Logging
CCE Logging
The CCE logging feature allows users to manage service logs and container logs within Kubernetes clusters. This feature supports exporting logs from the cluster to external Elasticsearch services or Baidu AI Cloud’s BOS storage for analysis or long-term retention.
Create log rules
Click "Monitor Logs" - "Logging" in the left navigation bar to access the log rule list page. Then, click "Create Log Rule" from the log rule list.

- Rule name: User-defined name, which is used to identify and describe different log rules
- Log type: The “container stdout” refers to logs output by the container itself during runtime, which can be viewed via the docker logs command. The “internal logs of container” refers to logs from service processes running inside the container, which are stored at a specific path in the container
- The cluster name and log source can be obtained from the object requiring log output. If “specified container” is selected, it supports selecting across five resource dimensions: Deployment, Job, CronJob, DaemonSet, and StatefulSet

- The address, port, index, and encryption configurations of Elasticsearch are used to assist the CCE log service in exporting logs to the corresponding Elasticsearch service. Please fill in Elasticsearch service information to ensure the CCE cluster can establish a proper connection with this Elasticsearch service. For production environments, it is recommended to directly use the BES (Baidu Elasticsearch) service.
- To integrate with BOS storage, create a Secret resource in the following format that can connect to BOS storage. After that, when choosing BOS storage, specify the namespace and name of the Secret. If the machine has internet access, BOS Endpoint can be set to any region. Otherwise, it needs to match the region of the CCE cluster.
