Hotlink Protection
Introduction
Website A hosts its static resources like images and videos on Baidu AI Cloud Object Storage (BOS). However, Website B uses Website A’s resources on its own site without permission. Since BOS billing is based on usage, Website B effectively steals Website A's storage space and bandwidth, while Website A has to pay for these resources without any benefit. This act, where Website B misuses Website A's resources by embedding them on its own site, is known as hotlinking.
Basic principles
The primary methods to prevent hotlinking involve restricting the originating page and include techniques like referer-based hotlinking prevention and signature URL-based hotlinking prevention.
- The principle behind referer-based hotlinking prevention is to compare the referer attribute in the HTTP request header (which indicates the URL of the requesting page) against an allowlist approved by the server. If the referer matches, it’s treated as a legitimate request from a trusted or internal site; otherwise, it’s flagged as hotlinking.
- However, the referer attribute can be maliciously altered. In such cases, hotlinking prevention can be implemented using a signature URL.
Configure BOS hotlinking prevention function
Set referer-based hotlinking prevention
What is referer
Referer is a parameter in the HTTP request header. The referer attribute in the HTTP request header varies in different scenarios:
- Directly accessing server resources: If the browser directly requests resources from BOS, the HTTP request does not contain the referer attribute
- Referencing BOS resources in Website A: The browser accesses the index page of website test.com, and the page references resources from BOS. When the browser requests resources from BOS, the HTTP request header contains the referer attribute, which indicates that the resource is referenced by the
http://test.com/indexpage.
Test results of different referer settings
To test the hotlinking prevention feature, two websites are needed. One site, test.com, serves as the source website, while the other, test-steal.com, acts as the hotlinking site. Each site hosts an index page referencing image resources from BOS. The testing code is as follows:

For the operation and principle of configuring the referer of the bucket, please refer to [Setting Referer Allow List](BOS/Console Operation Guide/Managing Bucket/Set referer allow list.md). The following details the different test results corresponding to different settings:
-
Configuring the bucket's access control to "disallow null referer" and setting up a referer allowlist can effectively implement the hotlinking prevention feature.
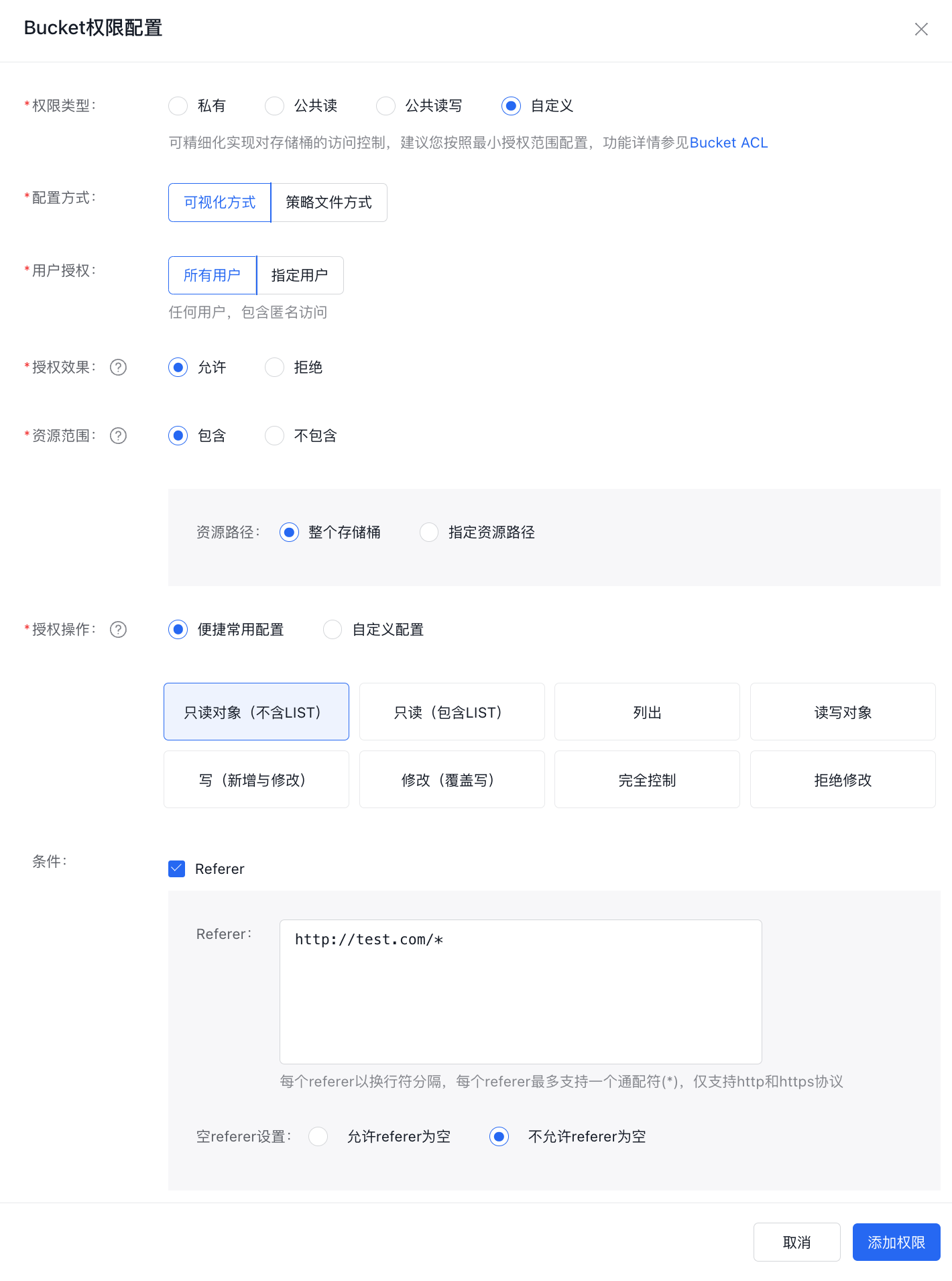
The test results are as follows:
Browser input Description Result http://bos-test-f.bj.bcebos.com/bos.jpgDirect access, referer is null Requests with null referer are not allowed, returning 403 http://test.com/indexRequest from the source site, referer is not null Access successful http://test-steal.com/indexRequest from the hotlinking website When BOS returns a 403 error, it indicates that hotlinking prevention has been successfully applied. -
Allowing "null referers" combined with a referer allowlist can also implement the hotlinking prevention feature.
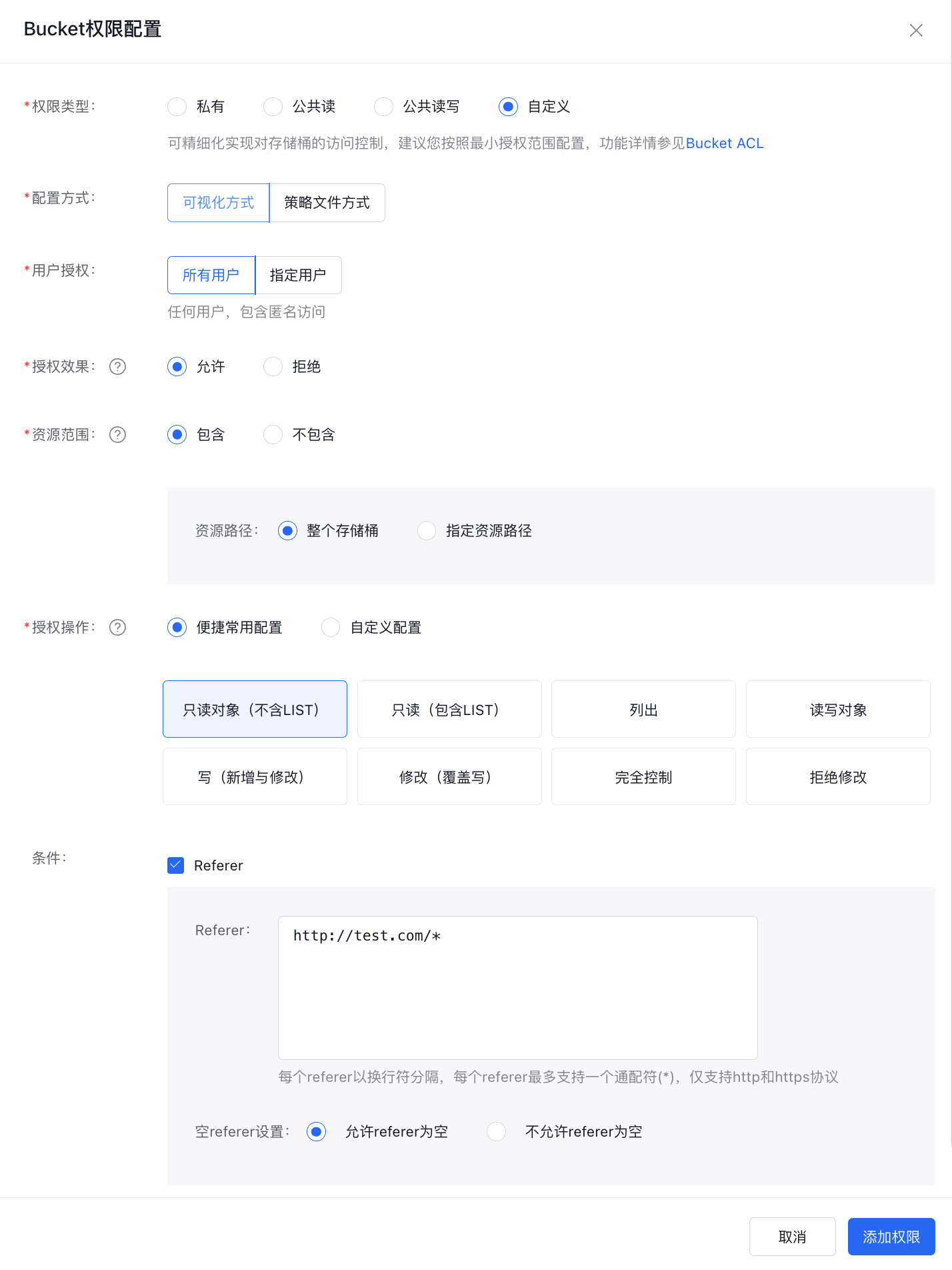
The test results are as follows:
