Set access logs
Updated at:2025-11-03
Overview
When users need to track requests to access BOS, they can enable the logging function for the BOS. The logging function can be applied in access statistics and security audits, etc. Each access log records detailed information of a single access request, including requester, bucket name, request time, and request operation. For format of access logs, please refer to [Set Access Logs](BOS/Developer Guide/Bucket Basic Operations/Set access logs.md). When a bucket enables the access log function, it will automatically write the access requests to this bucket into the user-specified bucket as log files in accordance with a fixed naming rule on an hourly basis.
Description:
- Storing access logs in the target bucket is a "best-effort" process. Generally, it takes 2 to 3 hours for an access request to progress from its occurrence to the corresponding logs being stored in the target bucket. However, due to factors such as network conditions, certain logs may be delayed for a comparatively longer period before being stored in the target bucket.
- Log files are the same as regular files in nature. BOS cannot clear them, and you must manually delete unwanted log files. If you do not delete them, log files will be retained indefinitely. If you need to delete outdated log files regularly, it is recommended to configure lifecycle rules to remove outdated files.
Set access logs
- Sign in to the Baidu AI Cloud Object Storage (BOS) Management Console.
- From the bucket list on the left, select the bucket for which you want to set permissions, then click its name to enter the bucket management directory.
- Select the Configuration Management tab in the top navigation bar.
- On the Configuration Management page, select Basic Configuration, and click Modify Configuration in the Logging region to configure the logging of the bucket. By default, the logging function is not enabled.
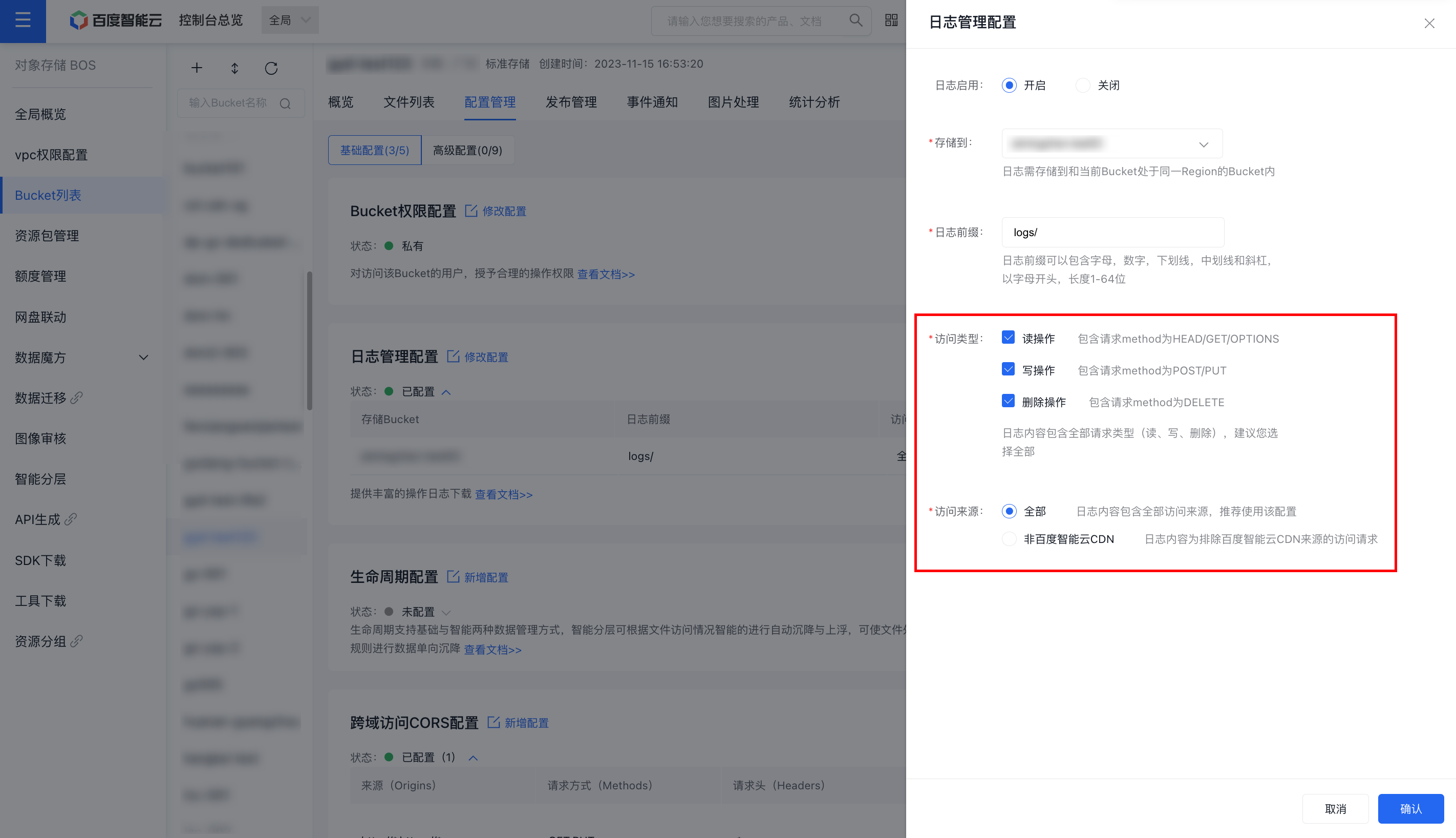
- In the log management configuration panel, enable the log feature by setting its status to "On" and specify the bucket location where the current log files will be stored along with a log prefix.
