Use Direct Pod Mode LoadBalancer Service
Comparison between Traditional Mode and Direct Connection Mode
Features
LoadBalancer Service in Traditional Mode uses the IP addresses of cluster nodes as the BLB's real servers. When accessing the LoadBalancer Service in traditional mode, the request is forwarded by Baidu Load Balancer (BLB) provided by Baidu AI Cloud to a node, and then further routed via iptables or IPVS to a specific Pod. During this process, the request undergoes two load balancer operations.
LoadBalancer Service in pod direct connection mode uses the IP addresses of pod as the real servers. When accessing the LoadBalancer Service in Pod direct connection mode, the request only needs to undergo one load balancer operation before being forwarded to the specific Pod. The service in this mode has the following advantages:
- Preserve the source IP of the request;
- Reducing one request forwarding step improves overall system performance.
- Ensure more uniform load balancers at the Pod level
Performance
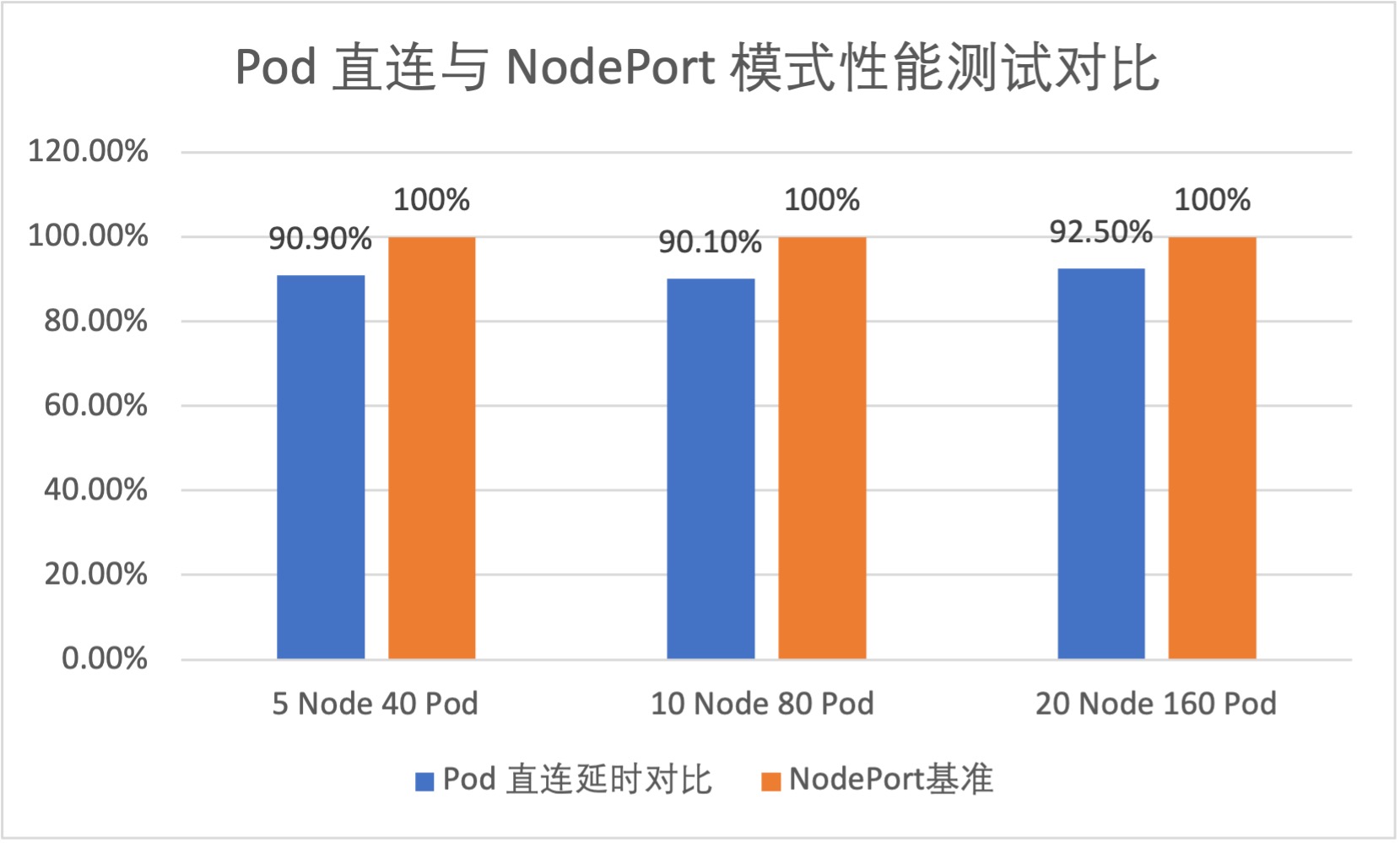
We conducted tests on the average network latency for LoadBalancer Services in both modes. Test results show that LoadBalancer Service in Pod direct connection mode can reduce network latency by approximately 10% on average.