Browser input Description Result http://bos-test-f.bj.bcebos.com/bos.jpgDirect access, referer is null Access successful http://test.com/indexRequest from the source site, referer is not null Access successful http://test-steal.com/indexRequest from the hotlinking website When BOS returns a 403 error, it indicates that hotlinking prevention has been successfully applied. -
Merely setting the bucket's access control to "disallow null referer" without any additional configuration cannot enforce hotlinking prevention and is therefore not recommended.
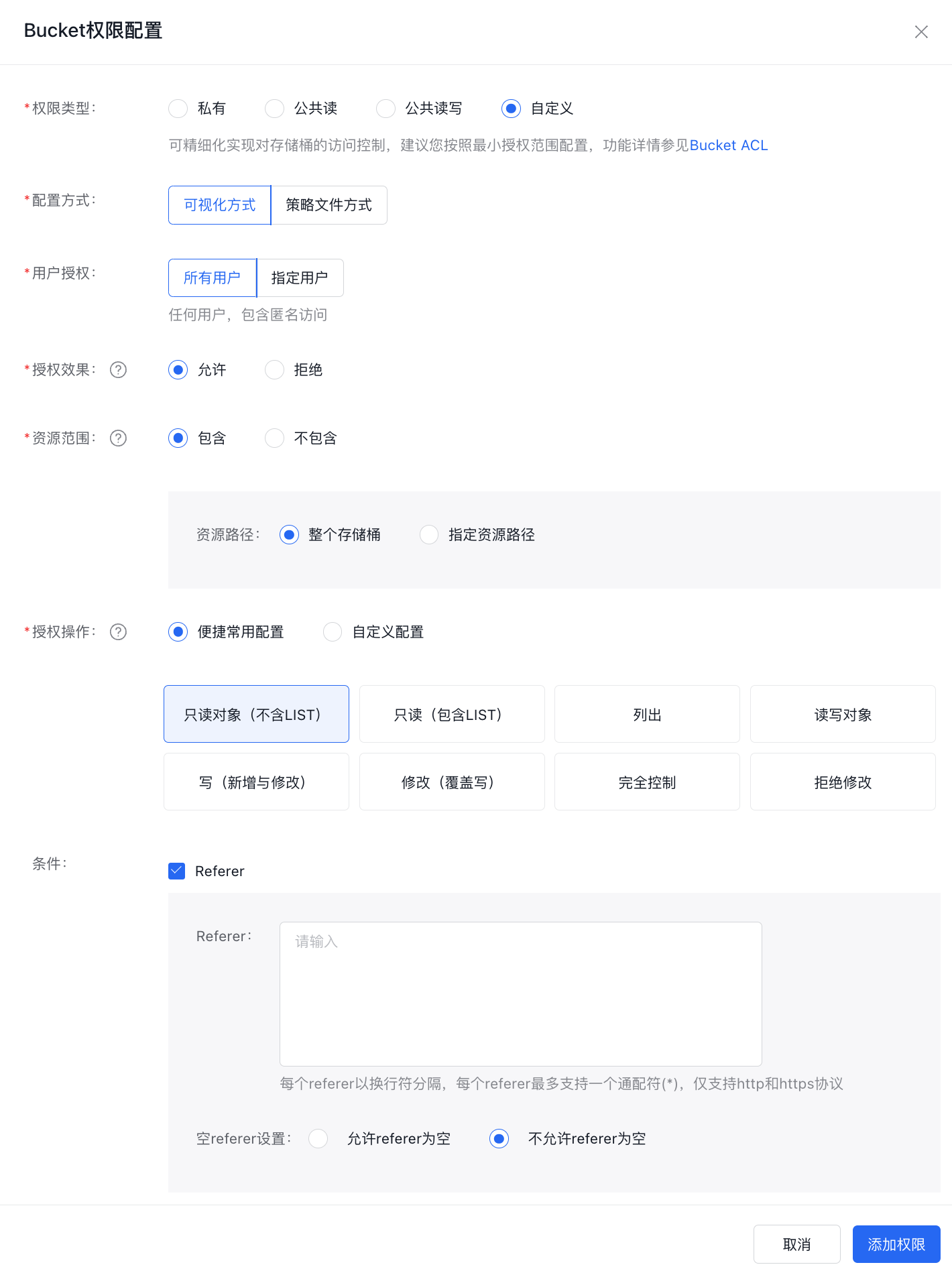
The test results are as follows:
Browser input Description Result http://bos-test-f.bj.bcebos.com/bos.jpgDirect access detected; referer is null. Requests with null referer are not allowed, returning 403 http://test.com/indexRequest from the source site, referer is not null Access successful http://test-steal.com/indexRequest from the hotlinking website, but referer is not null Access was successful.
Advantages and disadvantages of referer-based hotlinking prevention
The main advantage of using referer-based hotlinking protection is its simplicity to configure and its ability to be managed via the console. However, it is not effective against malicious referer spoofing. If hotlinking is performed by simulating HTTP requests and forging the referer through a program, it can bypass the protection settings. For stricter hotlinking prevention, implementing signature-based URLs is recommended.
Configure signature URL-based hotlinking prevention
