CCE supports dual-stack networks of IPv4 and IPv6
CCE supports dual-stack networks of IPv4 and IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) represents the inevitable progression of Internet upgrades and evolution, serving as a key direction for network technology innovation and a foundational support for building a robust network infrastructure. CCE now supports IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack clusters with the following features:
11. Nodes support both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, enabling dual-address communication within the cluster;
2 2. Pod dual stack supports both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, and supports two types of IP access;
3 3. Services support both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses and can expose services externally via IPv6.IPv6 dual-stack network reference: VPC using IPv6
Instructions for use
IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack container networks are only supported in standard CCE clusters.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes v1.20 or above
- cce-network plugin v2.7.7 or above
Create a new IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack VPC and subnet
CCE's IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack cluster must operate in a subnet of a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) that supports IPv6. Therefore, before creating a dual-stack cluster, ensure you have created a VPC with IPv6 support and its corresponding subnet.
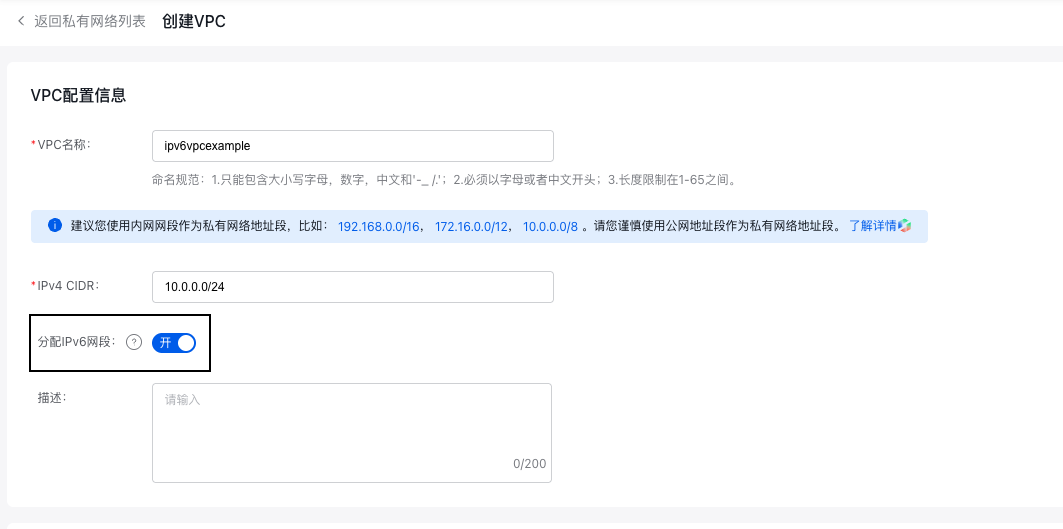
Create a VPC
Create a new VPC in the VPC console and enable Allocate IPv6 Network Segments.
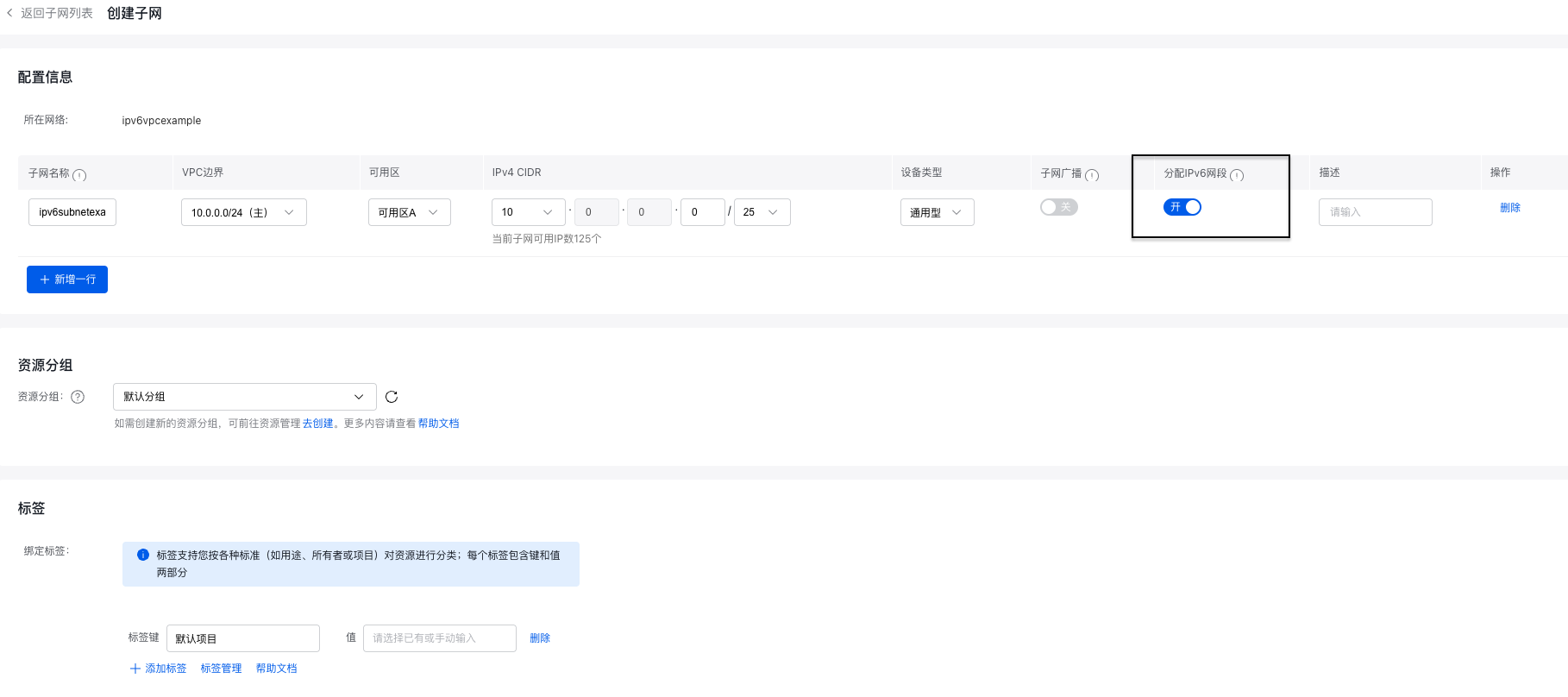
Create subnet
Create a subnet in the VPC and enable the "Allocate IPv6 Network Segments" option.
Create a new IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack K8S cluster
Enter the CCE console and create a dual-stack cluster as follows:
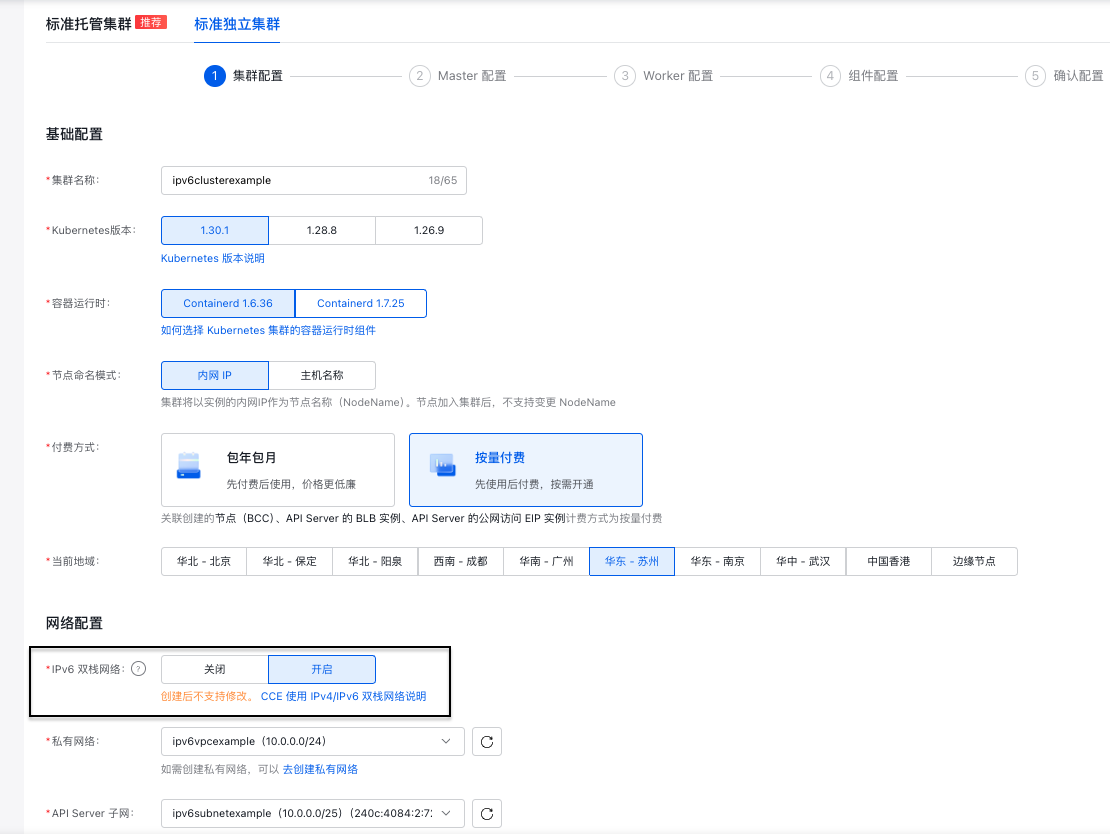
- On the Basic Configuration page
, select to enable IPv6 Dual-Stack Network and select a VPC supporting IPv6 and its subnet.
