Create LoadBalancer_Service via YAML
This guide provides steps to create a LoadBalancer-type service in CCE.
Note: The following annotation may not work for cluster versions below 1.16.3. Please contact the administrator via a ticket
Kubernetes official tutorial: Services
Quick start
When you create a service of type LoadBalancer, CCE will, by default, automatically create a BLB and bind an elastic public network (EIP) to this BLB.
Example: Create a simple Nginx service
1 kind: Service
2 apiVersion: v1
3 metadata:
4 name: nginx-service
5 spec:
6 selector:
7 app: nginx
8 type: LoadBalancer
9 ports:
10 - name: nginx-port
11 port: 80
12 targetPort: 80
13 protocol: TCP
14 ---
15 apiVersion: apps/v1
16 kind: Deployment
17 metadata:
18 name: nginx-deployment
19 spec:
20 selector:
21 matchLabels:
22 app: nginx
23 replicas: 1
24 template:
25 metadata:
26 labels:
27 app: nginx
28 spec:
29 containers:
30 - name: nginx
31 image: registry.baidubce.com/public/nginx:latest
32 ports:
33 - containerPort: 80(1) Creation
$ kubectl create -f nginx.yaml
(2) Query EIP
The IP 8.8.8.8 represents the EIP for this nginx-service.
1$ kubectl get svc
2NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
3nginx-service 1.1.1.1 8.8.8.8 80:30274/TCP 5m(3) Query BLB
1$ kubectl get svc nginx-service -o jsonpath={.metadata.annotations}
2map[service.beta.kubernetes.io/cce-load-balancer-id:lb-xxxxxx]lb-xxxxxx is the unique identifier of the BLB associated with this service.
(4) Access test
$ curl -i http://8.8.8.8
External traffic policy
CCE supports three external traffic policies for LoadBalancer Services: cluster mode, local mode, and LB-Pod direct connection mode.
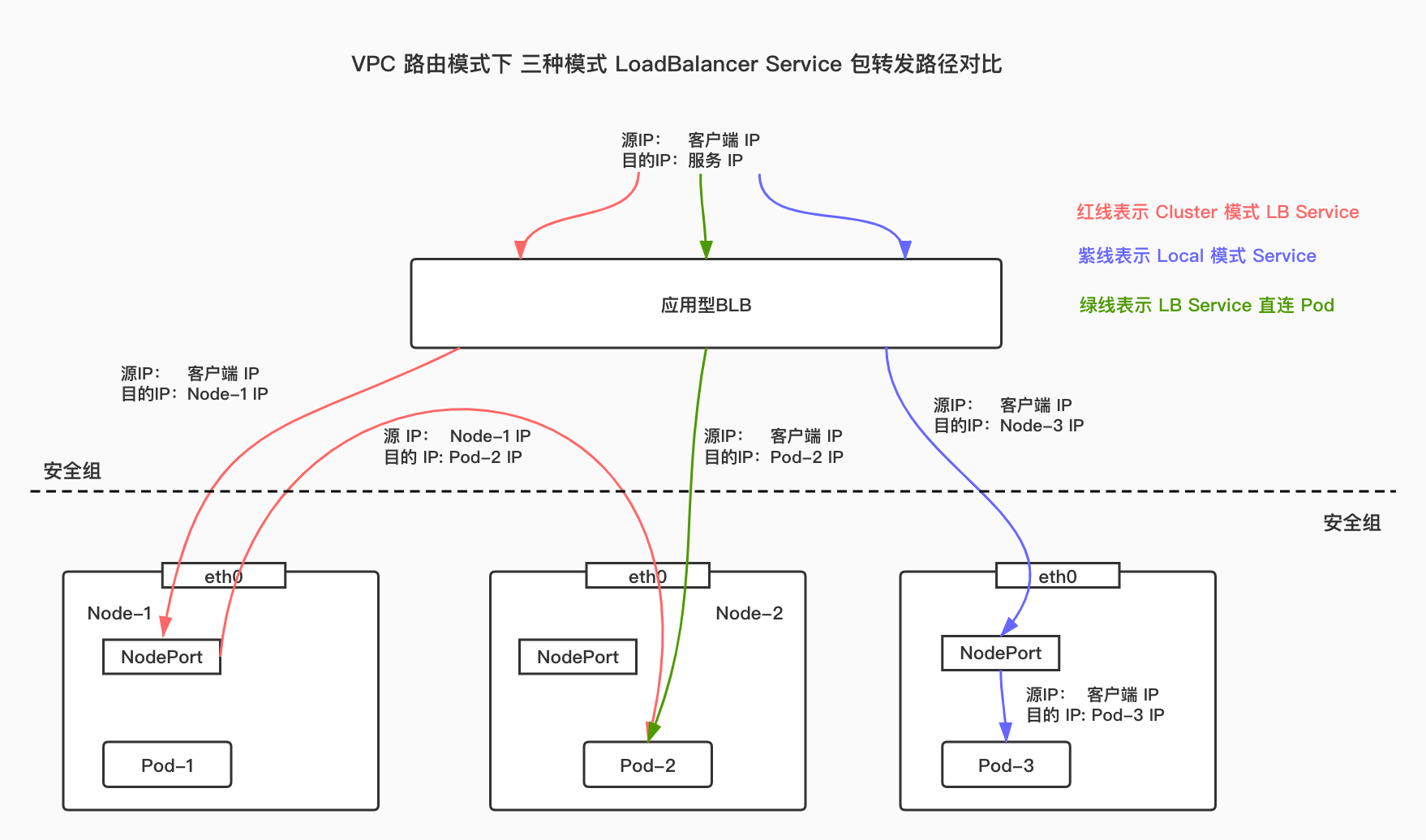
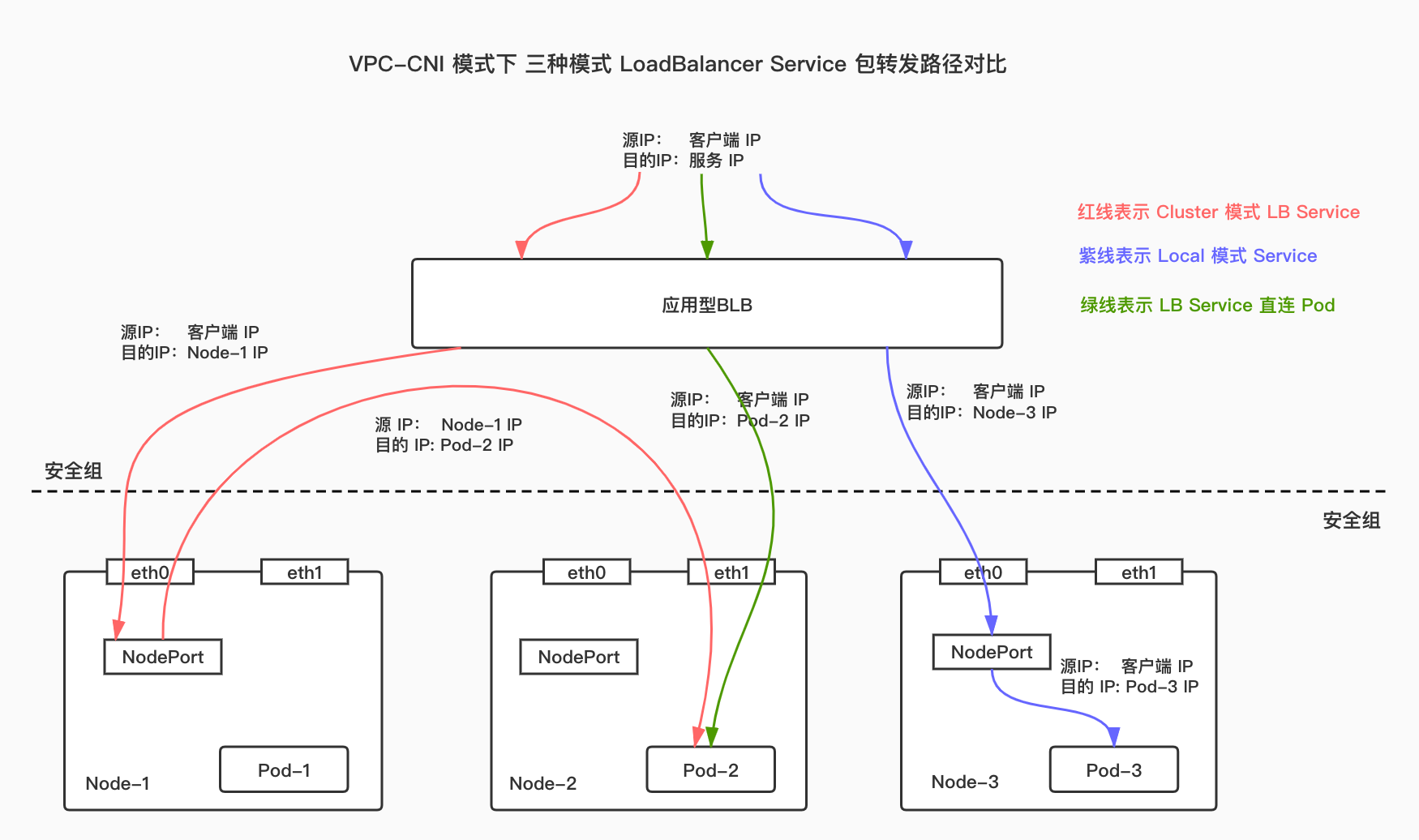
For LB Service in cluster mode, upon receiving a packet, the load balancer sends it to a node in the cluster, which then forwards the packet to a Pod in the cluster. The host node of target Pod and the node forwarding the packet may not be the same. In this case, the source IP address of the packet will be lost.
