Service Introduction
Service overview:
The hierarchical namespace is a structured metadata management feature introduced by Baidu AI Cloud Object Storage (BOS). By creating and using HNS buckets, it enables seamless directory-level move and rename operations, optimizes common read operations such as list and head, and enhances data processing efficiency and performance, making it well-suited for data lake computing scenarios in the big data domain.
Feature activation
- Step 1: Submit a ticket to specify your requirements. The system will grant you the necessary access permissions for HNS buckets.
- Step 2: After receiving the permissions, create HNS buckets using BOS tools or by logging into the console.
Feature architecture:
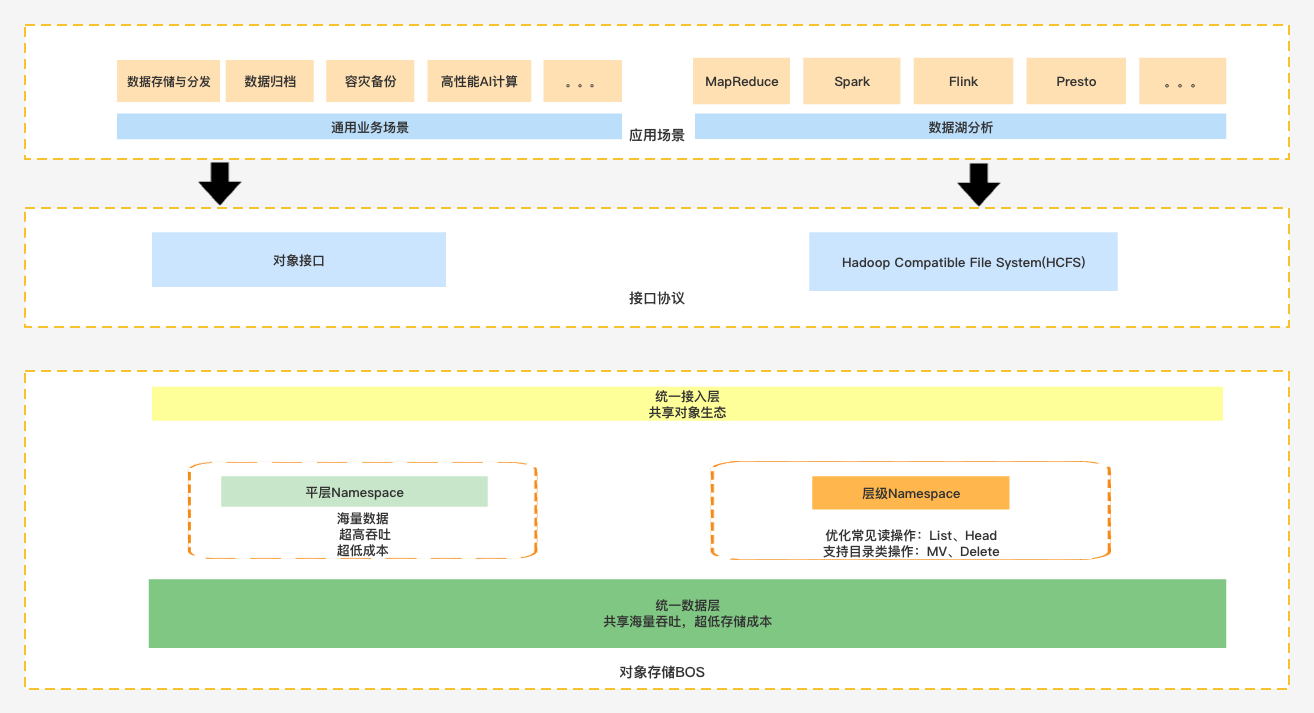
Advantages:
- Directly leverage the advantages of object storage in big data scenarios: automated data management, low storage costs, and strong data security
-
Natively object-based hierarchical namespace delivers high performance for file semantics in big data computing scenarios
- Support high-performance atomic operations such as Rename, Delete Dir, and Delete Object
- Significantly lower List/Head request latency compared to flat object storage
- Big data analytics directly based on object storage (“All in Object”), eliminating additional costs for data replication, transfer, storage, and third-party services
- No extra costs for O&M, management, or learning - fully utilize the ecosystem and tools of object storage
Application scenarios:
Big data analytics and computing
As the leading cloud storage solution, Baidu AI Cloud Object Storage (BOS) offers a suite of high-performance big data computing solutions. In big data applications, BOS excels as the underlying storage system for on-premises or cloud-based computing clusters like MapReduce, Hive, and Spark offline data warehouse clusters. Its built-in hierarchical namespace functionality significantly decreases the latency of large-scale batch operations (e.g., Rename, List, Head) by roughly 70%, effectively overcoming traditional object storage latency bottlenecks in big data computing.
