CCE QoS Agent Description
Component introduction
cce-qos-agent, based on BaiduLinux capabilities, provides Kubernetes-native QoS-based service quality assurance, container isolation and hardening capabilities for containers while improving resource utilization.
Note: QoS-related capabilities are supported only on nodes running BaiduLinux3 as the operating system. For nodes using other operating systems, these capabilities will not be applied.
Component function
- Configure node resource utilization. When the overall resource usage exceeds the configured resource utilization, it will trigger the suppression or eviction of low-priority containers;
- Enhanced container QoS, including the capabilities listed in the table below
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced CPU QoS | Support for CPU priority configuration allows high-priority workloads to secure resources during competition while limiting resources for lower-priority workloads. |
| Enhanced memory QoS | Support for memory background reclamation, OOMKill priority adjustments, and more to enhance overall memory performance. |
| Enhanced network QoS | Support for network bandwidth priority configuration, ingress/egress rate limiting, and flexible regulation of container network usage. |
Limitations
- Cluster version 1.18.9 or higher
- BaiduLinux3 as the node OS
- Be able to access the cluster using kubectl. For operation steps, refer to: Connect to the Cluster via Kubectl
Install component
- Sign in to the Baidu AI Cloud official website and enter the management console.
- Go to Product Services - Cloud Native - Cloud Container Engine (CCE) to access the CCE management console.
- Click Cluster Management > Cluster List in the left navigation bar.
- Click on the target cluster name in the Cluster List page to navigate to the cluster management page.
- On the Cluster Management page, click Component Management.
- Select the CCE QoS Agent component from the component management list and click Install.
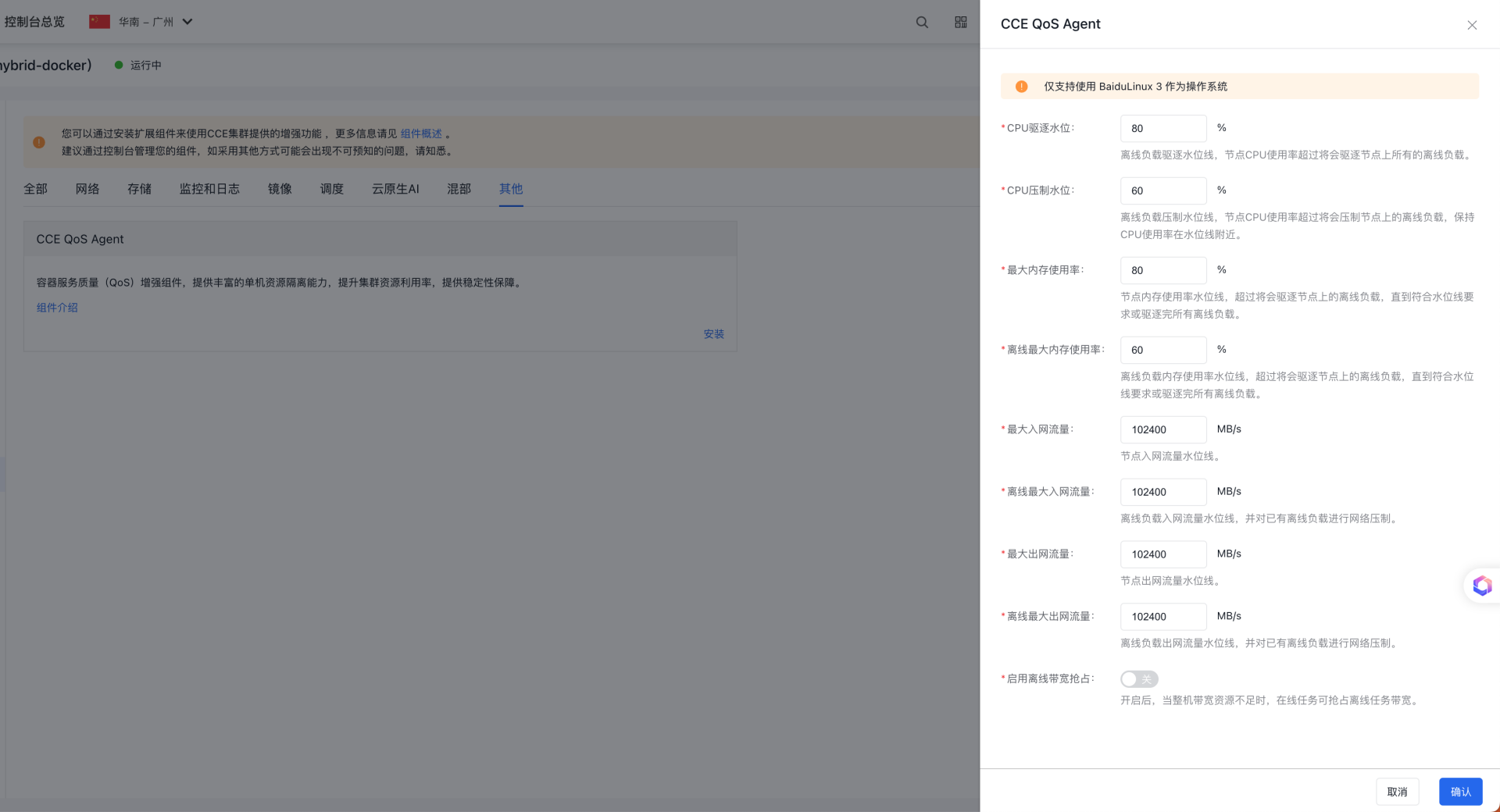
- Complete node resource utilization configuration on the Component Configuration page.
- Click the OK button to finalize the component installation.
Configure node resource utilization
The meanings of configuration items are as follows:
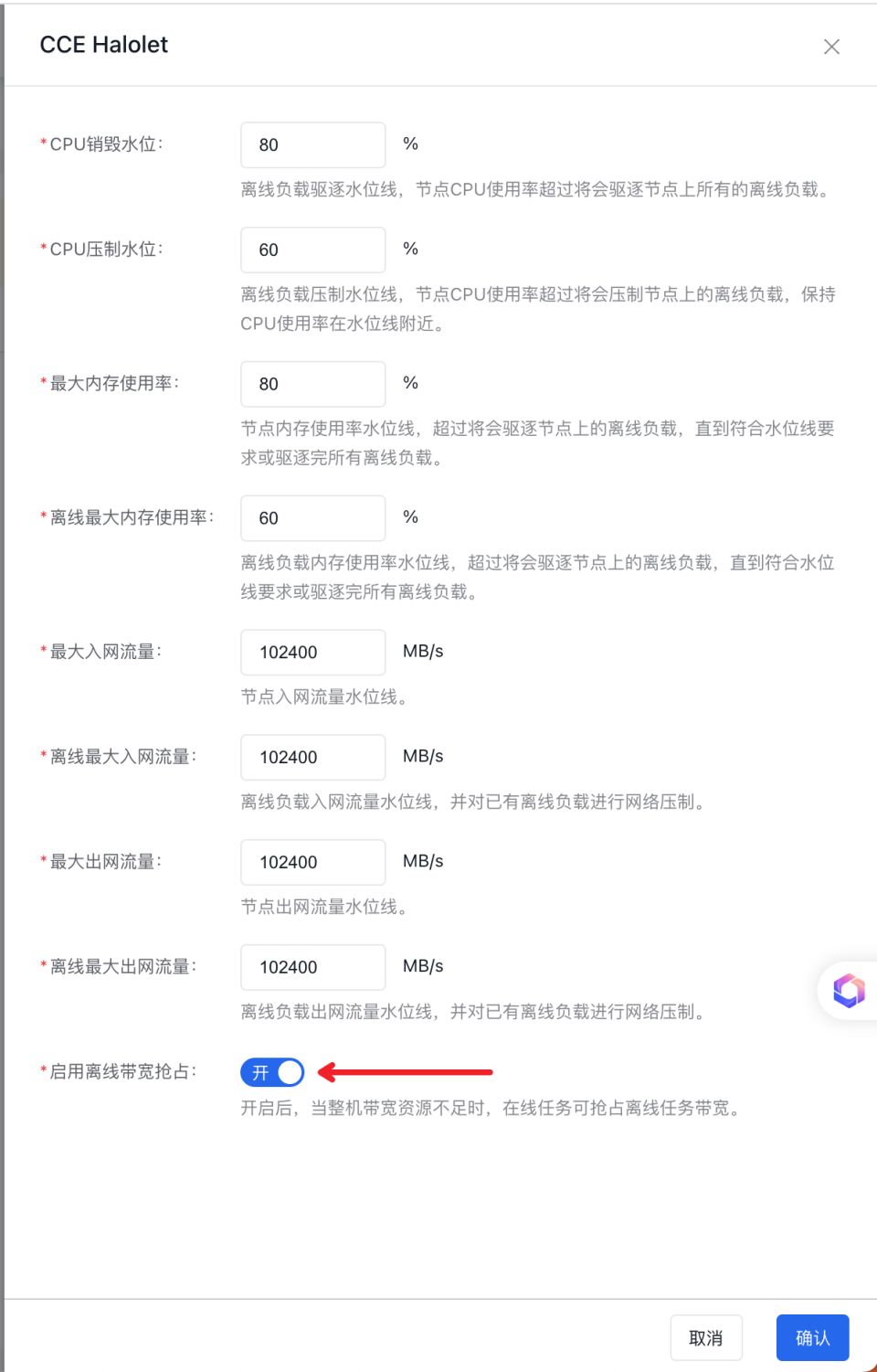
- CPU eviction watermark: When the overall CPU usage reaches the eviction watermark, all low-priority services will be evicted to protect high-priority services. The default is 80%;
- CPU throttling watermark: When the overall CPU usage reaches the throttling watermark, all low-priority services will be throttled to protect high-priority services. The default is 60%;
- Overall maximum watermark: When the overall memory usage exceeds the maximum limit, low-priority services will be evicted to protect high-priority services. The default is 80%;
- Low-priority memory maximum watermark: When the low-priority memory usage exceeds the maximum limit, low-priority services will be evicted to protect high-priority services. The default is 60%;
- Overall maximum ingress traffic: When the overall ingress traffic exceeds this limit, offline applications will be prohibited from being scheduled to the node;
- Offline maximum ingress traffic: When the offline ingress traffic exceeds this limit, existing offline workloads will be subject to network throttling;
- Overall maximum egress traffic: When the overall ingress traffic exceeds this limit, offline applications will be prohibited from being scheduled to the node;
- Offline maximum egress traffic: When the offline ingress traffic exceeds this limit, existing offline workloads will be subject to network throttling;
- Enable network bandwidth preemption: When overall bandwidth is insufficient, online tasks will preempt bandwidth from offline tasks (disabled by default);
Apply resource utilization to nodes
After installing the cce-qos-agent component, add the label cce.baidu.com/sla-pool="default" to the node to apply resource utilization to nodes.
Taking node 10.0.3.13 as an example, execute the following command in the terminal:
1kubectl label node 10.0.3.13 cce.baidu.com/sla-pool="default"Configure Pod QoS
After installing the standalone engine, users can extend the enhanced isolation and hardening capabilities of Pods through Pod labels. The supported configuration items are as follows:
| Capability | Capability descriptions | Pod Label | Parameter description | Unit | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU priority | Configure CPU priority settings. | cpu.priority | Support configuring Pods as online and offline tasks | - | None |
