ZIP packaging and compression
Introduction
ZIP multi-file packaging and compression is provided by Baidu AI Cloud Object Storage (BOS) based on Cloud Function Compute (CFC), as a data processing solution for users. After users add multi-file packaging and compression rules to the bucket, specify the URLs of the files that need to be packaged and compressed, and then trigger the CFC function to execute the packaging and compression action, and deliver the final compressed package to the specified path in the bucket.
Note
- The aggregate size of the final ZIP package generated after compressing multiple files must not exceed 50 GB.
- If you add a ZIP multi-file packaging and compression rule for a bucket on the object storage console, the ZIP multi-file packaging and compression function you created will be checked on the Cloud Function Compute (CFC) Console. Please do not delete this function; otherwise, it may cause your rules to be invalid.
- In the case of any error during packaging and compression, click View Logs on the right side of the created function to redirect to the cloud function compute (CFC) console for detailed error logs.
- Archive storage class files must first be restored before packaging and compression. Packaging will fail if files are not restored. If you need to package and compress this type of object, restore it first before proceeding.
- This function is only available in regions supported by CFC. Currently supported regions include: North China-Beijing, South China-Guangzhou, East China-Suzhou. Functions can be created based on these regions.
Operation steps
- Before using the file packaging and compression feature in the console, activate the CFC service to create packaging and compression rules.
- Users can also create and invoke functions on the Cloud Function Compute Console.
Steps to use the multi-file packaging and compression function on the console are as follows:
- Open the Baidu AI Cloud Console to access the BOS control API.
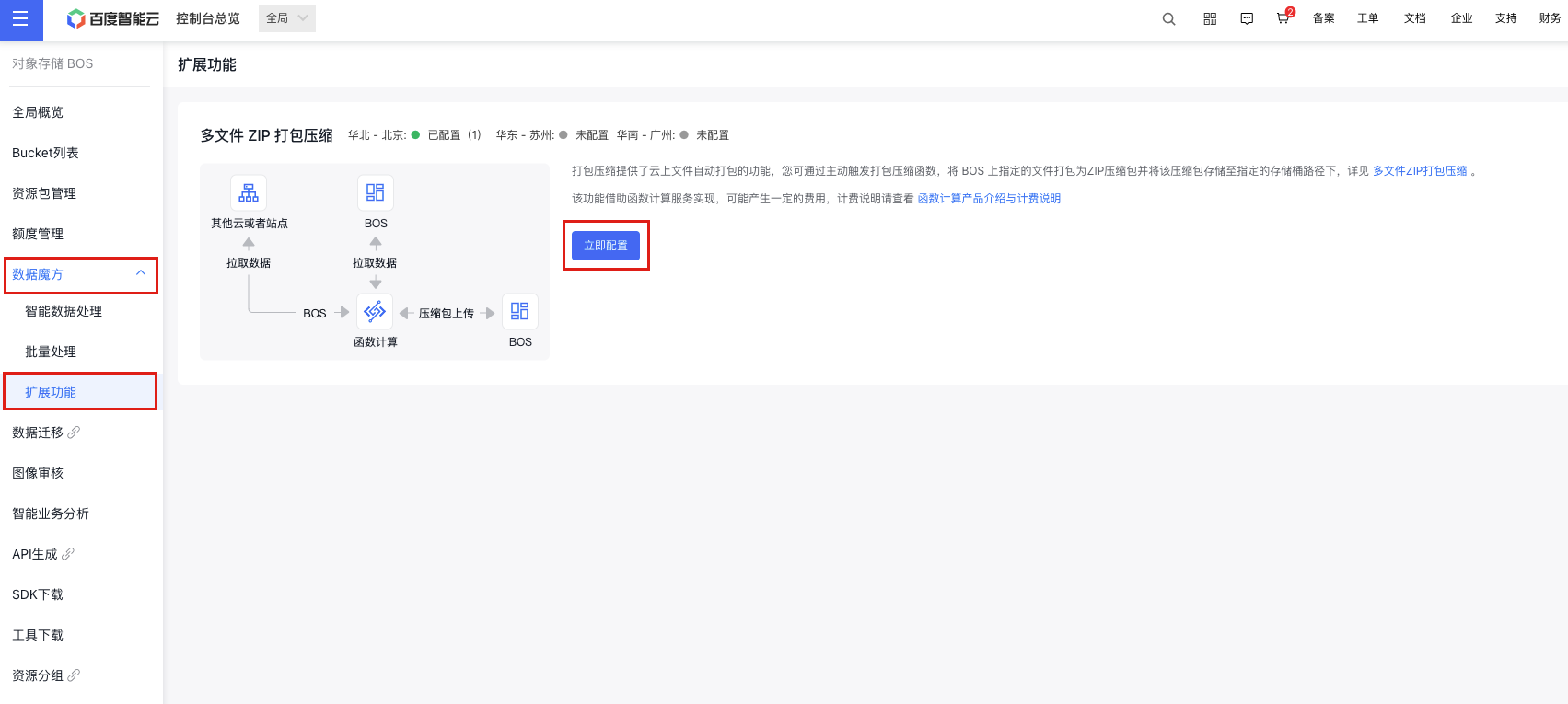
- From the left navigation bar, click on Data Cube, select Extension Function, and then activate the multi-file ZIP packaging and compression feature. Users who haven't activated the CFC service will be guided to enable it.