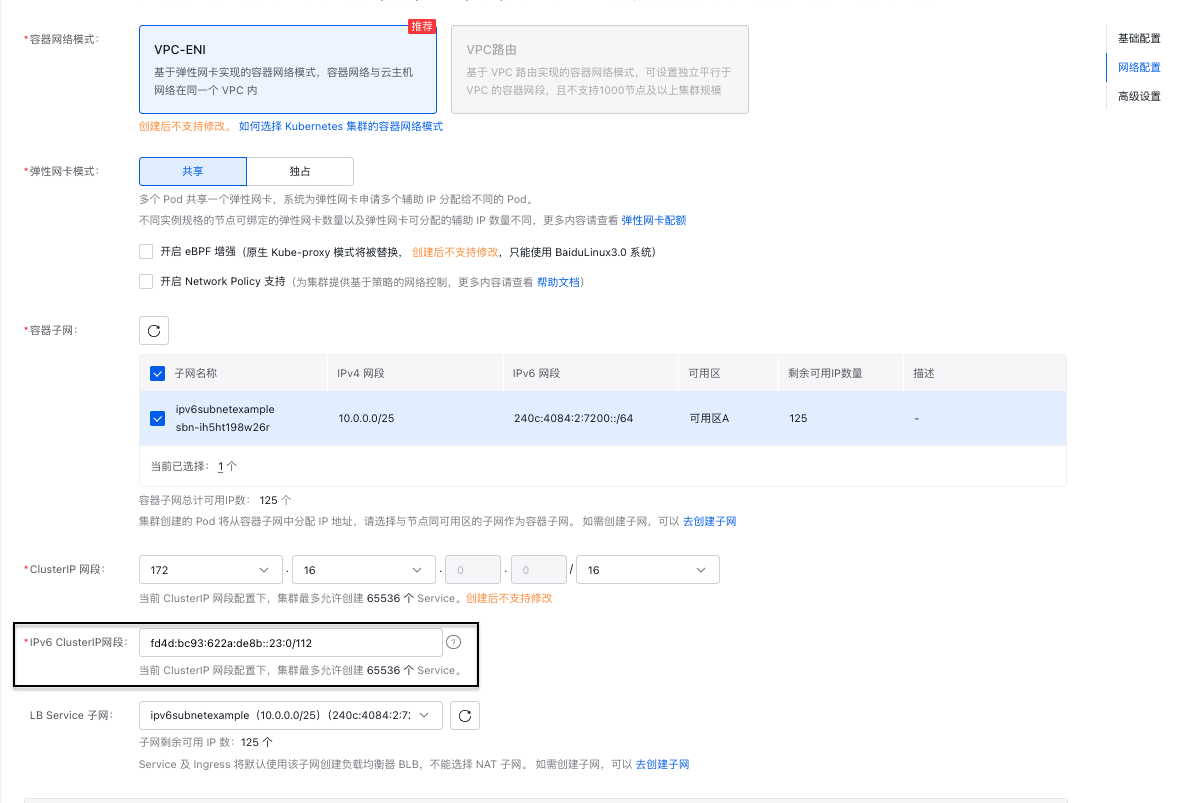
- On the Network Configuration page
, the system will automatically recommend suitable IPv4/IPv6 ClusterIP network segments and display them below. IPv6 network segments support manual user specification of Unique Local Addresses (ULA) as defined by RFC 4193, with the address range being a subset of
fd00::/8.
- Follow the subsequent prompts to complete the cluster creation process.
