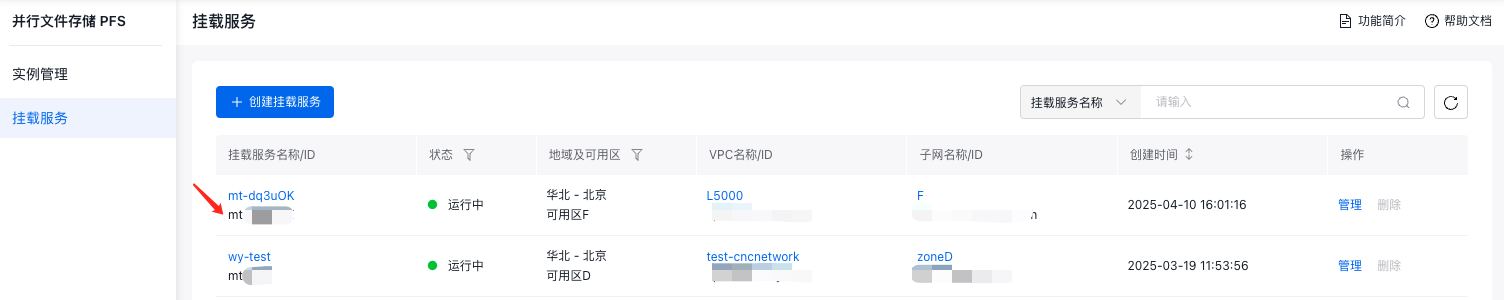
10reclaimPolicy: Delete- Obtain the PFS mount service ID
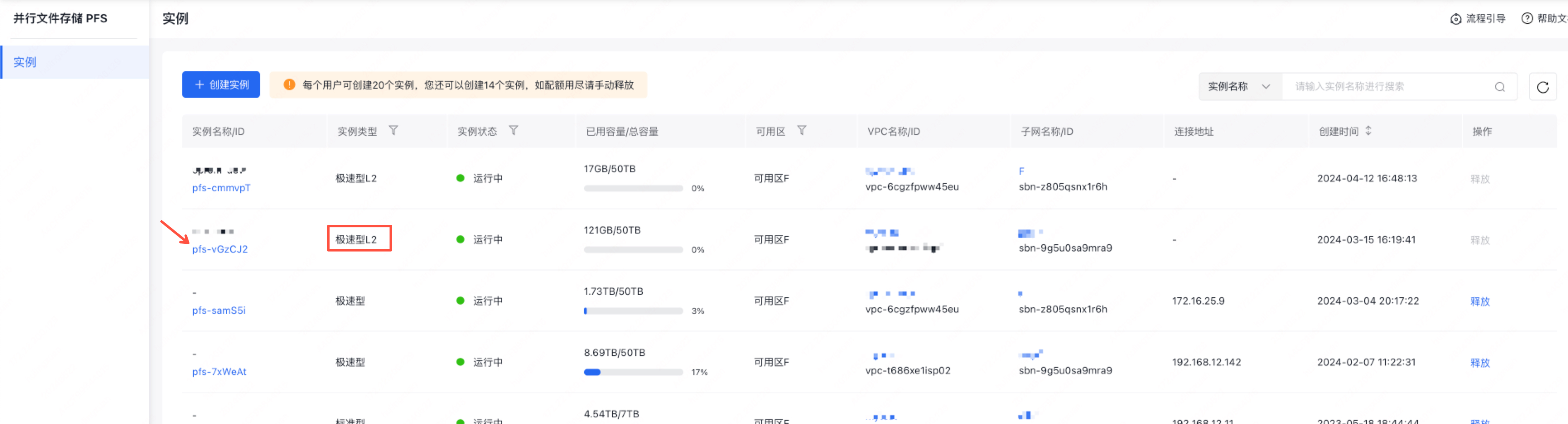
- Obtain the PFS L2 instance ID
2. Create a persistent volume claim (PVC)
Note: The storageClassName field must match the name of the StorageClass specified when deploying the StorageClass mentioned above.
1kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
2apiVersion: v1
3metadata:
4 name: dynamic-pvc
5spec:
6 accessModes:
7 - ReadWriteMany
8 storageClassName: pfsl2-sc
9 resources:
10 requests:
11 storage: 50Gi # Specify the PVC storage space size3. Check that the PVC status is bound
1$ kubectl get pvc dynamic-pvc
2NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
3dynamic-pvc Bound pvc-1ab36e4d1d2711e9 50Gi RWX pfsl2-sc 4s4. Mount the PVC in the Pod
The Pod and PVC must reside within the same namespace.
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Pod
3metadata:
4 name: test-pvc-pod
5 namespace: default
6 labels:
7 app: test-pvc-pod
8spec:
9 containers:
10 - name: test-pvc-pod
11 image: nginx
12 volumeMounts:
13 - name: pfs-pvc
14 mountPath: "/pfs-volume"
15 volumes:
16 - name: pfs-pvc
17 persistentVolumeClaim:
18 claimName: dynamic-pvcStatically mount the parallel filesystem service
1. Create a persistent volume (PV)
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: PersistentVolume
3metadata:
4 name: static-pv-pfsl2
5spec:
6 accessModes:
7 - ReadWriteMany
8 capacity:
9 storage: 100Gi
10 csi:
11 driver: spectrumscale.csi.ibm.com #Required
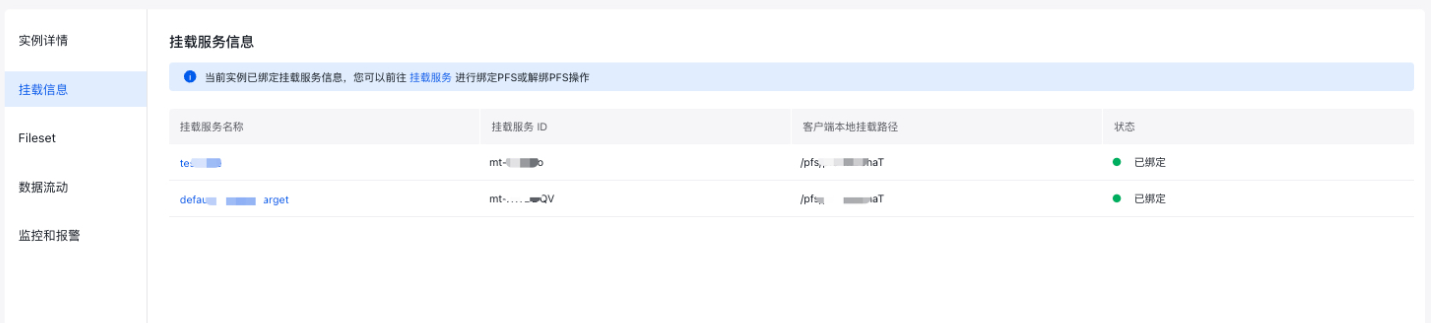
12 volumeHandle: <mountTargetId>;<pfsId>;<mountPath> # Required; corresponding to the mount service ID, PFS L2 instance ID, and domain name of a mount target respectively. Among them, mountPath is the absolute path of the PFS directory to be mounted on the node.- Obtain the absolute path
Navigate to the PFS L2 instance details page, select the mount information, and note that the client's local mount path is an absolute path.
2. Create a persistent volume claim (PVC)
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
3metadata:
4 name: static-pvc-pfsl2 # static PVC name
5spec:
6 volumeName: static-pv-pfsl2 # static PV name
7 accessModes:
8 - ReadWriteMany
9 resources:
10 requests:
11 storage: 100Gi2. Check that the PVC status is bound and bound to the corresponding PV.
1$ kubectl get pvc
2NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
3static-pvc-pfsl2 Bound static-pv-pfsl2 1Gi RWX 10s3. Mount the PVC in the Pod
The Pod and PVC must reside within the same namespace.
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Pod
3metadata:
4 name: test-pvc-pod
5 namespace: default
6 labels:
7 app: test-pvc-pod
8spec:
9 containers:
10 - name: test-pvc-pod
11 image: nginx
12 volumeMounts:
13 - name: pfs-pvc
14 mountPath: "/pfs-volume"
15 volumes:
16 - name: pfs-pvc
17 persistentVolumeClaim:
18 claimName: static-pvc-pfsl2