- BOS allows customization of the access types and sources recorded in the logs. By default, logs include all access sources and types. You can adjust these settings according to your specific requirements.
Note:
- The target bucket for log storage and the source bucket must be in the same region;
- The logging feature is free of additional charges; however, you will incur storage costs for the log files. There are no fees for transmitting log files, but accessing the generated log files will be billed like regular data transmission costs.
- The log prefix can include letters, numbers, underscores, hyphens, and slashes. It must start with a letter and have a length of 1 to 64 characters.
- By default, all access types (e.g., read, write, delete operations) are included in the logs. It is recommended that you select all types.
- All access sources are included in the logs by default. It is advisable to maintain this configuration.
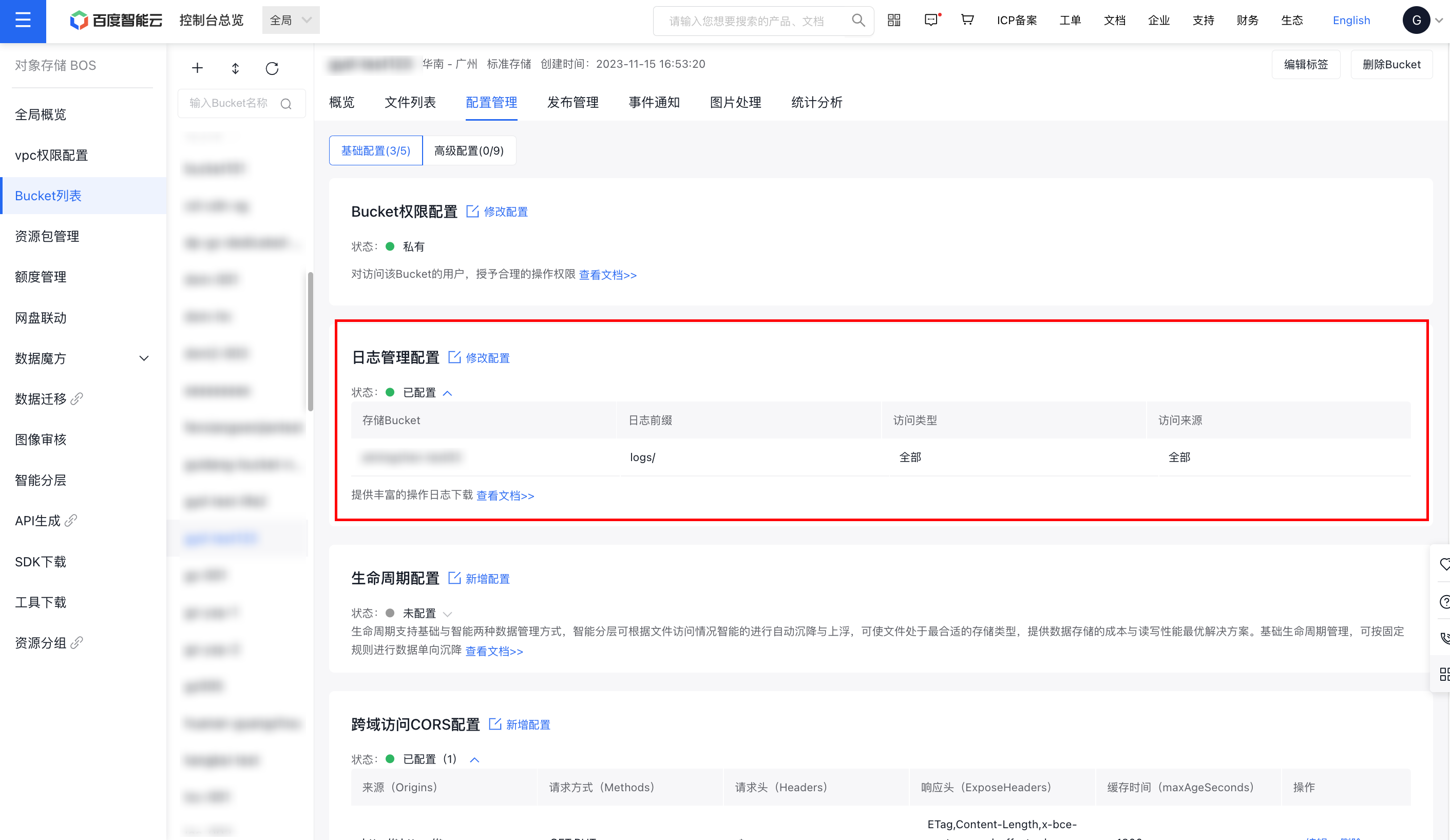
- After the settings are completed, click OK to finish the log configuration. You can view and modify the relevant information on the current page.
Related APIs
- PutBucketLogging API: Use the PutBucketLogging API to enable access logging for the bucket and specify the bucket where the logs will be stored and the file prefix of the access logs.
- GetBucketLogging API: Use the GetBucketLogging API to obtain the access log configuration of a certain bucket.
- DeleteBucketLogging API: Use the DeleteBucketLogging API to disable the access log recording function of the bucket.