- Due to permission restrictions, creating a BOS Secret currently requires the root account's AK/SK; otherwise, the certification and authorization process cannot be completed.
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Secret
3metadata:
4 name: bos-secret
5data:
6 bosak: dXNlcm5hbWU= # echo -n "bosak...." | base64
7 bossk: cGFzc3dvcmQ= # echo -n "bossk...." | base64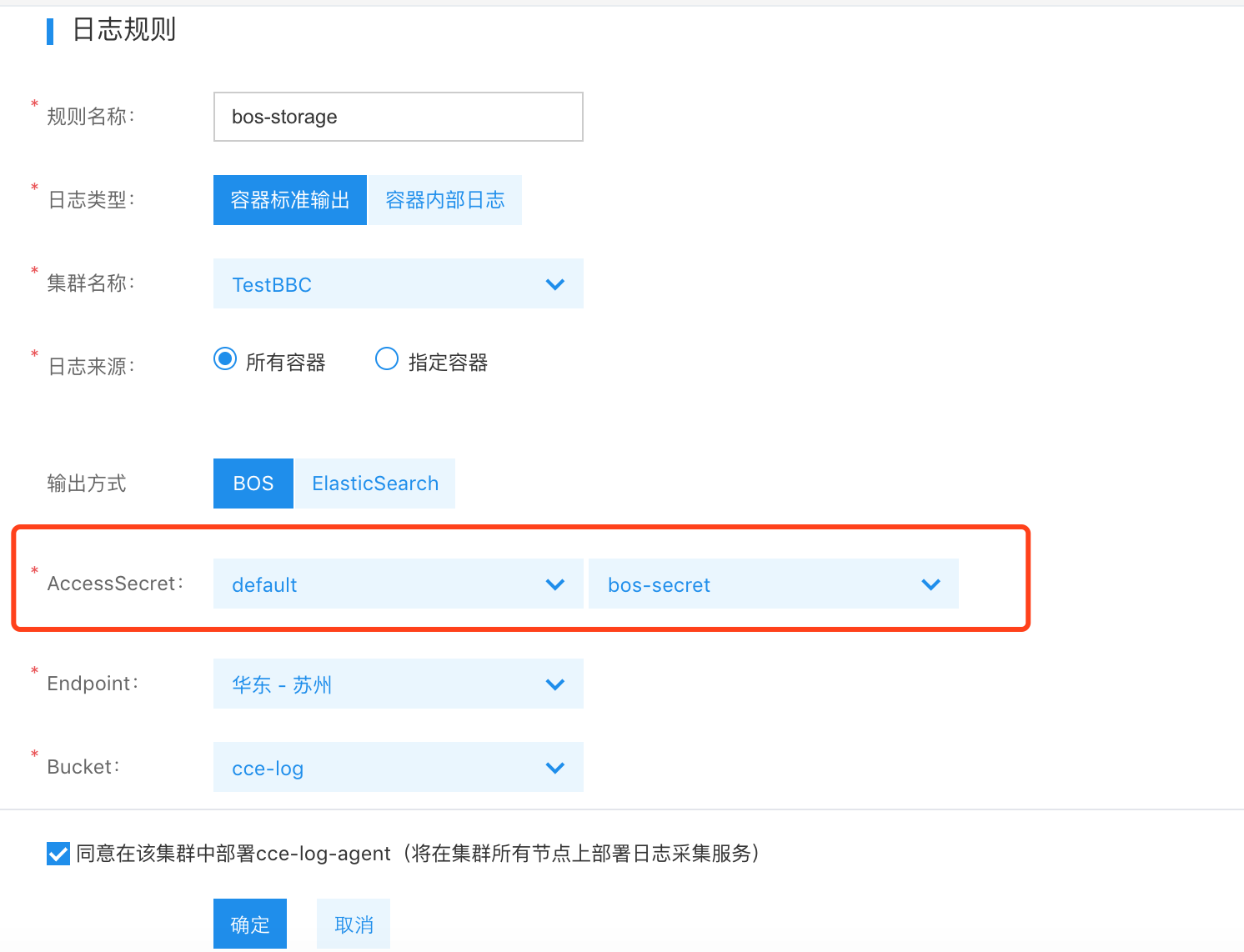
Configure kubernetes resources
After configuring logging rules, ensure logs in Kubernetes are correctly output by passing specified environment variables when creating relevant Kubernetes resources:
- Pass the environment variable cce_log_stdout and set the value to true for indicating the container’s stdout to be correct. If collection is not required, it is unnecessary to pass this environment variable
- Pass the environment variable cce_log_internal and specify the value as the absolute path of the log file in the container. A file path not a directory must be entered here
- When collecting files from a container, the directory containing the log files must be mounted to the host using the emptydir format.
Refer to the following YAML example:
1apiVersion: apps/v1
2kind: Deployment
3metadata:
4 name: tomcat
5spec:
6 selector:
7 matchLabels:
8 app: tomcat
9 replicas: 4
10 template:
11 metadata:
12 labels:
13 app: tomcat
14 spec:
15 containers:
16 - name: tomcat
17 image: "tomcat:7.0"
18 env:
19 - name: cce_log_stdout
20 value: "true"
21 - name: cce_log_internal
22 value: "/usr/local/tomcat/logs/catalina.*.log"
23 volumeMounts:
24 - name: tomcat-log
25 mountPath: /usr/local/tomcat/logs
26 volumes:
27 - name: tomcat-log
28 emptyDir: {}Modify and delete log rules
Once log rules are created, users can modify or delete them at any time. Click "Modify" to edit existing log rules. The logic for editing is similar to that of creation, but changing the cluster or log type is not allowed.