| Set memcg background reclamation capability | Background reclamation capability: Control Pod-level asynchronous cache reclamation actions. When the Pod’s cache reaches the high watermark (memory.high_wmark_distance), cache reclamation will start and continue until the cache drops to the low watermark (memory.low_wmark_distance) | memory.background_reclaim | Enable memory background reclamation | bool | 0 |
| memory.low_wmark_distance | Low watermark for memory background reclamation | byte | 0 | ||
| memory.high_wmark_distance | High watermark for memory background reclamation | byte | 0 | ||
| Set the priority value for Pods to be killed during OOM | During OOM operations, cgroup priority is assessed first, and lower-priority cgroups are chosen for OOM. Higher cgroup priority values (memory.oom_kill_priority) indicate lower actual priority. | memory.oom_kill_priority | Set OOM kill priority (higher priority means being killed first) | int | 5000 |
| Control the kill mode for process groups in cgroup during OOM | Control the kill mode for process groups in cgroup during OOM: 0: Do not kill all processes in the process group 1: Kill all processes in the process group | memory.kill_mode | Control the OOM kill mode, determining whether to terminate all processes within a process group. | bool | 0 |
| Set network priority | Set Pod network priority | net.priority | Optional values: besteffort | bool | 0 |
Configure CPU QoS
The supported CPU priorities and their corresponding relationships with Kubernetes QoS are as follows:
| CPU priority | K8S QoS | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sensitive | Guaranteed | CPU binding: CPU must be an integer multiple of 1,000 m |
| stable | Guaranteed/Burstable | To achieve better resource elasticity and more flexible resource adjustment capabilities, it is required to fill in at least requests |
| batch | BestEffort | Offline tasks: Compared to BestEffort, CPU usage ratio is twice that of BE |
| besteffort | BestEffort | Offline tasks |
Scenario I: Offline tasks support multi-level CPU priorities, divided by CPU ratio with no preemption
Scenario description:
- Deploy two offline CPU tasks with priorities set as batch and besteffort.