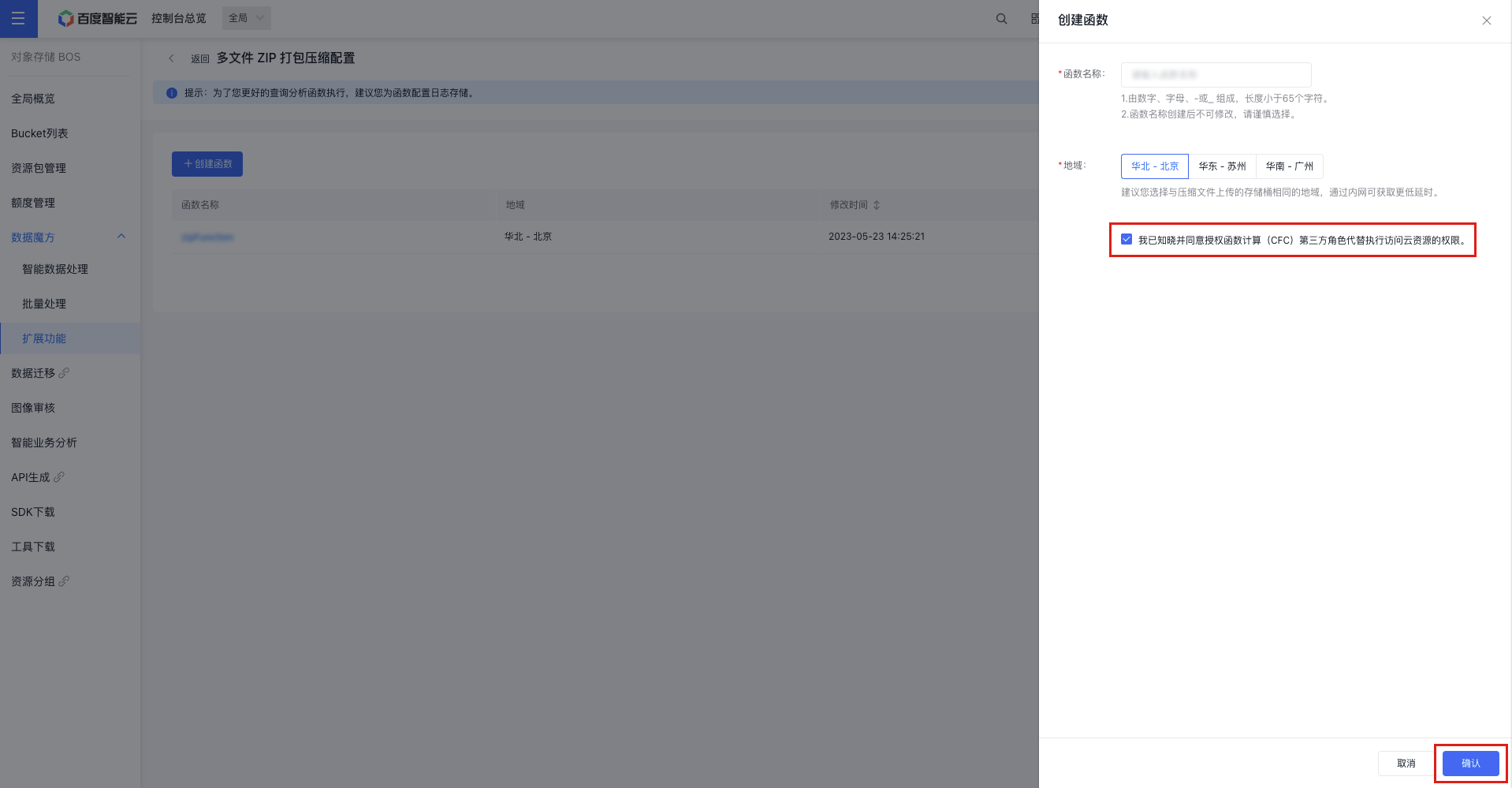
- Click Configure Now to access the packaging feature configuration API. Then, click Create Function in the upper left corner to set up a new packaging function. Provide a function name, select the region, grant CFC permissions, and click OK to complete the function creation.
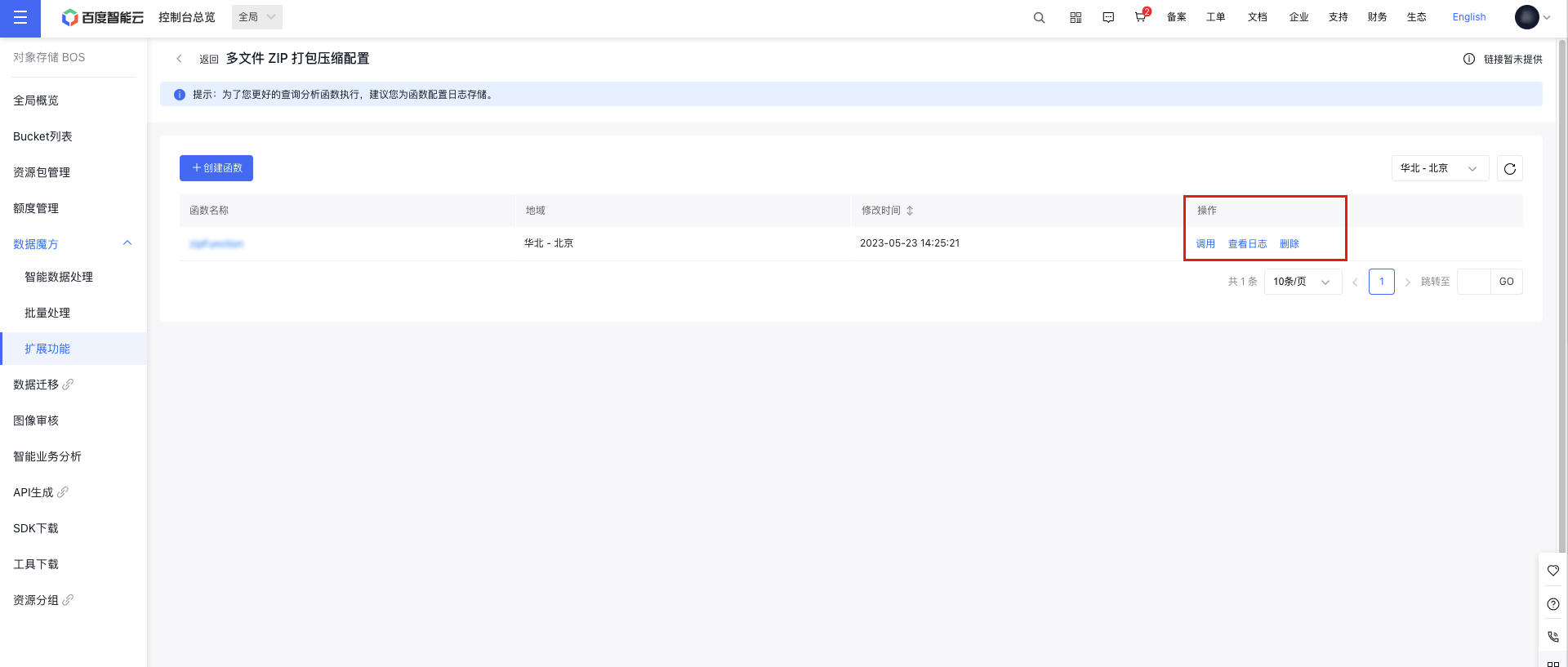
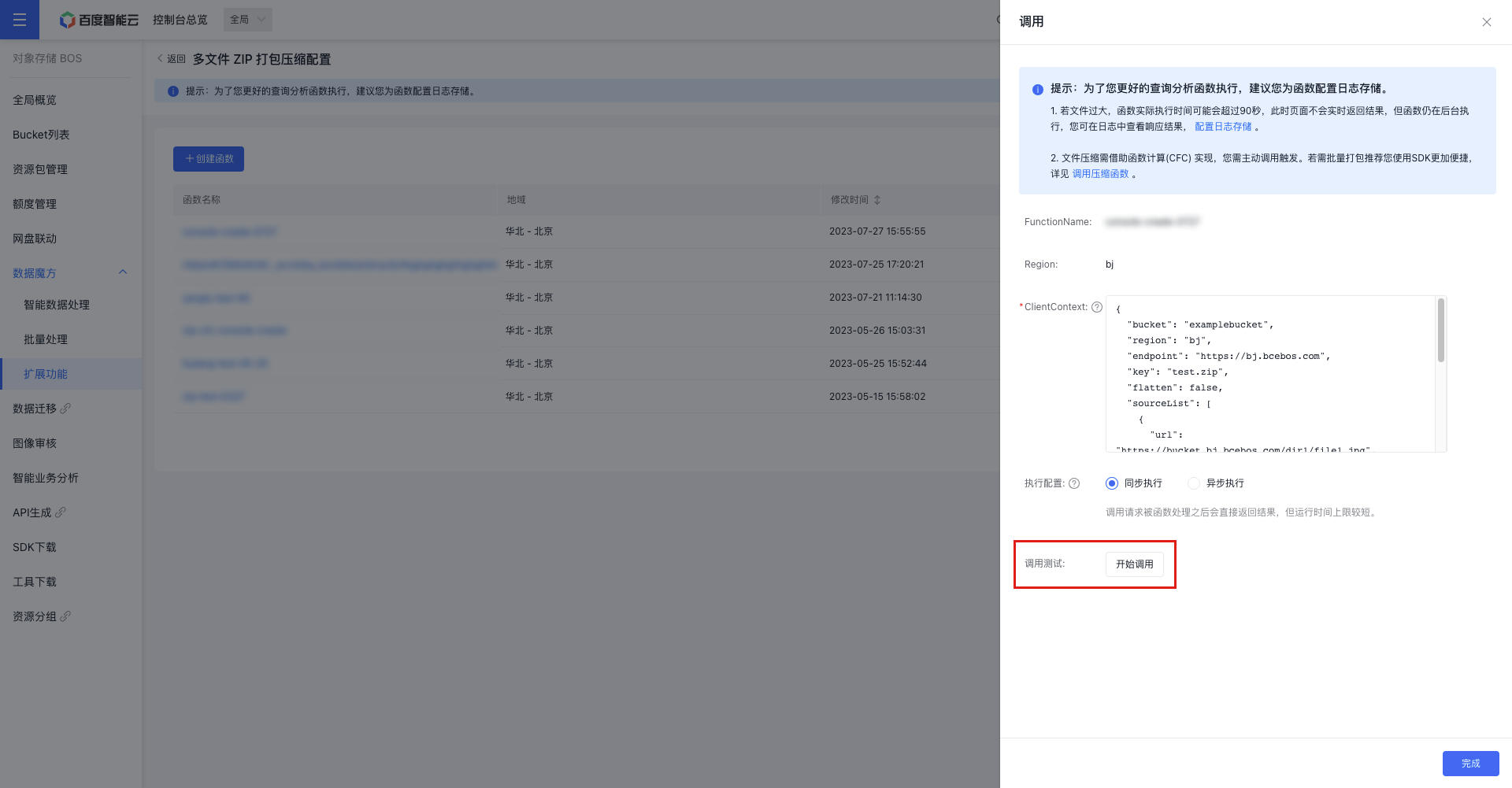
- Select the function you want to invoke from the function list, and click Invoke in the operation bar to access the function configuration API. Parameters are explained below in Multi-file Compression Parameter Explanations.