Usage restrictions
Clusters using LoadBalancer Service in Pod direct connection mode must meet three prerequisites: cluster version, plugin, and container network type:
Confirm the cluster version
New CCE clusters (cluster IDs prefixed with cce-) support this function.
Old CCE clusters (cluster IDs prefixed with c-) do not support this function.
Confirm the container network interface card type
- The requirement is satisfied when the network interface card type is either
vethorkubenet. -
When the network interface card type is IPVLAN, set the
masqOutBoundandmasqOutBoundIPv6attributes of ConfigMapcce-ip-masq-agentto false. The procedure is as follows:Connect to the cluster using Kubectl, enter the command
kubectl describe configmap cce-ip-masq-agent -n kube-system, and you may receive the following output. At this point,masqOutBoundandmasqOutBoundIPv6are true:Plain Text1# kubectl describe configmap cce-ip-masq-agent -n kube-system 2Name: cce-ip-masq-agent 3Namespace: kube-system 4Labels: addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode=EnsureExists 5Annotations: 6Data 7==== 8config: 9---- 10nonMasqueradeCIDRs: 11 - 10.0.0.0/8 12 - 172.16.0.0/12 13 - 192.168.0.0/16 14 - fc00::/7 15masqOutBound: true 16masqOutBoundIPv6: true 17masqLinkLocal: false 18masqLinkLocalIPv6: false 19resyncInterval: 60s 20Events: <none>Enter the command
kubectl edit configmap cce-ip-masq-agent -n kube-system, modifymasqOutBoundandmasqOutBoundIPv6to false and save them, and the cce-ip-masq-agent configuration information will be updated automatically. At this point, enter the commandkubectl describe configmap cce-ip-masq-agent -n kube-systemagain, and you may receive the following output. At this point,masqOutBoundandmasqOutBoundIPv6are already false.Plain Text1# kubectl describe configmap cce-ip-masq-agent -n kube-system 2Name: cce-ip-masq-agent 3Namespace: kube-system 4Labels: addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode=EnsureExists 5Annotations: 6Data 7==== 8config: 9---- 10nonMasqueradeCIDRs: 11 - 10.0.0.0/8 12 - 172.16.0.0/12 13 - 192.168.0.0/16 14 - fc00::/7 15masqOutBound: false 16masqOutBoundIPv6: false 17masqLinkLocal: false 18masqLinkLocalIPv6: false 19resyncInterval: 60s 20Events: <none>
Note
Check the quota limits
The LoadBalancer Service in Pod direct-connection mode uses an application BLB and by default supports a maximum of 50 associated Pods on the backend. If more Pods are required, submit a ticket to request the removal of the backend count limit.
Open security group ports
When the container network mode of the CCE cluster is VPC network, traffic must be allowed to the destination port Service TargetPort in the security group bound to the cluster nodes. Otherwise, packets cannot reach the Pod.
When the container network mode of the CCE cluster is VPC-CNI, traffic must be allowed to the destination port Service TargetPort in the security group bound to the elastic network interface (ENI). Otherwise, packets cannot reach the Pod.
Operation steps
When creating the LoadBalancer Service in Pod direct connection mode, add service.beta.kubernetes.io/cce-load-balancer-backend-type: "eni" to the annotations attribute.
The example YAML is as follows:
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Service
3metadata:
4 name: pod-direct-service-example
5 annotations:
6 prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
7 service.beta.kubernetes.io/cce-load-balancer-backend-type: "eni"
8spec:
9 selector:
10 app: nginx
11 type: LoadBalancer
12 sessionAffinity: None
13 ports:
14 - name: nginx
15 protocol: TCP
16 port: 80
17 targetPort: 80FAQs
Zero-downtime rolling updates for Pods
Using the LB Service in Pod direct-connection mode might cause service interruptions during Pod rolling updates.
Reason
When a Pod is terminated, the following events occur:
- Pod enters Terminating status;
- The Pod is removed from Endpoints; the LB Controller detects Endpoints changes and removes the Pod backend from the application BLB;
- Pod termination;
Steps 2 and 3 are executed in parallel. When a Pod is terminated but the LB Controller has not yet removed it, Traffic may still be forwarded to the terminated Pod, resulting in service interruption.
Solution
Set a preStopHook for the Pod to sleep for a period (typically 40 s) until the application BLB removes the Pod before termination.
Reference is as follows:
1 lifecycle:
2 preStop:
3 exec:
4 command: ["sleep", "40"]