- The CPU runtime for tasks with batch priority is approximately double that of tasks with besteffort priority.
Operation steps:
- Deploy offline CPU tasks; the following YAML includes two CPU stress tasks with priority configured as batch and best effort respectively
1apiVersion: apps/v1
2kind: Deployment
3metadata:
4 name: stress-batch
5spec:
6 selector:
7 matchLabels:
8 app: stress-batch
9 template:
10 metadata:
11 labels:
12 app: stress-batch
13 cpu.priority: batch
14 spec:
15 nodeSelector:
16 kubernetes.io/hostname: 10.0.3.13
17 containers:
18 - name: stress
19 image: registry.baidubce.com/public-tools/stress-ng:latest
20 command:
21 - "stress-ng"
22 args:
23 - --cpu
24 - "0"
25 - --cpu-method
26 - all
27 - -t
28 - 1h
29---
30apiVersion: apps/v1
31kind: Deployment
32metadata:
33 name: stress-besteffort
34spec:
35 selector:
36 matchLabels:
37 app: stress-besteffort
38 template:
39 metadata:
40 labels:
41 app: stress-besteffort
42 cpu.priority: besteffort
43 spec:
44 nodeSelector:
45 kubernetes.io/hostname: 10.0.3.13
46 containers:
47 - name: stress
48 image: registry.baidubce.com/public-tools/stress-ng:latest
49 command:
50 - "stress-ng"
51 args:
52 - --cpu
53 - "0"
54 - --cpu-method
55 - all
56 - -t
57 - 1h- After deployment, calculate the runtime of the two containers in the past 1 s on the node where the Pod is located
1#!/bin/bash
2batchPodID="eccb11ba-b875-4614-ac07-2e811397239a"
3batchContainerID="6e677ceb30c28438bf32d1191d74e7fa0131124ea08fe8647950e07c7a34bef5"
4bePodID="8339d083-5aae-48bd-a2cf-9c91a777dc53"
5beContainerID="6c10640a79479f8d6606d3823a4666cffb225913990b6aab1bfdf8bcf3a6cf47"
6batch_start=`cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/kubepods/besteffort/pod${batchPodID}/${batchContainerID}/cpuacct.bt_usage`
7be_start=`cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/kubepods/besteffort/pod${bePodID}/${beContainerID}/cpuacct.bt_usage`
8sleep 1
9batch_end=`cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/kubepods/besteffort/pod${batchPodID}/${batchContainerID}/cpuacct.bt_usage`
10be_end=`cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/kubepods/besteffort/pod${bePodID}/${beContainerID}/cpuacct.bt_usage`
11expr "${batch_end}" - "${batch_start}"
12expr "${be_end}" - "${be_start}"The calculation results show that:
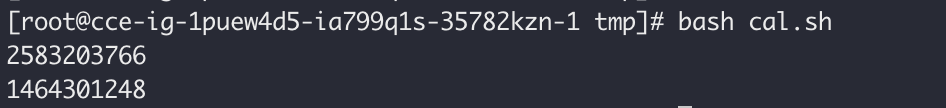
Tasks with batch priority utilize roughly twice the CPU time compared to those with besteffort priority.
Scenario II: Offline tasks support multi-level CPU priorities, divided by CPU ratio with no preemption
Scenario description:
- Based on deploying offline tasks in case 1, deploy online tasks
- Online tasks can preempt CPU resources from offline tasks.
