Basics (Must-Read) - Generation of authentication string
Updated at:2025-11-03
Generation of authentication string
To access BOS with the original API, you must manually compute the authentication details. The process involves the following steps:
- Prepare ak/sk
- Python 3.6 or higher environment
Complete demo for generating authentication string
Example of generating auth_key using a GET request to access a bucket
- Authentication string algorithm code
Python
1import hashlib
2import hmac
3import string
4import datetime
5AUTHORIZATION = "authorization"
6BCE_PREFIX = "x-bce-"
7DEFAULT_ENCODING = 'UTF-8'
8# Class for saving AK/SK
9class BceCredentials(object):
10 def __init__(self, access_key_id, secret_access_key):
11 self.access_key_id = access_key_id
12 self.secret_access_key = secret_access_key
13# According to RFC 3986, except for the following:
14# 1. Uppercase and lowercase English characters
15# 2. Arabic numerals
16# 3. Dot '.', tilde '~', hyphen '-' and underscore '_'
17# All other characters need to be encoded
18RESERVED_CHAR_SET = set(string.ascii_letters + string.digits + '.~-_')
19def get_normalized_char(i):
20 char = chr(i)
21 if char in RESERVED_CHAR_SET:
22 return char
23 else:
24 return '%%%02X' % i
25NORMALIZED_CHAR_LIST = [get_normalized_char(i) for i in range(256)]
26# Normalized string
27def normalize_string(in_str, encoding_slash=True):
28 if in_str is None:
29 return ''
30# If the input is unicode, first encode it using UTF8 and then perform encoding
31 # in_str = in_str.encode(DEFAULT_ENCODING) if isinstance(in_str, unicode) else str(in_str)
32 in_str = in_str if isinstance(in_str, str) else str(in_str)
33# When generating the canonical URI. There is no need to encode the slash '/'; in other cases, encoding is required
34 if encoding_slash:
35 encode_f = lambda c: NORMALIZED_CHAR_LIST[ord(c)]
36 else:
37# When generating the canonical URI only. No need to encode the slash '/'
38 encode_f = lambda c: NORMALIZED_CHAR_LIST[ord(c)] if c != '/' else c
39# Encode according to RFC 3986
40 return ''.join([encode_f(ch) for ch in in_str])
41# Generate canonical URI
42def get_canonical_uri(path):
43# The format of the canonical URI is: /{bucket}/{object}, and all characters except the slash "/" need to be encoded
44 return normalize_string(path, False)
45# Generate canonical query string
46def get_canonical_querystring(params):
47 if params is None:
48 return ''
49# Except for authorization, all query strings are included in the encoding
50 result = ['%s=%s' % (k, normalize_string(v)) for k, v in params.items() if k.lower != AUTHORIZATION]
51# Sort in lexicographical order
52 result.sort()
53# Connect all strings with the & symbol and return
54 return '&'.join(result)
55# Generate canonical header
56def get_canonical_headers(headers, headers_to_sign=None):
57 headers = headers or {}
58# If header_to_sign is not specified, the default is to use:
59 # 1.host
60 # 2.content-md5
61 # 3.content-length
62 # 4.content-type
63# 5. All header items starting with x-bce-
64# Generate canonical header
65 if headers_to_sign is None or len(headers_to_sign) == 0:
66 headers_to_sign = {"host", "content-md5", "content-length", "content-type"}
67# For the key in the header, after removing leading and trailing whitespaces, it needs to be converted to lowercase
68# For the value in the header, after converting to str, remove leading and trailing whitespaces
69 # f = lambda (key, value): (key.strip().lower(), str(value).strip())
70 f = lambda item: (item[0].strip().lower(), str(item[1]).strip())
71 result = []
72 for k, v in map(f, headers.items()):
73# In any case, header items starting with x-bce- need to be added to the canonical header
74 if k.startswith(BCE_PREFIX) or k in headers_to_sign:
75 result.append("%s:%s" % (normalize_string(k), normalize_string(v)))
76# Sort in lexicographical order
77 result.sort()
78# Connect all strings with the \n symbol and return
79 return '\n'.join(result)
80# Main signature algorithm
