Use K8S_Service via CCE
Overview
In Kubernetes, users can deploy various containers—some offering external Layer 7 network services via HTTP/HTTPS protocols, while others provide Layer 4 network services through TCP/UDP protocols. The service resource defined by Kubernetes manages Layer 4 network service access within the cluster.
Kubernetes ServiceTypes allow you to specify the type of service, with ClusterIP as the default. The available options and their behaviors are described as follows:
| Types | Description |
|---|---|
| ClusterIP | Expose the service through the cluster's internal IP. Use this type when the service should only be accessed internally within the cluster. This is the default ServiceType. |
| NodePort | Note: Except for testing and non-production environment, it is not recommended to provide services directly through cluster nodes or even public networks in production environment. For security reasons, using this type will directly expose cluster nodes, making them vulnerable to attacks. |
| LoadBalancer | Using Baidu Load Balancer of Baidu AI Cloud, services can be exposed to either the public network or intranet. The load balancer can be routed to the NodePort service or forwarded directly to the container. For specific usage, refer to Create LoadBalancer_Service via YAML. |
Create a service
- Sign in to the Baidu AI Cloud official website and enter the management console.
- Select Product Tour - Containers - Cloud Container Engine and click to enter the CCE management console.
- Click Cluster Management - Cluster List in the left navigation bar.
- Click on the target cluster name in the Cluster List page to navigate to the cluster management page.
- On the cluster management page, click Network - Services to access the service list page.
Method 1: Through the Console Service
Click Create Service to enter the Create Service page and configure service-related parameters.
| ConfigMap | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Service name | Enter the service name | my-nginx-svc |
| Service type | Support three modes for client access from different sources and types: Intra-cluster access (ClusterIP), node port access (NodePort), and load balancer (LoadBalancer) | None |
| IP dual-stack configuration | Single-stack: Single-stack service, where the control plane uses the first configured service cluster IP range to assign cluster IPs to services; Dual-stack: When dual-stack is enabled, assign .spec.clusterIPs for services from both IPv4 and IPv6 address ranges. If dual-stack is not enabled or not supported, the creation of the service API object will fail; Prefer dual-stack: when dual-stack is enabled, both IPv4 and IPv6 cluster IP addresses are assigned to the service. If dual-stack is not enabled or not supported, it will return to single-stack behavior; |
None |
| Service association | Choose the backend application to be bound to the service. If no corresponding deployment is configured, the related Endpoints object will not be created. | Name: app, value: nginx |
| Port mapping | Add the service port and container port. The container port must match that exposed in the backend Pod | Service port: 80, container port: 80, protocol: TCP |
| Annotations | Add an annotation to the service and configure the load balancer parameters. | None |
Method 2: Create a service using YAML
Click Create Resource via YAML to enter the Create Service page to specify the service type and complete other configurations.
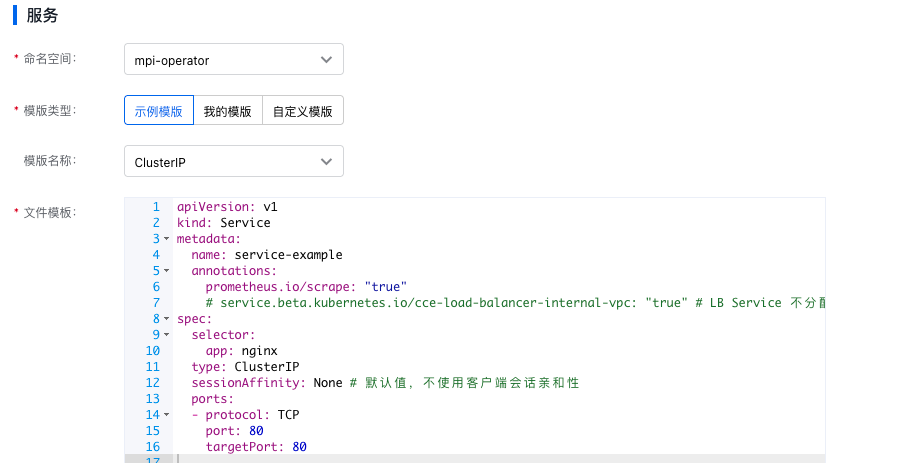
Click OK button to complete service creation.
Modify service
On the service list page, select the target service, click the Modify button, make modifications, and then click the Update button to submit.
Delete service
From the service list page, locate the target service, click the Delete button, confirm the information, and then click OK to finalize the deletion.