Operation steps:
- Deploy an online CPU task with the priority configured as stable
1apiVersion: apps/v1
2kind: Deployment
3metadata:
4 name: stress-stable
5spec:
6 selector:
7 matchLabels:
8 app: stress-stable
9 template:
10 metadata:
11 labels:
12 app: stress-stable
13 cpu.priority: stable
14 spec:
15 nodeSelector:
16 kubernetes.io/hostname: 10.0.3.13
17 containers:
18 - name: stress
19 image: registry.baidubce.com/public-tools/stress-ng:latest
20 command:
21 - "stress-ng"
22 args:
23 - --cpu
24 - "0"
25 - --cpu-method
26 - all
27 - -t
28 - 1h
29 resources:
30 requests:
31 cpu: 1
32 memory: 2Gi- Re-execute the script from case 1 and observe that offline tasks barely execute
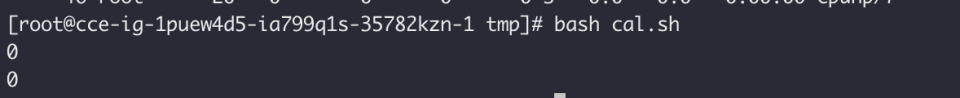
Online tasks demonstrate absolute resource preemption over offline tasks. When overall resources are scarce, online tasks are guaranteed to run, while offline tasks may not be executed.
Scenario III: Deploy an online CPU task with sensitive priority to implement CPU binding
Scenario description:
- Deploy a task with CPU priority set to sensitive to achieve CPU binding
Operation steps:
- Deploy the task and configure its CPU priority as sensitive
1apiVersion: apps/v1
2kind: Deployment
3metadata:
4 name: stress-sensitive
5spec:
6 selector:
7 matchLabels:
8 app: stress-sensitive
9 template:
10 metadata:
11 labels:
12 app: stress-sensitive
13 cpu.priority: sensitive
14 spec:
15 nodeSelector:
16 kubernetes.io/hostname: 10.0.3.13
17 containers:
18 - name: stress
19 image: registry.baidubce.com/public-tools/stress-ng:latest
20 command:
21 - "stress-ng"
22 args:
23 - --cpu
24 - "0"
