Set cross-origin access
Overview
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a HTML5-based standard cross-domain solution, where cross-origin access refers to a access form when the domain of the resource initiating a request is different from the domain of the resource targeted by the request For security reasons, browsers restrict such non-same-origin access, but in practice, cross-origin access needs are common. For example, if a user's website A (http://domainA.example) uses BOS storage in the backend, and the user wants to reference resources stored in BOS within the web application of this site. According to HTML5 protocol requirements, this reference operation can only send requests to the website domain name http://domainA.example. Requests sent to other websites will be restricted by the browser.
BOS supports cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) settings in the HTML5 protocol to help users achieve cross-origin access. CORS indicates its source domain by including the origin header in the HTTP request. As in the example above, the origin header is http:// domainA.example. After receiving the request, the server will determine whether to allow the request from this source domain based on specific rules. If allowed, the server will attach an Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to the returned response, with the value http:// domainA.example, indicating that this cross-origin access is permitted. If the server allows cross-domain requests from any domain name, set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin Header to *. The browser determines whether the cross-domain request is successful based on whether the corresponding Header is returned. If the corresponding Header is not attached, the browser will intercept the return result. For not-so-simple requests, the browser will first send an OPTIONS request (preflight request) to check if the cross-origin request is secure and acceptable to the server. If the server does not support the subsequent operation, the browser will block the cross-origin request.
Set cross-origin access
- Sign in to the Baidu AI Cloud Object Storage (BOS) Management Console.
- From the bucket list on the left, select the bucket for which you want to set permissions, then click its name to enter the bucket management directory.
- Select the Configuration Management tab in the top navigation bar.
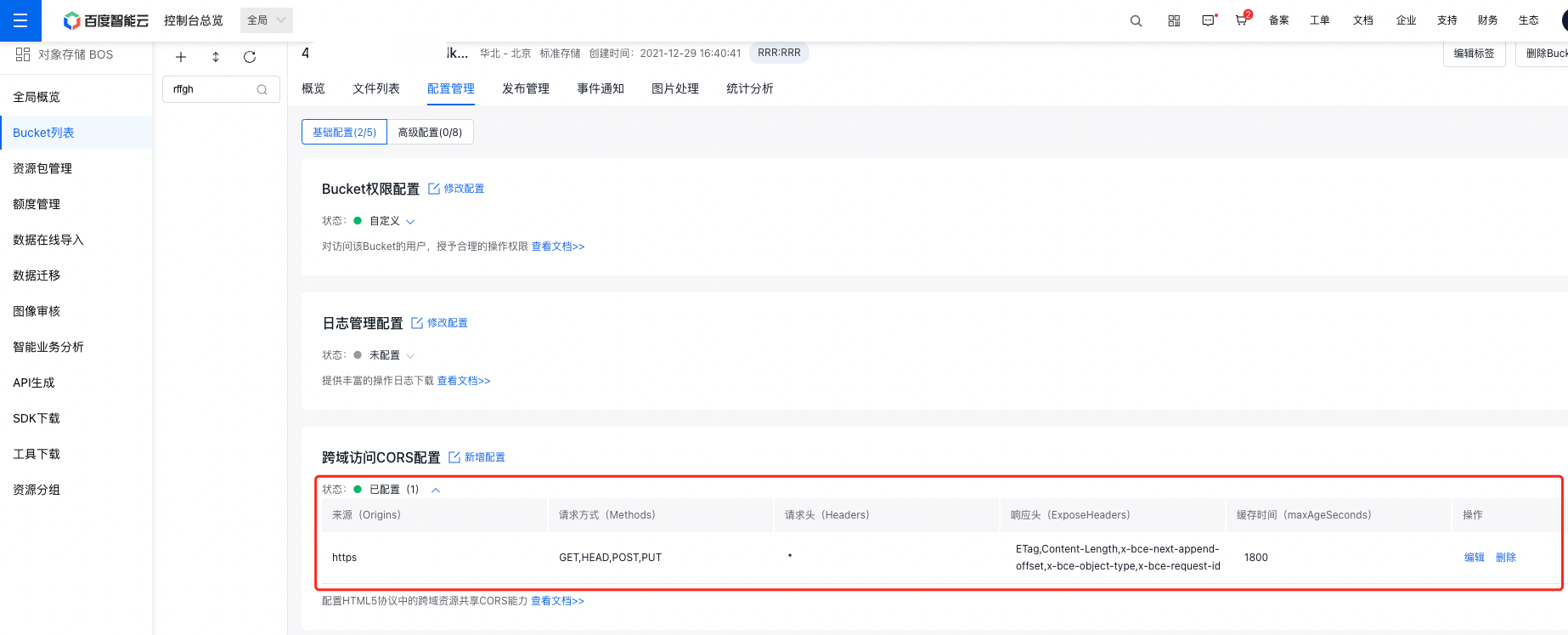
- On the Configuration Management page, select Basic Configuration, and click Add Configuration in the Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) Configuration area to configure cross-origin access for the bucket.
Parameter setting:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Origins | Specify the allowed cross-origin request origins. You can set multiple origins, one per line, with a maximum of one \ symbol per line. Using \ allows cross-origin requests from all sources, and you can use \ as a suffix to represent certain types of websites, e.g., abc \ to support websites starting with “abc.” |
| Methods | Specify the allowed cross-origin request methods |
| Headers | Specify the allowed cross-origin request headers. Multiple headers can be set, one per line, with a maximum of one \* symbol per line. |
| ExposeHeaders | Specify the response headers that users are allowed to access from the application (such as a Javascript XMLHttpRequest object) . Multiple ExposeHeaders can be set, one per line, and the * symbol cannot appear |
| maxAgeSeconds | Specify the cache duration in the browser for the response results of prefetch (OPTIONS) request |
Note
- CORS is only relevant in browser environments. The browser automatically manages the attachment of related headers, so no manual action is required by the user.
- CORS requests are entirely independent of BOS’s identity authentication. CORS rules merely determine whether to attach CORS-related headers, while request interception is solely determined by the browser.
- When using cross-origin requests, you need to pay attention to whether the browser has enabled the Cache function. When two pages running on the same browser, originating from different domains
http://domainA.exampleandhttp://domainB.example, simultaneously request the same cross-origin resource, if the request fromhttp://domainA.examplearrives at the server first, the server will return the resource to the user with the Access-Control-Allow-Origin Header set tohttp://domainA.example. At this time, ifhttp://domainB.exampleinitiates a request, the browser will return the cached result of the previous request to the user. At this point, the content of the Header does not match the requirements of CORS, which will cause subsequent requests to fail.
For more introductions about CORS, you can refer to Cross-Origin Resource Sharing.
- Click OK to complete the configuration.
- After adding a CORS rule, click Modify on the right side of the list to modify the CORS rule.
- After adding a CORS rule, if you want to delete the rule, you can click Delete on the right side of the list to delete a single CORS rule.
Related APIs
- PutBucketCors API: Use the PutBucketCors API to set a cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) rule on the specified bucket.
- GetBucketCors API: Use the GetBucketCors API to obtain the current CORS rules of the specified bucket.
- DeleteBucketCors API: Use the DeleteBucketCors API to disable the CORS function of the specified bucket and clear all rules.
