Usage Instructions for Logical Queues and Physical Queues
overview of queue functions
Queues, as subsets of resource pools, are used to handle workloads such as training tasks and model services. Users can partition resource pools into multiple independent queues (logical or physical queues) to execute different workloads. A default queue is automatically created once a resource pool is successfully set up. This document provides guidance on creating, updating, and utilizing queues through YAML templates.
Prerequisites
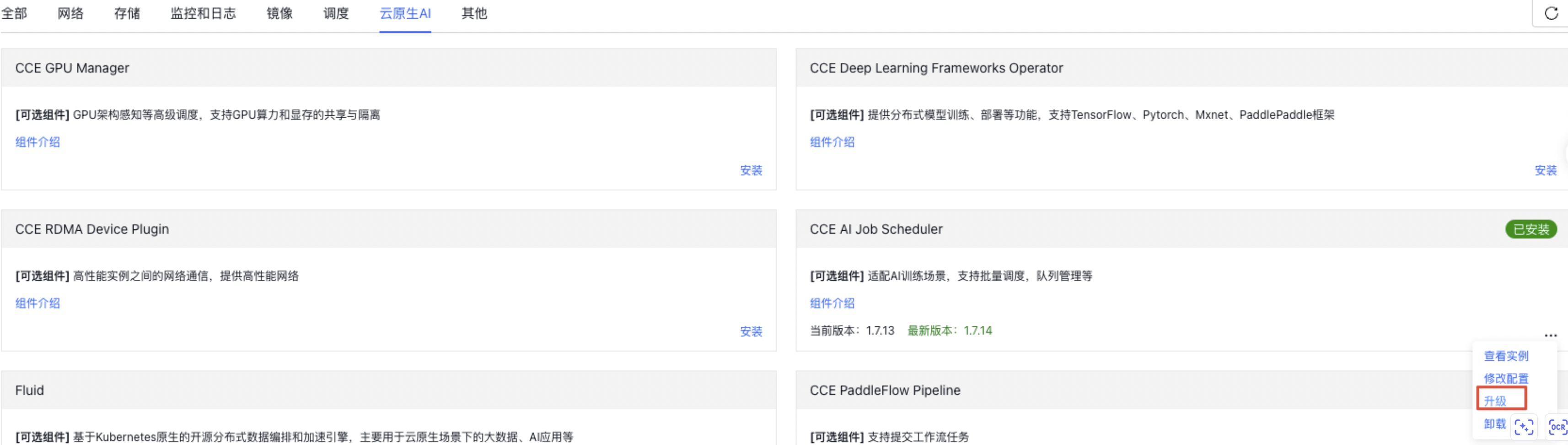
On the CCE Component Management page, navigate to the Cloud Native AI section and upgrade the CCE AI Job Scheduler component to version 1.7.14 or above to access queue-related features, as shown in the figure below.
Logical queue
Ordinary queue
Standard queues are the most common way to allocate resource quotas among various application workloads. They assign fixed-quantity quota resources to different departments to enable basic resource allocation functionalities.
Elastic queue
Elastic queues are designed to help platform-based customers allocate resource quotas more dynamically and efficiently across different application departments. These queues enable borrowing idle resource quotas from one queue to another, supporting features such as resource lending/reclaiming and task oversell/preemption, thus enhancing GPU/NPU resource utilization. Detailed task oversell and resource preemption strategies can be found in the appendix.
Hierarchical queues
Hierarchical queues cater to medium and large-scale customers with complex organizational frameworks or scenarios requiring multi-level resource quota management. They enable resource quota management across multiple levels and queues.
Physical queue
Utilize physical queues to ensure GPU/NPU resources are physically isolated, guaranteeing resource availability for critical applications while preventing resource preemption. Additionally, multiple sub-logical queues can be created within a physical queue.
Description of queue functions
Instructions for quota setting
For elastic queues, configure three types of quotas: guaranteed quota, deserved quota, and capability quota. This classification divides computing resources into exclusive, shared, and preemptive categories, optimizing costs and enhancing GPU/NPU resource utilization.