25 - --cpu-method
26 - all
27 - -t
28 - 1h
29 resources:
30 requests:
31 cpu: 1
32 memory: 2Gi
33 limits:
34 cpu: 1
35 memory: 2Gi- Check the CPU binding result via cgroups by executing the following script on the node where the Pod is located
1#!/bin/bash
2sensitivePodID="f203ffd5-8618-4568-8547-836db6a906f2"
3sensitiveContainerID="2c551bfde9d0f5e9f46f049ac8acf856567bd9441dbdedac5fec1151f8a93721"
4cat /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset/kubepods/pod${sensitivePodID}/${sensitiveContainerID}The results show that:

The container is bound to CPU core 7.
Configure network QoS
Enable the network priority function
In the component center, modify the standalone isolation engine configuration and enable the "network priority function"
Scenario I: Online tasks can preempt bandwidth from offline tasks
Scenario description:
- On the same node, deploy a low-network-priority task first, followed by a task with the default network priority. Observe the bandwidth changes of the tasks; it is expected that the bandwidth of the low-network-priority task will be preempted
Operation steps:
- Deploy the server service
1 apiVersion: apps/v1
2kind: Deployment
3metadata:
4 name: net-server-1
5 labels:
6 app: net-server-1
7spec:
8 replicas: 1
9 selector:
10 matchLabels:
11 app: net-server-1
12 template:
13 metadata:
14 labels:
15 app: net-server-1
16 spec:
17 nodeSelector:
18 kubernetes.io/hostname: 10.0.3.14
19 containers:
20 - name: server
21 image: registry.baidubce.com/public-tools/iperf3:latest
22 args: [ "-s", "-p", "5201"]
23 ports:
24 - name: http
25 containerPort: 5201
26 hostPort: 5201