- Once the function parameters are configured, click Start Invoking to execute the function. You can view the results of the invocation in the response details.
- To facilitate better tracking and analysis of function executions, you can configure log storage for functions in the View Logs option in the function list operation bar. After completing the configuration, function logs will be accessible for viewing.
Multi-file Compression Parameter Explanations
Function parameter configuration example
In practical applications, remove any annotations from the code before proceeding.
1{
2 "bucket": "examplebucket", // Bucket for finally delivered ZIP file
3 "region": "bj", // Region of the bucket where the ZIP file will be finally delivered
4 "endpoint":"https://bj.bcebos.com", // Access domain name of the bucket for the finally delivered ZIP file
5 "key": "test.zip", // Name of the finally delivered ZIP file
6 "flatten": false, // Whether to flatten the source file path
7 /**
8 * sourceList is used to specify the source file list to be packaged in JSON array format
9 * Each item includes the source file URL, the renamed path renamePath, etc.
10 *
11 */
12 "sourceList": [
13 {
14 "url": "https://bucket.bj.bcebos.com/dir1/file1.jpg",
15 "renamePath": "dir1_rename/file1.jpg"
16 },
17 {
18 "url": "https://bucket.bj.bcebos.com/dir2/file2.mp4",
19 "renamePath": "file2.mp4"
20 },
21 {
22 "url": "https://bucket.bj.bcebos.com/file3.md"
23 }
24 ]
25}The parameter description is as follows:
| Parameter name | Parameter description | Types | Required or not |
|---|---|---|---|
| bucket | Bucket for finally delivered ZIP file, named in BucketName format (e.g., examplebucket) | String | Yes |
| region | Region of the bucket where the ZIP file is finally delivered; for enumerated values, refer to Region Selection Guide | String | Yes |
| endpoint | Endpoint of the bucket where the ZIP file is finally delivered; for enumerated values, refer to Region Selection Guide | String | Yes |
| key | The name of the finally delivered ZIP file (object name), which is the unique identifier of the object in the bucket。 | String | Yes |
| flatten | Is path flattening necessary, meaning the removal of the source directory structure? For instance, if the source file URL is https://domain/source/test.mp4, its path is source/test.mp4. If path flattening is enabled (set to true), the file path in the ZIP package will be test.mp4. If not, it will remain source/test.mp4 in the ZIP package. The default is set to false. | Boolean | No |
| sourceList | Source file list: sourceList | Array | Yes |
| sourceList[].url | URL of the source file | String | Yes |
| sourceList[].renamePath | Rename the path, i.e., the file path of the source file in the ZIP package. For example, rename dir1/file1.jpg to dir1_rename/file1.jpg. Note: renamePath has higher priority than flatten, and the renamed path is unaffected by flattening |
String | No |
Function response result example
Synchronous invoke result example:
1{
2 "Code": 0,
3 "Message": "zip success!",
4 "Data": {
5 "Bucket": "<bucket_name>",
6 "Key": "package1.zip",
7 "Location": "http://bj.bcebos.com/<bucket_name>/package1.zip",
8 "Etag": "-cf3cac621791214721d845becc3e9906"
9 },
10 "Error": null
11}The response parameter description is as follows:
| Parameter name | Parameter description | Types |
|---|---|---|
| Code | Service error code: 0 indicates execution succeeded; otherwise, execution failed | Number |
| Message | Text description of execution results (it may be null) | String |
| Data | Execution success message, which includes the ZIP package URL if execution is successful | Object |
| Error | Execution error message; it is null if the execution is successful | Object or String |
Asynchronous invoke result returns 202. For detailed execution logs, refer to the log path configured for the function
Invoke the compression function
- The file is compressed using Cloud Function Compute (CFC), and you need to manually trigger the function.