- Guaranteed quota: The portion of resources exclusively reserved for the queue, which will never be borrowed by other queues.
- Deserved quota: The portion of resources requested by the queue based on estimated confirmed usage. If inter-queue preemption is enabled, other queues may use idle shared resources allocated to this queue.
- Capability quota: The maximum resources available to the queue.
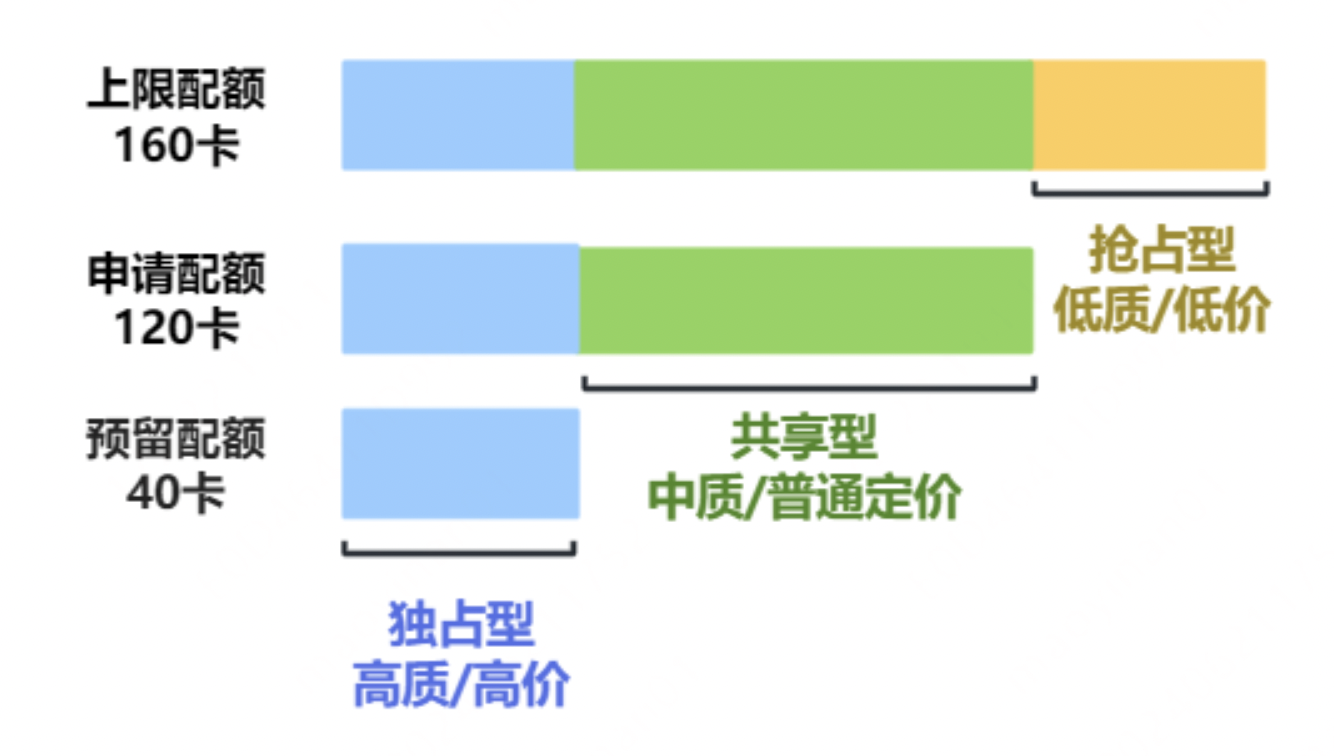
For a better understanding of the above quota concepts, refer to the following examples:
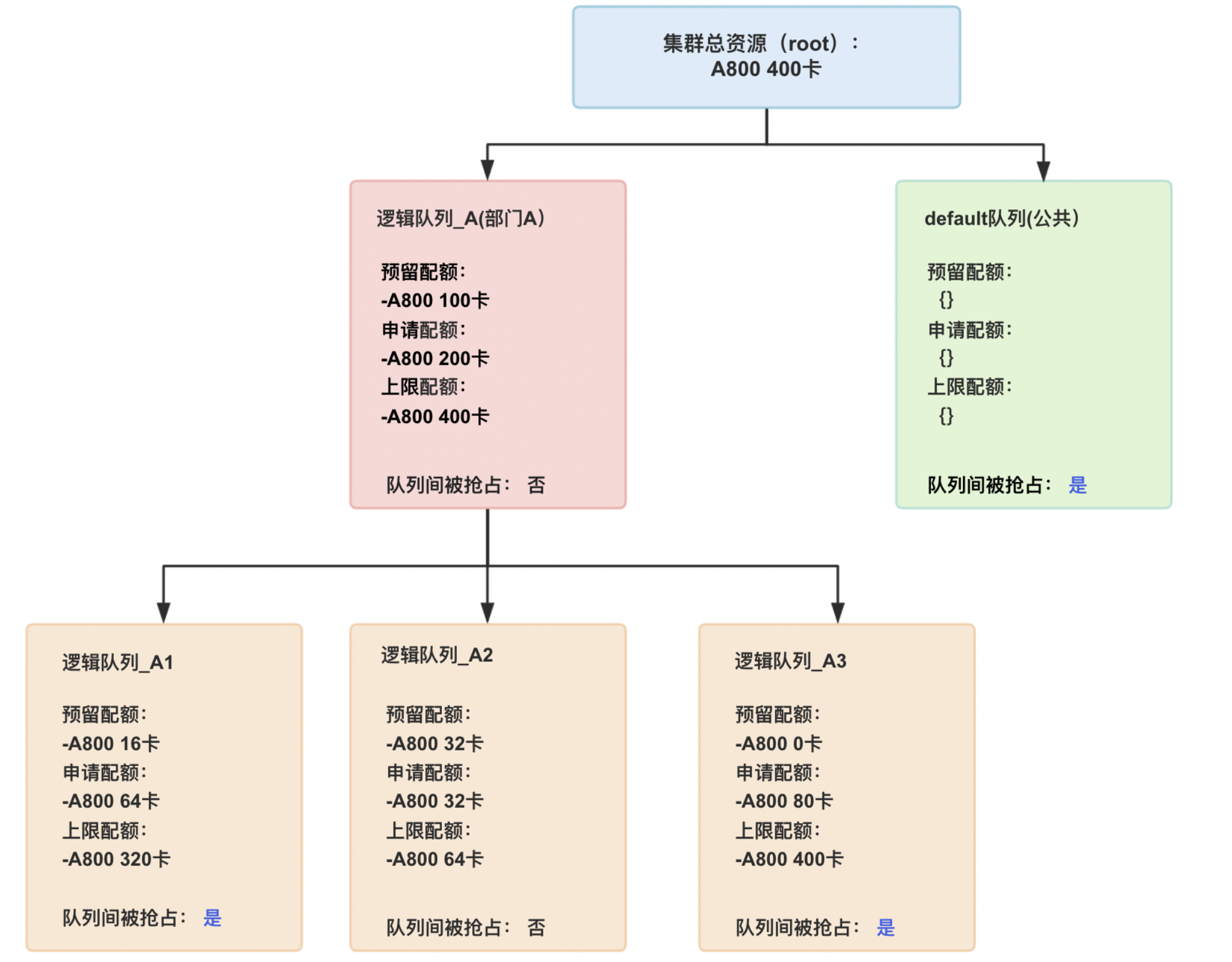
Queue parameter description
| Parameters | Parameter type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | Metadata | Queue name: The name of the new queue; “root” is not allowed | |
| labels | Metadata | The name of the parent queue to which this queue belongs. When creating a queue, the default queue and the second-level queues of hierarchical queues are prohibited from being set as parent queues | |
| Guarantee | Spec | Guaranteed resources: Reserved resources for the queue that cannot be borrowed by others, even if unallocated. The summed guaranteed resources of sub-queues should not exceed that of the parent queue, which in turn should not exceed cluster resources. By default, this is not configured; idle cluster resources are usable. | |
| Deserved | Spec | Deserved resources: Resources requested by the queue. The summed deserved resources of sub-queues should not exceed that of the parent queue, which in turn should not exceed cluster resources. By default, this is not configured; idle cluster resources are usable. | |
| Capability | Spec | Capability resources: The maximum permissible resources for the queue. The capability quota of sub-queues should not exceed that of the parent queue, which itself should not exceed cluster resources. By default, this is not configured. | |