The principle of signature URL-based hotlinking prevention is to set the file as private access, then generate a pre-signed URL, and provide users with a temporary access URL. When generating a pre-signed URL, you can restrict users from accessing it for a long time by specifying the valid duration of the URL. For example, to call the Java SDK to implement a pre-signed URL, please refer to [Obtaining the URL of an object](BOS/SDK/Java-SDK/File management.md#Get file download URL).
Signature URL-based hotlinking prevention uses the Node.js Sails framework to call BOS’s JavaScript SDK to realize this function. The expiration time of the URL can be specified in the code as expirationInSeconds. The specific implementation code is as follows:
1var BosClient = require("@baiducloud/sdk").BosClient;
2
3module.exports = {
4
5 showImage:function(req,res){
6 var config = {
7 endpoint: "http://bj.bcebos.com",
8 credentials: {
9 ak: "AK", //Your AK
10 sk: "SK" //Your SK
11 }
12 };
13
14 var client = new BosClient(config);
15
16 var bucketName = "bos-test-f";
17 var key = "bos.jpg";
18 var timestamp = Date.now() / 1000;
19 var expirationInSeconds = 1800;
20 var headers = {};
21 var params = {};
22 var headersToSign = {};
23
24 var signedUrl = client.generatePresignedUrl(bucketName, key, timestamp, expirationInSeconds, headers, params, headersToSign, config);
25
26 return res.view("image", {signedUrl : signedUrl});
27 }
28};Specify the address of the image resource as the signature URL:
1Hi Test
2img(src="#{signedUrl}")Test results
As illustrated in the diagram, each time the page is accessed, a new signed URL is generated to retrieve BOS resources. These signed URLs have defined expiration periods, and when expired, a 403 error is returned to block access, effectively implementing hotlinking protection.
-
Result of unexpired signature URL

-
Result of access rejection after expiration

