Configure Cluster OIDC Authentication
This document explains CCE cluster OIDC authentication, its enabling steps, and how to integrate it with RBAC.
Certification notes
- Kubernetes Cluster CCE OIDC authentication is based on Baidu AI Cloud IAM identity authentication. It supports both IAM users and IAM roles.
- K8S Cluster CCE only supports X509 certificate-based certification by default. Only support to enable OIDC certification when the new version of K8S Cluster CCE is created.
- After enabling OIDC authentication for a Kubernetes Cluster CCE, X509 certificate-based authentication capabilities remain available.
- After enabling OIDC certification for K8S Cluster CCE, it supports operating cluster resources via AssumeRole.
Operation steps
Enable OIDC certification
- Sign in to Baidu AI Cloud console, and navigate to Products & Services > Cloud Container Engine (CCE);
- On the Cluster List page, click Create Cluster to enter the Cluster Creation page:
-
Under Cluster Configuration > Advanced Settings, check Enable OIDC Certification.
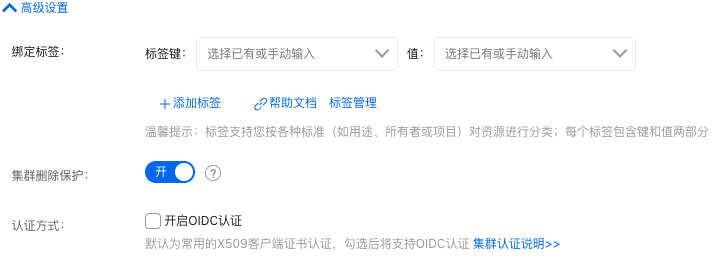
- On the Target Cluster List Details page, click View Cluster Credentials to download the OIDC-based KubeConfig file. Based on this file, you can access the cluster through OIDC certification.
- When operating cluster resources via KubeConfig or directly in the console, ensure that IAM users performing the operation (when accessed via IAM users) or the IAM Role switched by the users (when accessed via AssumeRole) have been granted the corresponding RBAC permissions in advance.
Configure RBAC permissions
OIDC handles only cluster authentication. Once cluster authentication is passed, authorization operations begin (typically based on RBAC). Users or IAM Roles must first bind the corresponding RBAC permissions to manage cluster resources effectively.
- Primary users by default possess cluster administrator permissions, allowing them to manage all cluster resources without requiring additional RBAC permission bindings.
- IAM user: For permission binding of IAM users, the following two methods are available:
Authorization via pre-configured RBAC
Bind RBAC permissions for IAM users via the CCE console. For details, refer to Configuring Preset RBAC Permission Policies
Custom RBAC policy authorization
Manually create ClusterRole/Role and ClusterRoleBinding/RoleBinding in the Cluster. For details, refer to K8s RBAC Official Document. An example is as follows:
1kind: ClusterRole
2apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
3metadata:
4 name: custom-cluster-role
5rules:
6- apiGroups: [""]
7 resources: ["pods"]
8 verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
9---
10apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
11kind: RoleBinding
12metadata:
13 namespace: default
14 name: custom-role-binding
15roleRef:
16 apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
17 kind: ClusterRole
18 name: custom-cluster-role
19subjects:
20- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
21 kind: User
22 name: 294ae2c68794fb1ab58e71fbc8ef338Note: In ClusterRoleBinding/RoleBinding, subjects.kind = User,subjects.name = IAM user ID.
IAM Role
IAM Roles can currently only be bound with RBAC permissions by manually creating ClusterRole/Role and ClusterRoleBinding/RoleBinding in the cluster, as shown below:
1kind: ClusterRole
2apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
3metadata:
4 name: custom-cluster-role
5rules:
6- apiGroups: [""]
7 resources: ["pods"]
8 verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
9---
10apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
11kind: RoleBinding
12metadata:
13 namespace: default
14 name: custom-role-binding
15roleRef:
16 apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
17 kind: ClusterRole
18 name: custom-cluster-role
19subjects:
20- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
21 kind: Group
22 name: 7e442e97bba54d9ea0d8da1fcacecd7aNote:
subjects.kind = Group, subjects.name = IAM Role ID in ClusterRoleBinding/RoleBinding. Do not confuse IAM Role with K8s Role. IAM Role is mapped to a group within the cluster, and the group name corresponds to the IAM Role ID. Once RBAC permissions are assigned to the group as shown in the example, users assuming the IAM Role will inherit the same RBAC permissions.