| Reclaimable | Spec | Enable inter-queue preemption and allow borrowed resources to be preempted by default. | |
| State | Status | Queue status: Defaults to Open; supports setting to Close to disable the queue. Once closed, the queue will reject new task submissions | |
| baidu.com/elastic-queue-is-parent | Annotations | Is parent queue: Defaults to No. Direct task submission to parent queues is not supported, and sub-queues cannot be created if the parent queue has running tasks | |
| baidu.com/elastic-queue-parent | Annotations | The name of the parent queue can be specified; defaults to the cluster root queue (root). Cannot be specified as the default queue, second-level queues in hierarchical queues, or queues with running tasks |
Queue notes
Create a queue
- If the system root queue is not initialized, queue creation/modification is not allowed
- Creating queues with duplicate names is not allowed
- If no parent queue is specified, the root queue is set as the parent queue by default
-
Queue quota is subject to the following restrictions:
- Applying for negative quotas is not allowed
- Queues must meet the configuration rule: capability ≥ deserved ≥ guarantee
- The capability quota of a queue cannot exceed that of its parent queue
- The sum of deserved or guarantee quotas of queues at the same level in the cluster cannot exceed those of their parent queue
-
Hierarchical queues are subject to the following restrictions:
- The specified parent queue must exist
- Specify the default queue as a parent queue
- Specify a Level 2 queue as a parent queue
- Adding sub-queues to queues with running tasks is not allowed