Access pods via IPv4 and IPv6
In IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack clusters, Pods can be assigned both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Note: Backend pods must also listen on the ports under the IPv6 protocol stack; otherwise, pods may be assigned IPv6 addresses but connections will be rejected
Via the Workloads page of CCE console, create an example deployment using the following example deployment, where the image listens on port 80 of both IPv4 and IPv6 protocol stacks:
1apiVersion: apps/v1
2kind: Deployment
3metadata:
4 name: deployment-example-ipv6
5 labels:
6 app: nginx
7spec:
8 replicas: 2
9 minReadySeconds: 0
10 strategy:
11 type: RollingUpdate
12 rollingUpdate:
13 maxSurge: 25%
14 maxUnavailable: 25%
15 selector:
16 matchLabels:
17 app: nginx
18 template:
19 metadata:
20 labels:
21 app: nginx
22 spec:
23 restartPolicy: Always
24 containers:
25 - name: nginx
26 image: registry.baidubce.com/cce/nginx-alpine-go:ipv6
27 imagePullPolicy: Always
28 ports:
29 - containerPort: 80
View pod IPv4/IPv6 address:
1# kubectl get pods deployment-example-64445974b7-8s6zc -o go-template --template='{{range .status.podIPs}}{{printf "%s \n" .ip}}{{end}}'
2172.17.0.12
3fc00::cAccess pod IPv4 address:
1# curl 172.17.0.12Access pod IPv6 address:
1# curl -g [fc00::c]:80Note: The image registry.baidubce.com/cce/nginx-alpine-go:latest supports IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack.
Access service via IPv4 or IPv6
In IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack cluster, services can be assigned either IPv4 or IPv6 address.
Specify the service's IP address type using the .spec.ipFamilies attributes of the service, with values of IPv4 or IPv6.
Note
- If the
.spec.ipFamiliesconfiguration is unspecified, Kubernetes will use the first IP range from the --service-cluster-ip-range parameter in kube-controller-manager to allocate IP addresses for services. To avoid confusion, we recommend always configuring the.spec.ipFamiliesattributes when deploying services in dual-stack clusters..spec.ipFamiliesis a mutable field: Addition or deletion of the secondary IP address of the service can be controlled by modifying the value of this field. However, the primary IP address of the service must not be modified.- When using an IPv6 LoadBalancer Service, backend Pods cannot retrieve the original IP address of the request from the network packet.
Create an IPv4 single-stack service
Specify spec.ipFamily: IPv4 assigns IPv4 addresses to services:
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Service
3metadata:
4 name: service-example-ipv4
5 annotations:
6 prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