- Using the SDK is recommended for batch packaging.
- You can visit SDK Overview to view installation guide for SDKs in various languages and install the corresponding SDKs accordingly.
- After installing the SDK, you can invoke CFC’s invocations function API through the SDK to trigger the corresponding cloud function. For specific parameters, please refer to the Function Invocation API.
Practical case
Case I: Simple case
Parameter configuration
1{
2 "bucket": "<bucket_name>",
3 "region": "bj",
4 "endpoint":"https://bj.bcebos.com",
5 "key": "mypack.zip",
6 "flatten": false,
7 "sourceList": [
8 {
9 "url": "https://<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/dir1/file1.jpg"
10 },
11 {
12 "url": "https://<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/dir2/file2.mp4"
13 },
14 {
15 "url": "https://<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/file3.md"
16 }
17 ]
18}Final ZIP compressed package structure
1mypack.zip
2 ├── dir1/file1.jpg
3 ├── dir2/file2.mp4
4 └── file3.mdCase II: Source file path flattening
Parameter configuration
1{
2 "bucket": "<bucket_name>",
3 "region": "bj",
4 "endpoint":"https://bj.bcebos.com",
5 "key": "mypack.zip",
6 "flatten": true, // When flatten is true, the source file paths are flatten
7 "sourceList": [
8 {
9 "url": "<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/dir1/file1.jpg"
10 },
11 {
12 "url": "<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/dir2/file2.mp4"
13 },
14 {
15 "url": "<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/file3.md"
16 }
17 ]
18}Final ZIP compressed package structure
1mypack.zip
2 ├── file1.jpg
3 ├── file2.mp4
4 └── file3.mdCase III: Source file path renaming
Parameter configuration
1{
2 "bucket": "<bucket_name>",
3 "region": "bj",
4 "endpoint":"https://bj.bcebos.com",
5 "key": "mypack.zip",
6 "flatten": false,
7 "sourceList": [
8 {
9 "url": "https://<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/dir1/file1.jpg",
10 // Rename the path dir1/file1.jpg to dir1_rename/file1.jpg
11 "renamePath": "dir1_rename/file1.jpg"
12 },
13 {
14 "url": "https://<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/dir2/file2.mp4",
15 // Rename dir2/file2.mp4 to file2.mp4
16 "renamePath": "file2.mp4"
17 },
18 {
19 "url": "https://<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/file3.md"
20 }
21 ]
22}Final ZIP compressed package structure
1mypack.zip
2 ├── dir1_rename/file1.jpg
3 ├── file2.mp4
4 └── file3.mdCase IV: Source file path renaming + flattening
Parameter configuration
1{
2 "bucket": "<bucket_name>",
3 "region": "bj",
4 "endpoint":"https://bj.bcebos.com",
5 "key": "mypack.zip",
6 "flatten": true, // When flatten is true, the source file paths are flatten
7 "sourceList": [
8 {
9 "url": "https://<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/dir1/file1.jpg"
10 },
11 {
12 "url": "https://<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/dir2/file2.mp4"
13 },
14 {
15 "url": "https://<bucket_name>.bj.bcebos.com/file3.md",
16 // Rename file3.md to dir3/file3.md. The renamePath has higher priority than flatten, so the renamed path will not be flattened
17 "renamePath": "dir3/file3.md"
18 }
19 ]
20}Final ZIP compressed package structure
1mypack.zip
2 ├── file1.jpg
3 ├── file2.mp4
4 └── dir3/file3.md