-
Physical queue is subject to the following restrictions:
- Configuration of capability, deserved and guarantee must be the same
Queue deletion
- In hierarchical queues, directly deleting a parent queue is not allowed. It is required to delete the sub-queues before deleting the parent queue;
- Queues with active tasks cannot be deleted.
Queue update
- Physical queues cannot be converted to ordinary queues
- The physical queue binding label of logical queues under a physical queue cannot be modified
- The capability quota cannot be less than the allocated (already allocated) resources
-
After modifying the parent queue
- The capability quota of the queue cannot be less than the sum of capability quotas of its sub-queues
- The parent queue’s deserved or guarantee quota cannot be less than the sum of those of its sub-queues
- Violations of the queue creation rules are not allowed
YAML template operation steps
Logical queue usage
Create elastic queues and hierarchical queues
- Prepare the YAML file for queue creation (see the example below)
1apiVersion: scheduling.volcano.sh/v1beta1
2kind: Queue
3metadata:
4 name: demo-queue
5 labels:
6 baidu.com/queue-parent: xxxx
7spec:
8 capability:
9 baidu.com/a800_80g_cgpu: "6"
10 guarantee:
11 resource:
12 baidu.com/a800_80g_cgpu: "1"
13 deserved:
14 baidu.com/a800_80g_cgpu: "2"
15 reclaimable: false
16status:
17 allocated:
18 cpu: "0"
19 memory: "0"
20 reservation: {}
21 state: Open- Submit the YAML file to create the queue in the cluster
kubectl apply -f demo-queue.yaml
Update logical queue
Run the following command to modify the queue configuration:
kubectl edit queue demo-queue
Submit tasks to logical queues
Submit tasks using YAML to test and verify queue functionalities.