7spec:
8 ipFamilies:
9 - IPv4
10 ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
11 selector:
12 app: nginx
13 type: LoadBalancer
14 externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
15 sessionAffinity: None
16 ports:
17 - name: nginx
18 protocol: TCP
19 port: 80
20 targetPort: 80View IPv4 service details:
1# kubectl describe svc service-example-ipv4
2Name: service-example-ipv4
3Namespace: default
4Labels: <none>
5Annotations: prometheus.io/scrape: true
6 service.beta.kubernetes.io/cce-load-balancer-id: lb-bedc26c1
7Selector: app=nginx
8Type: LoadBalancer
9IP: 172.16.63.112
10LoadBalancer Ingress: 106.13.103.101
11Port: nginx 80/TCP
12TargetPort: 80/TCP
13NodePort: nginx 30009/TCP
14Endpoints: 172.17.0.12:80,172.17.0.13:80
15Session Affinity: None
16External Traffic Policy: Cluster
17Events:
18 Type Reason Age From Message
19 ---- ------ ---- ---- -------
20 Normal EnsuringLoadBalancer 6m56s service-controller Ensuring load balancer
21 Normal EnsuredLoadBalancer 6m37s service-controller Ensured load balancerAccess IPv4 ClusterIP:
1# curl 172.16.63.112
2<!DOCTYPE html>
3<html>
4<head>
5<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
6<style>
7 body {
8 width: 35em;
9 margin: 0 auto;
10 font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
11 }
12</style>
13</head>
14<body>
15<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
16<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
17working. Further configuration is required.</p>
18<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
19<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
20Commercial support is available at
21<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
22<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
23</body>
24</html>Create an IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack service
Specify spec.ipFamily: IPv6 assigns IPv6 addresses to services:
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Service
3metadata:
4 name: service-example-ipv6
5 annotations:
6 prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
7spec:
8 ipFamilyPolicy: PreferDualStack
9 ipFamilies:
10 - IPv6
11 - IPv4
12 selector:
13 app: nginx
14 type: LoadBalancer
15 externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
16 sessionAffinity: None
17 ports:
18 - name: nginx
19 protocol: TCP
20 port: 80
21 targetPort: 80View IPv6 service details:
1# kubectl describe svc service-example-ipv6
2Name: service-example-ipv6
3Namespace: default
4Labels: <none>
5Annotations: prometheus.io/scrape: true
6 service.beta.kubernetes.io/cce-load-balancer-id: lb-da9b6673
7Selector: app=nginx
8Type: LoadBalancer