81def sign(credentials, http_method, path, headers, params, expiration_in_seconds=1800, headers_to_sign=None):
82 headers = headers or {}
83 params = params or {}
84 x_bce_date = headers.get("x-bce-date")
85 # timestamp = int(datetime.datetime.strptime(x_bce_date, "%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ").timestamp())
86# 1. Generate sign key
87# 1.1. Generate auth-string in the format: bce-auth-v1/{accessKeyId}/{timestamp}/{expirationPeriodInSeconds}
88 sign_key_info = 'bce-auth-v1/%s/%s/%d' % (
89 credentials.access_key_id,
90 x_bce_date,
91 expiration_in_seconds)
92# 1.2. Use auth-string and SK to generate sign key with SHA-256
93 sign_key = hmac.new(
94 credentials.secret_access_key.encode("utf-8"),
95 sign_key_info.encode("utf-8"),
96 hashlib.sha256).hexdigest()
97# 2. Generate canonical URI
98 canonical_uri = get_canonical_uri(path)
99# 3. Generate canonical query string
100 canonical_querystring = get_canonical_querystring(params)
101# 4. Generate canonical header
102 canonical_headers = get_canonical_headers(headers, headers_to_sign)
103# 5. Use '\n' to concatenate the HTTP METHOD and the results from 2, 3, and 4 into a single large string
104 string_to_sign = '\n'.join(
105 [http_method, canonical_uri, canonical_querystring, canonical_headers])
106# 6. Use the signature string generated in 5 and the sign key generated in 1 to generate the signature result with the SHA-256 algorithm
107 sign_result = hmac.new(sign_key.encode("utf-8"), string_to_sign.encode("utf-8"), hashlib.sha256).hexdigest()
108# 7. Splice the final signature result string
109 if headers_to_sign:
110# Specify header to sign
111 result = '%s/%s/%s' % (sign_key_info, ';'.join(headers_to_sign), sign_result)
112 else:
113# Default signature result string when header to sign is not specified
114 result = '%s//%s' % (sign_key_info, sign_result)
115 return result
116def get_x_bce_date(date=None):
117 """Get time in UTC format"""
118 if date is None:
119 format_string = "%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ"
120 date = datetime.datetime.utcnow().strftime(format_string)
121 return date
122def generate_bos_auth(path, ak, sk, method, headers, params, expire_seconds=1800):
123 """Generate BOS authentication string, default expiration time is 1,800 s"""
124 credentials = BceCredentials(ak, sk)
125 return sign(credentials, method, path, headers, params, expire_seconds, headers.keys())- Calling the authentication string
Python
1access_key = "AK"
2secret_key = "SK"
3 bucket_name = "bucketName" # Replace with the bucketName to be accessed
4 object_key = "/aaa.png" # When there are no parameters in the request url, the name of the accessed key is the path, note that it starts with '/'
5 region = "bj.bcebos.com" # The region where the bucket is located; the service domain name varies by region
6 request_method = "GET" # Type of request method: GET, PUT, HEAD, POST, DELETE
7 host = f"{bucket_name}.{region}" # Assemble the access domain name based on the bucket and service domain name
8# Construct the accessed header information; additional fields can be added as needed, such as the content-type field
9header = {
10 "host": host,
11 "x-bce-date": get_x_bce_date()
12}
13# If the request has parameters in the url, they must also participate in authentication
14param = {}
15# Generate the authentication string
16auth_key = generate_bos_auth(object_key, access_key, secret_key, request_method, header, param)
17# Construct the complete access url
18request_url = f"http://{host}{object_key}?{AUTHORIZATION}={auth_key}"Combine the two parts of code:
Note:
- The generated
auth_keyis only anauthorizationfield, which needs to be spliced into therequest_urlfor normal access. When accessing request_url, thex-bce-datefield needs to be included, and this field should be as consistent as possible with thex-bce-datefield used when generating the signature. Example of Postman request: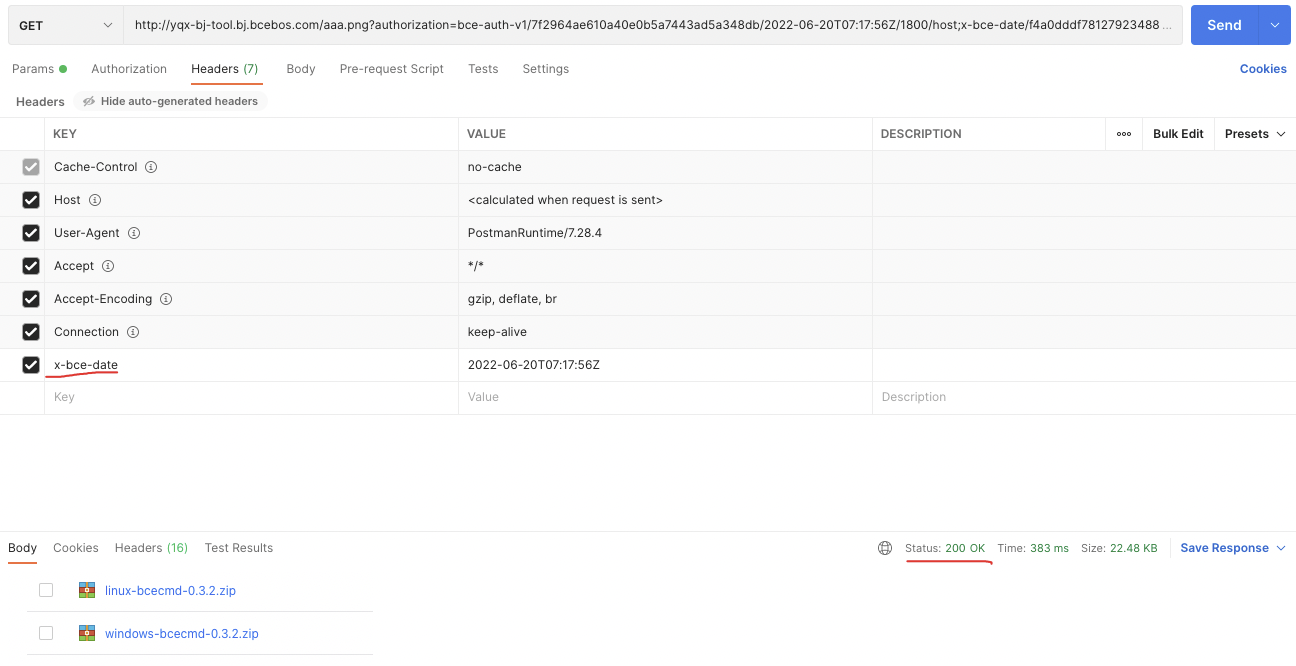
- For more details, refer to Generating Signature String.