Use the BES (Baidu AI Cloud Elasticsearch) service
For production environments, it is recommended to use the BES service. For details, refer to: Elasticsearch Create Cluster
Self-built Elasticsearch in K8S cluster (for reference only)
This method is only intended for testing purposes. For production environments, it is recommended to use the BES service directly. Use the following YAML file to deploy Elasticsearch in a CCE cluster:
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Service
3metadata:
4 name: elasticsearch-logging
5 namespace: kube-system
6 labels:
7 k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
8 kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
9 addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
10 kubernetes.io/name: "Elasticsearch"
11spec:
12 ports:
13 - port: 9200
14 protocol: TCP
15 targetPort: db
16 selector:
17 k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
18---
19# RBAC authn and authz
20apiVersion: v1
21kind: ServiceAccount
22metadata:
23 name: elasticsearch-logging
24 namespace: kube-system
25 labels:
26 k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
27 kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
28 addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
29---
30kind: ClusterRole
31apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
32metadata:
33 name: elasticsearch-logging
34 labels:
35 k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
36 kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
37 addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
38rules:
39- apiGroups:
40 - ""
41 resources:
42 - "services"
43 - "namespaces"
44 - "endpoints"
45 verbs:
46 - "get"
47---
48kind: ClusterRoleBinding
49apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
50metadata:
51 namespace: kube-system
52 name: elasticsearch-logging
53 labels:
54 k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
55 kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
56 addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
57subjects:
58- kind: ServiceAccount
59 name: elasticsearch-logging
60 namespace: kube-system
61 apiGroup: ""
62roleRef:
63 kind: ClusterRole
64 name: elasticsearch-logging
65 apiGroup: ""
66---
67# Elasticsearch deployment itself
68apiVersion: apps/v1
69kind: StatefulSet
70metadata:
71 name: elasticsearch-logging
72 namespace: kube-system
73 labels:
74 k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
75 version: v6.3.0
76 kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
77 addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
78spec:
79 serviceName: elasticsearch-logging
80 replicas: 2
81 selector:
82 matchLabels:
83 k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
84 version: v6.3.0
85 template:
86 metadata:
87 labels:
88 k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
89 version: v6.3.0
90 kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
91 spec:
92 serviceAccountName: elasticsearch-logging
93 containers:
94 - image: hub.baidubce.com/jpaas-public/elasticsearch:v6.3.0
95 name: elasticsearch-logging
96 resources:
97 # need more cpu upon initialization, therefore burstable class
98 limits:
99 cpu: 1000m
100 requests:
101 cpu: 100m
102 ports:
103 - containerPort: 9200
104 name: db
105 protocol: TCP
106 - containerPort: 9300
107 name: transport
108 protocol: TCP
109 volumeMounts:
110 - name: elasticsearch-logging
111 mountPath: /data
112 env:
113 - name: "NAMESPACE"
114 valueFrom:
115 fieldRef:
116 fieldPath: metadata.namespace
117 volumes:
118 - name: elasticsearch-logging
119 emptyDir: {}
120 # Elasticsearch requires vm.max_map_count to be at least 262144.
121 # If your OS already sets up this number to a higher value, feel free
122 # to remove this init container.
123 initContainers:
124 - image: alpine:3.6
125 command: ["/sbin/sysctl", "-w", "vm.max_map_count=262144"]
126 name: elasticsearch-logging-init
127 securityContext:
128 privileged: trueAfter successful deployment, a service named elasticsearch-logging will be created. As shown in the diagram below, when creating log rules, the service’s name can be used as the ES address and the service’s port is used as a port:

Deploy kibana using the following YAML. After successful deployment, access the kibana service via the created LoadBalancer named kibana-logging:
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Service
3metadata:
4 name: kibana-logging
5 namespace: kube-system
6 labels:
7 k8s-app: kibana-logging
8 kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
9 addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
10 kubernetes.io/name: "Kibana"
11spec:
12 ports:
13 - port: 5601
14 protocol: TCP
15 targetPort: ui
16 selector:
17 k8s-app: kibana-logging
18 type: LoadBalancer
19---
20apiVersion: apps/v1
21kind: Deployment
22metadata:
23 name: kibana-logging
24 namespace: kube-system
25 labels:
26 k8s-app: kibana-logging
27 kubernetes.io/cluster-service: "true"
28 addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
29spec:
30 replicas: 1
31 selector:
32 matchLabels:
33 k8s-app: kibana-logging
34 template:
35 metadata:
36 labels:
37 k8s-app: kibana-logging
38 annotations:
39 seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/pod: 'docker/default'
40 spec:
41 containers:
42 - name: kibana-logging
43 image: hub.baidubce.com/jpaas-public/kibana:v6.3.0
44 resources:
45 # need more cpu upon initialization, therefore burstable class
46 limits:
47 cpu: 1000m
48 requests:
49 cpu: 100m
50 env:
51 - name: ELASTICSEARCH_URL
52 value: http://elasticsearch-logging:9200
53 - name: SERVER_BASEPATH
54 value: ""
55 ports:
56 - containerPort: 5601
57 name: ui
58 protocol: TCPNote
In production environments, it is recommended to use Baidu AI Cloud’s Elasticsearch service or a dedicated self-built Elasticsearch cluster