9IP: fdff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:faa0
10LoadBalancer Ingress: 240c:4082:1:4202::8
11Port: nginx 80/TCP
12TargetPort: 80/TCP
13NodePort: nginx 30685/TCP
14Endpoints: [fc00::c]:80,[fc00::d]:80
15Session Affinity: None
16External Traffic Policy: Cluster
17Events:
18 Type Reason Age From Message
19 ---- ------ ---- ---- -------
20 Normal EnsuringLoadBalancer 4m8s service-controller Ensuring load balancer
21 Normal EnsuredLoadBalancer 3m56s service-controller Ensured load balancerAccess IPv6 ClusterIP:
1# curl -g [fdff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:faa0]:80
2<!DOCTYPE html>
3<html>
4<head>
5<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
6<style>
7 body {
8 width: 35em;
9 margin: 0 auto;
10 font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
11 }
12</style>
13</head>
14<body>
15<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
16<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
17working. Further configuration is required.</p>
18<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
19<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
20Commercial support is available at
21<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
22<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
23</body>
24</html>Public network accesses services via IPv6 addresses
The IPv6 gateway provides public network connectivity for IPv6 addresses within the VPC. To enable access to services using IPv6 from the public network or allow containers with IPv6 addresses to access the public network, the VPC must be configured with an IPv6 gateway and an associated route.
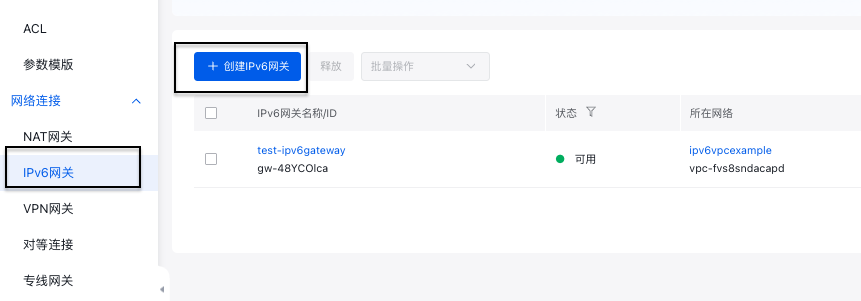
Create IPv6 gateway
Click Create IPv6 Gateway in the IPv6 Gateway tab of the VPC console
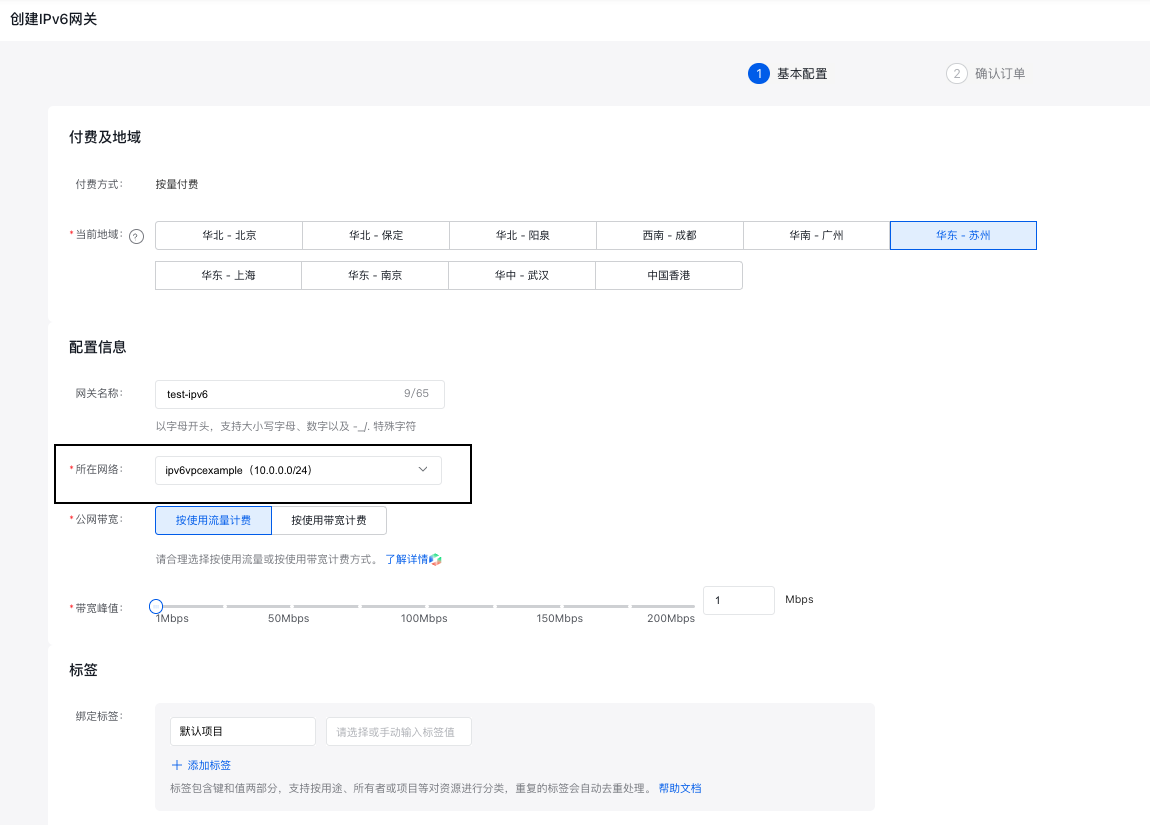
Enter the gateway information. In the Network section, select the VPC where the cluster resides.
Add IPv6 gateway route
In the VPC Instance page of VPC console, click the Route Table tab to create a new route table or use the default route table.
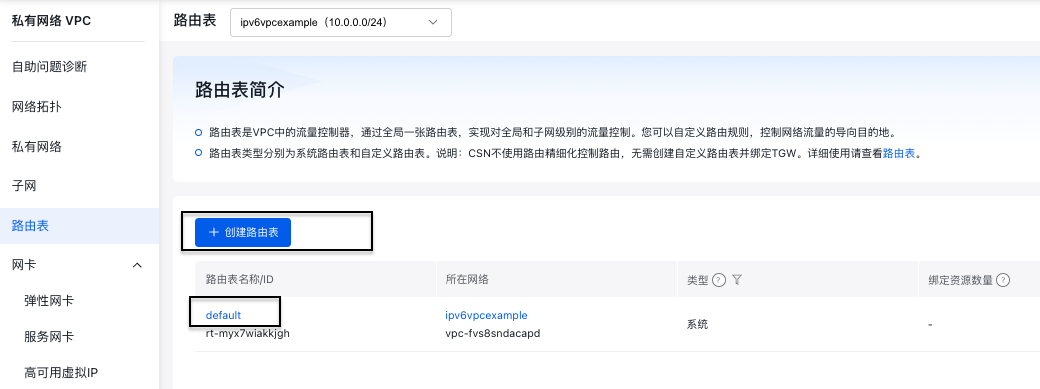
Select the route table to configure, click "Add Route," and enter the route table entry configuration details. The Source Network Segment refers to the subnet segment within the VPC, the Destination Network Segment is ::/0; the Route Type is IPv6 Gateway, and the Next Hop Instance is the gateway created in the previous step.
Note: If your cluster spans multiple subnets within a VPC, you need to create route entries for each subnet network segment.
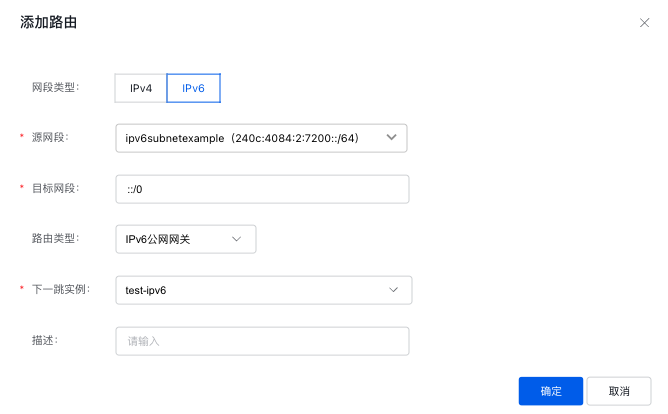
Access the aforementioned service IPv6 EIP:
1# curl -g [240c:4082:1:4202::8]:80