27 protocol: TCP
28 resources:
29 limits:
30 cpu: 4
31 memory: 2Gi
32 requests:
33 cpu: 4
34---
35apiVersion: v1
36kind: Service
37metadata:
38 name: net-server-1
39spec:
40 selector:
41 app: net-server-1
42 ports:
43 - port: 5201
44 targetPort: 5201
45---
46apiVersion: apps/v1
47kind: Deployment
48metadata:
49 name: net-server-2
50 labels:
51 app: net-server-2
52spec:
53 replicas: 1
54 selector:
55 matchLabels:
56 app: net-server-2
57 template:
58 metadata:
59 labels:
60 app: net-server-2
61 spec:
62 nodeSelector:
63 kubernetes.io/hostname: 10.0.3.15
64 containers:
65 - name: server
66 image: registry.baidubce.com/public-tools/iperf3:latest
67 args: [ "-s", "-p", "5201"]
68 ports:
69 - name: http
70 containerPort: 5201
71 hostPort: 5201
72 protocol: TCP
73 resources:
74 limits:
75 cpu: 4
76 memory: 2Gi
77 requests:
78 cpu: 4
79---
80apiVersion: v1
81kind: Service
82metadata:
83 name: net-server-2
84spec:
85 selector:
86 app: net-server-2
87 ports:
88 - port: 5201
89 targetPort: 5201- Deploy a task and configure its network priority as besteffort
1apiVersion: apps/v1
2kind: Deployment
3metadata:
4 name: offline-net-client
5 labels:
6 app: offline-net-client
7spec:
8 replicas: 1
9 selector:
10 matchLabels:
11 app: offline-net-client
12 template:
13 metadata:
14 labels:
15 app: offline-net-client
16 net.priority: besteffort
17 spec:
18 nodeSelector:
19 kubernetes.io/hostname: 10.0.3.13
20 containers:
21 - name: main
22 image: registry.baidubce.com/public-tools/iperf3:latest
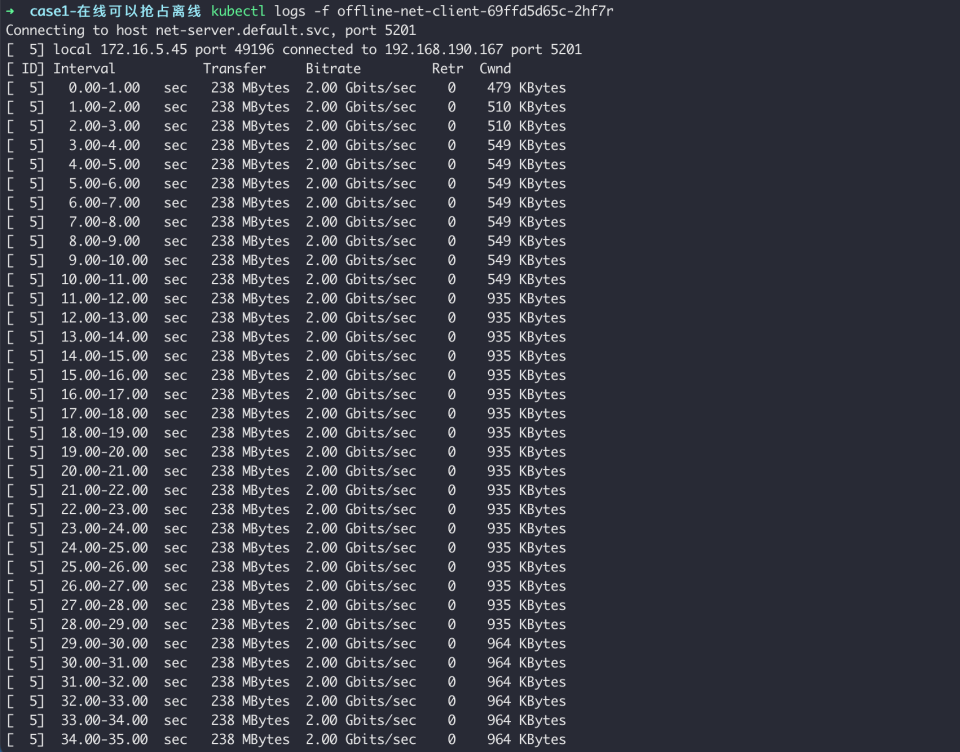
23 args: [ "-c", "net-server-1.default.svc", "-p", "5201", "-b", "2000Mb" ,"-t","3600"]Observe the task bandwidth:
- Deploy a task with online network priority and observe the bandwidth of both online and offline tasks
1apiVersion: apps/v1
2kind: Deployment
3metadata:
4 name: online-net-client
5 labels:
6 app: online-net-client
7spec:
8 replicas: 1
9 selector:
10 matchLabels:
11 app: online-net-client
12 template:
13 metadata:
14 labels:
15 app: online-net-client
16 spec:
17 nodeSelector:
18 kubernetes.io/hostname: 10.0.3.13
19 containers:
20 - name: main
21 image: registry.baidubce.com/public-tools/iperf3:latest
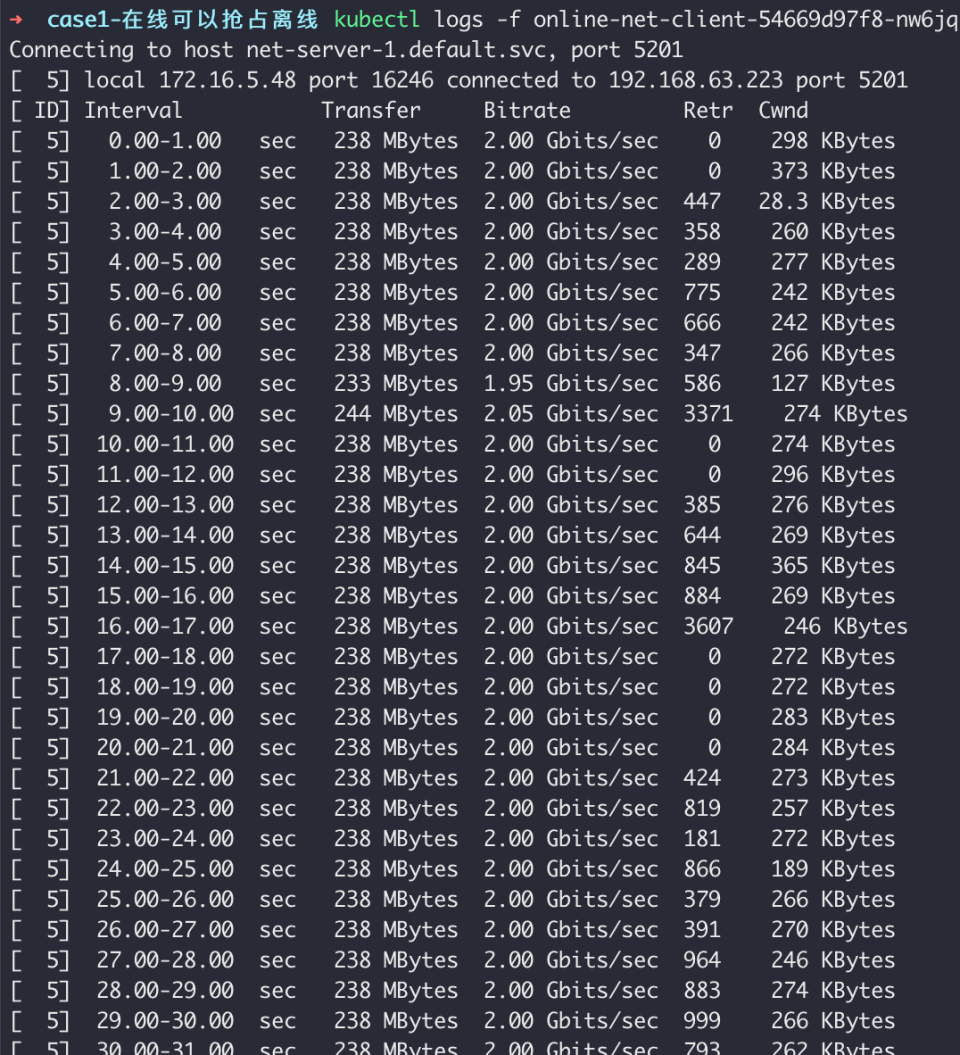
22 args: [ "-c", "net-server-2.default.svc", "-p", "5201", "-b", "2000Mb" ,"-t","3600"]Monitor the bandwidth of online tasks:
Monitor the bandwidth of offline tasks:
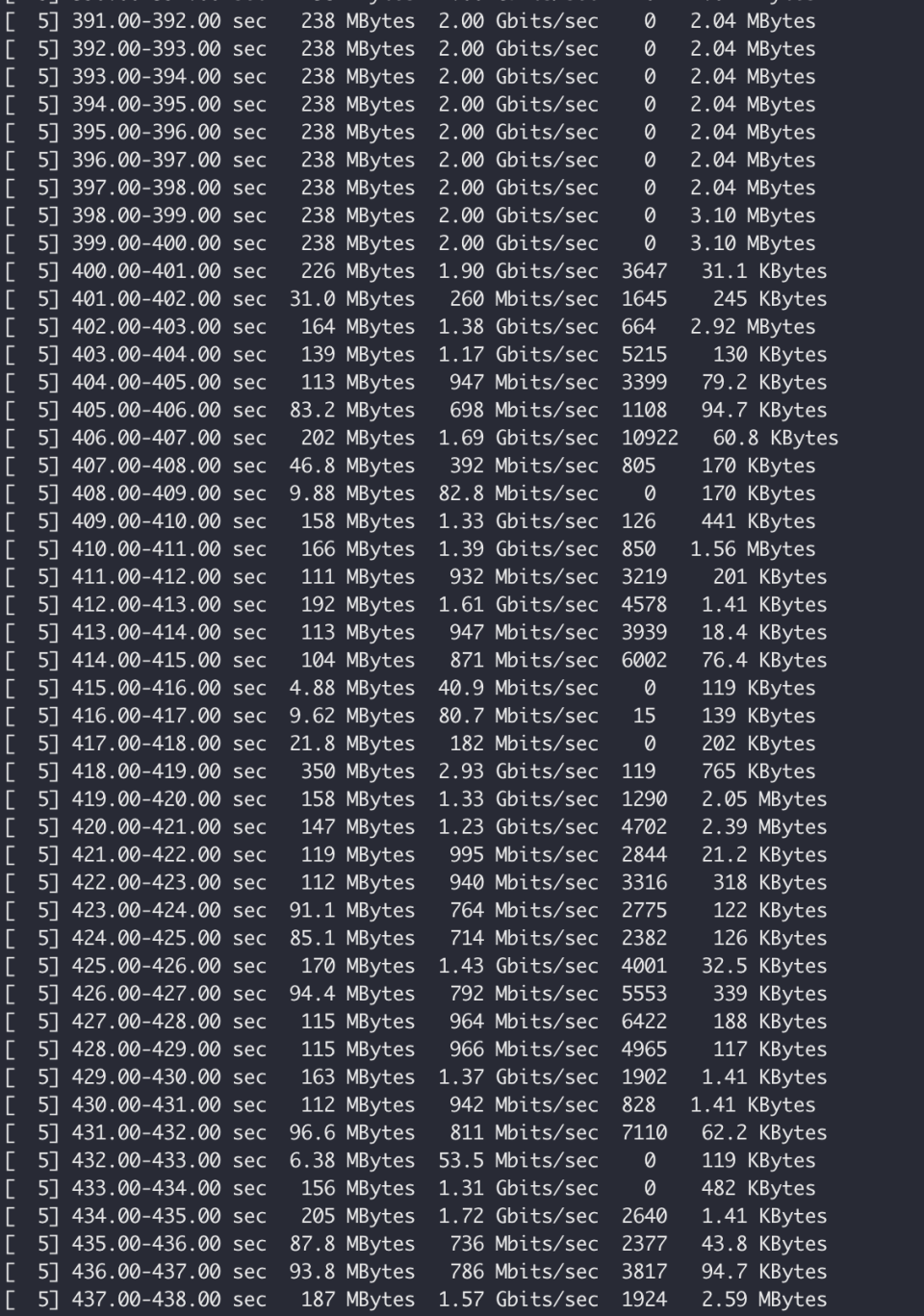
When overall bandwidth is insufficient, online tasks receive priority for bandwidth usage, while offline task bandwidth is preempted.
Version records
| Version No. | Cluster version compatibility | Update time | Update content | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1.0 | v1.18+ | 2023.09.13 | Enhanced CPU QoS: Support CPU priority configuration. By setting priorities for workloads, ensure the resource supply of high-priority services in the event of resource competition, and throttle low-priority services. Enhanced memory QoS: Support memory background reclamation, OOMKill priority, etc., to improve overall memory performance. Enhanced network QoS: Support network bandwidth priority configuration, ingress/egress rate limiting, etc., to flexibly restrict container network usage. |
None |