1apiVersion: "kubeflow.org/v1"
2kind: PyTorchJob
3metadata:
4 name: training-task
5spec:
6 runPolicy:
7 schedulingPolicy:
8 queue: "queue-name" // Specify the queue
9 priorityClass: "normal"
10 pytorchReplicaSpecs:
11 Worker:
12 replicas: 2
13 template:
14 spec:
15 tolerations:
16 - key: "kwok.x-k8s.io/node"
17 operator: "Equal"
18 value: "fake"
19 effect: "NoSchedule"
20 containers:
21 - name: pytorch
22 image: demo-image:1.0
23 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
24 resources:
25 limits:
26 nvidia.com/gpu: 4
27 schedulerName: volcano| Parameters | Parameter type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | Meta | Task name |
| runPolicy.schedulingPolicy.queue | Spec | Submit tasks to the specified queue |
| runPolicy.schedulingPolicy.priorityClass | Spec | Task priority: Supports three levels: high, medium, low |
| pytorchReplicaSpecs.Worker.replicas | Spec | Number of task replicas |
Physical queue usage
Node partitioning
Include target nodes in the physical queue. It's advisable to evacuate tasks from the relevant nodes beforehand; nodes with uncompleted tasks can also be directly added to the physical queue, but their GPU resources will only be released once the tasks are finalized.
Note: The resource application for the physical queue must match the resources of the incorporated nodes precisely. For example, if a physical queue requests 16 GPU cards, two nodes with 8 GPU cards each can be included. Over-partitioning wastes resources, while under-partitioning might cause scheduling issues.
Partitioning is divided into two steps:
- Add taints: This will only affect the scheduling of newly submitted tasks and will not impact tasks already in progress.
kubectl taint nodes targetNode aihc.baidu.com/dedicated-pool=queue-physical-name:NoSchedule
- Add tag
kubectl label nodes targetNode aihc.baidu.com/dedicated-pool=queue-physical-name
1Note: When adding labels and taints, replace targetNode with the node IP. Separate multiple IPs with spaces.Create physical queue
Define a physical queue using the YAML template below
1apiVersion: scheduling.volcano.sh/v1beta1
2kind: Queue
3metadata:
4 labels:
5 baidu.com/queue-is-physical-queue: "true"
6 name: queue-physical-name
7spec:
8 capability:
9 nvidia.com/gpu: "16"
10 deserved:
11 nvidia.com/gpu: "16"
12 guarantee:
13 resource:
14 nvidia.com/gpu: "16"
15 reclaimable: false
16 weight: 11Note: Only modify 4 parameters: name (queue name), capability, deserved, and guarantee. The three quota-related parameters (capability, deserved, guarantee) must be consistent and correspond to the number of GPU cards applied for by the physical queue. Keep other parameters unchanged.Create logical queues under a queue (optional)
To allocate more granular resources within a physical queue, you can establish logical sub-queues under it. Unlike physical queues, sub-queues are not tied to specific nodes and only ensure compliance with resource quotas.
1apiVersion: scheduling.volcano.sh/v1beta1
2kind: Queue
3metadata:
4 labels:
5 baidu.com/queue-parent: queue-physical-name
6 name: queue-logical-name
7spec:
8 deserved:
9 nvidia.com/gpu: "8"
10 guarantee:{}
11 reclaimable: false
12 weight: 1To request a fixed-quota logical queue, refer to the example above and set the desired quota. Ensure that the sum of desired quotas across all sub-queues does not exceed the total quota assigned to the physical queue.
1Note: The following actions are invalid:
2 * Adding sub-queues under a physical queue with running tasks
3 * Submitting tasks to a physical queue that already has sub-queuesModify physical queue
(1) Update physical queue quota
Use the command kubectl edit queue queue-physical-name to modify the physical queue quota. Set the quota to the total quota after incorporating new nodes
(2) Incorporate new nodes
Similar to the node partitioning steps, perform the following two operations on the new nodes
- Add taints
kubectl taint nodes targetNode aihc.baidu.com/dedicated-pool=queue-physical-name:NoSchedule
- Add tag
kubectl label nodes targetNode aihc.baidu.com/dedicated-pool=queue-physical-name