For LB Service in local mode, upon receiving a packet, the load balancer sends it to the node hosting the target Pod, which then forwards the packet to its own Pod. In this case, the source IP address of the packet will not be lost.
For LB Service in LB-Pod direct connection mode, upon receiving a packet, the load balancer directly sends it to each Pod. Compared to the previous two modes, this mode reduces one node forwarding operation. If the container network mode of the cluster is VPC-ENI, the source IP will not be lost. If the container network mode of the cluster is VPC routing, the source IP address will not be lost when the ttm module is installed in the host, and the source IP address will be lost when the ttm module is not installed in the host.
Under VPC routing network mode, the packet forwarding paths for the LoadBalancer Services in three modes are shown as follows:
Under VPC-CNI network mode, the packet forwarding paths for the LoadBalancer Services in three modes are shown as follows:
Cluster mode
To use service in cluster mode, specify externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster when creating the service, as shown in the following example:
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Service
3metadata:
4 name: service-example-cluster
5 annotations:
6 prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
7spec:
8 selector:
9 app: nginx
10 type: LoadBalancer
11 externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
12 sessionAffinity: None
13 ports:
14 - name: nginx
15 protocol: TCP
16 port: 80
17 targetPort: 80Local mode
To use service in local mode, specify externalTrafficPolicy: Local when creating the service, as shown in the following example:
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Service
3metadata:
4 name: service-example-local
5 annotations:
6 prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
7spec:
8 selector:
9 app: nginx
10 type: LoadBalancer
11 externalTrafficPolicy: Local
12 sessionAffinity: None
13 ports:
14 - name: nginx
15 protocol: TCP
16 port: 80
17 targetPort: 80Note
When the proxy mode of the kube-proxy component is -1-}ipvs, if a Service'sexternalTrafficPolicyis set toLocaland there is no backend Pod associated with the service on a node, accessing the service's BLB IP address on that node will fail.
This issue has been fixed in Kubernetes version 1.24. Related issue: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/pull/97081
LB-Pod direct connection mode
To use the service in LB-Pod direct connection mode, add the annotation service.beta.kubernetes.io/cce-load-balancer-backend-type: "eni" when creating the service, It is shown in the following example:
For more detailed instructions for use, please refer to Using LoadBalancer Service in Pod Direct Connection Mode.md.
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Service
3metadata:
4 name: service-example-direct
5 annotations:
6 prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
7 service.beta.kubernetes.io/cce-load-balancer-backend-type: "eni"
8spec:
9 selector:
10 app: nginx
11 type: LoadBalancer
12 sessionAffinity: None
13 ports:
14 - name: nginx
15 protocol: TCP
16 port: 80
17 targetPort: 80Use UDP-Service
To use UDP for the service, set spec.ports.protocol to UDP. Example steps:
1---
2apiVersion: v1
3kind: Service
4metadata:
5 name: udp-server-demo-svc
6 labels:
7 app: udp-server-demo
8spec:
9 type: LoadBalancer
10 ports:
11 - name: udp-server-demo-port
12 port: 3005
13 targetPort: 3005
14 protocol: UDP
15 selector:
16 app: udp-server-demo
17---
18apiVersion: apps/v1
19kind: Deployment
20metadata:
21 name: udp-server-demo
22 labels:
23 app: udp-server-demo
24spec:
25 replicas: 1
26 selector:
27 matchLabels:
28 app: udp-server-demo
29 template:
30 metadata:
31 labels:
32 app: udp-server-demo
33 spec:
34 containers:
35 - name: udp-server-demo
36 image: hub.baidubce.com/jpaas-public/udp-server-demo:latest
37 ports:
38 - containerPort: 3005
39 protocol: UDP(1) Deploy a UDP test service
1$ kubectl apply -f udp.yaml(2) Verify the UDP Service is created successfully
1$ kubectl get svc
2NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
3kubernetes ClusterIP 172.16.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 6h
4udp-server-demo-svc LoadBalancer 172.16.122.139 10.10.10.10 3005:31441/UDP 1m(3) View the service logs
1$ kubectl logs -f udp-server-demo-6fdf5d796f-h6595
2Received: HealthCheck
3Get Health Check, response OK
4Received: HealthCheck
5Get Health Check, response OK
6Received: HealthCheck
7Get Health Check, response OKNote
When using UDP services, the application BLB will perform health checks on the backend using UDP health check strings. Refer to the document [UDP Health Check Introduction](BLB/Operation guide/General-purpose BLB instance/Creating BLB Ordinary Instance.md#Configure UDP listener)
Users need to manually set up UDP health check strings on the application BLB and ensure that the backend Pods correctly respond to these health check strings.
