Setting Symlink
Updated at:2025-11-03
Overview
The symlink function is designed to provide quick access to frequently used files within the object storage space. Once a symlink is set up, you can use the symlink file to quickly access the source file, similar to shortcuts in the Windows operating system.
Note
- Symlink files and source files can be located in different buckets within the same region.
- Symlink files can now be set for standard, infrequent access, cold, and archive storage class source files. However, symlink files cannot be created for the archive storage class.
- When creating a symlink file, BOS does not verify the existence of the source file or the creator's access permissions for the source file. When reading a symlink file, BOS verifies both the existence of the symlink and source files as well as the read permissions.
- Creating a symlink file requires the corresponding write permission.
- If the "x-bce-forbid-overwrite" header is not specified and there is already a file with the same name as the symlink file, the existing file will be overwritten by default during the symlink operation. Please confirm carefully.
- Creating symlink files for existing symlink files (secondary symlinks) is not supported.
Configure symlink file
- Sign in to the BOS Management Console and navigate to the Global Overview page.
- In the left navigation bar of the BOS console, select the target bucket where the scanned file is located, then click to open the bucket’s File List page.
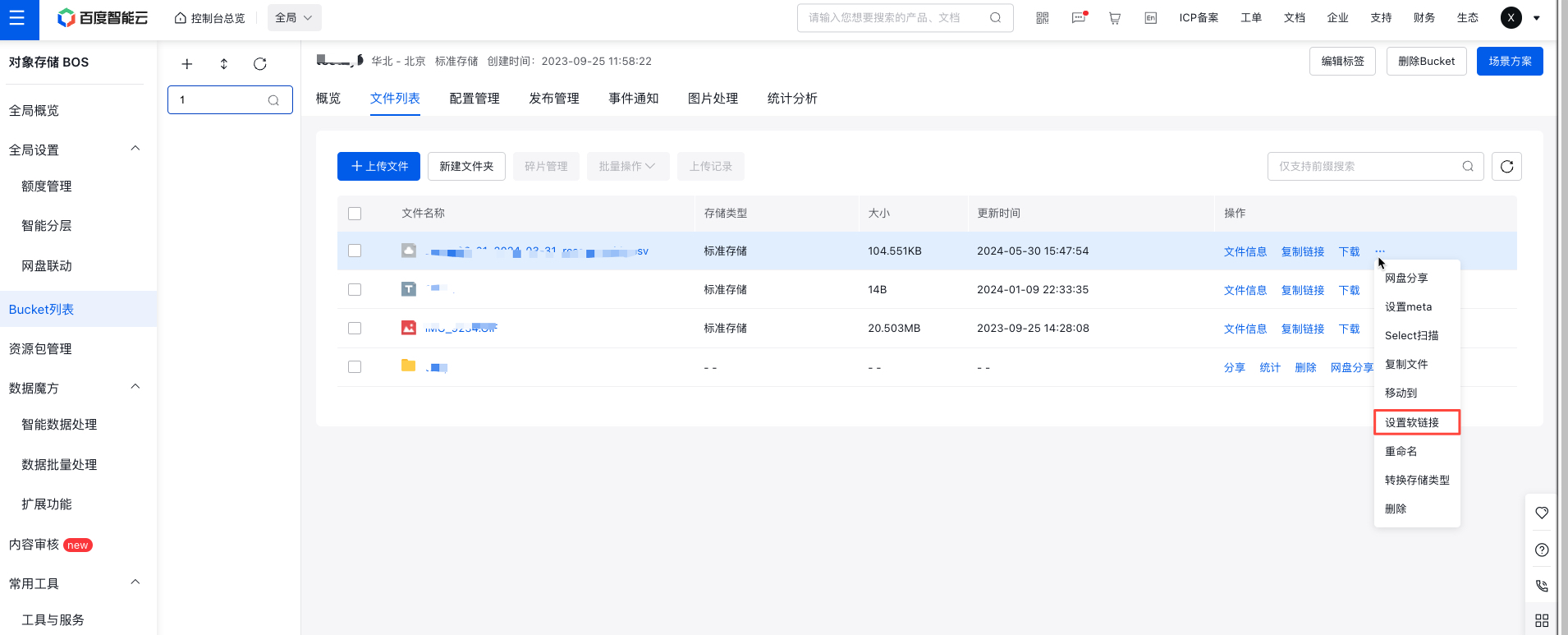
- Click More -> Symlink in the operation bar on the right side of the target file to set a symlink.
- Name the symlink file in the pop-up window. If you need to place the symlink file in a specific folder within the bucket, include the folder path in the symlink file name when naming it. If no path is included in the name, the file will automatically be placed in the bucket's root directory. For example, if the symlink file name is aaa/ruanlianjie1.csv, the symlink file will be stored in the aaa folder. If you name it ruanlianjie.csv, the file will be stored in the bucket's root directory.
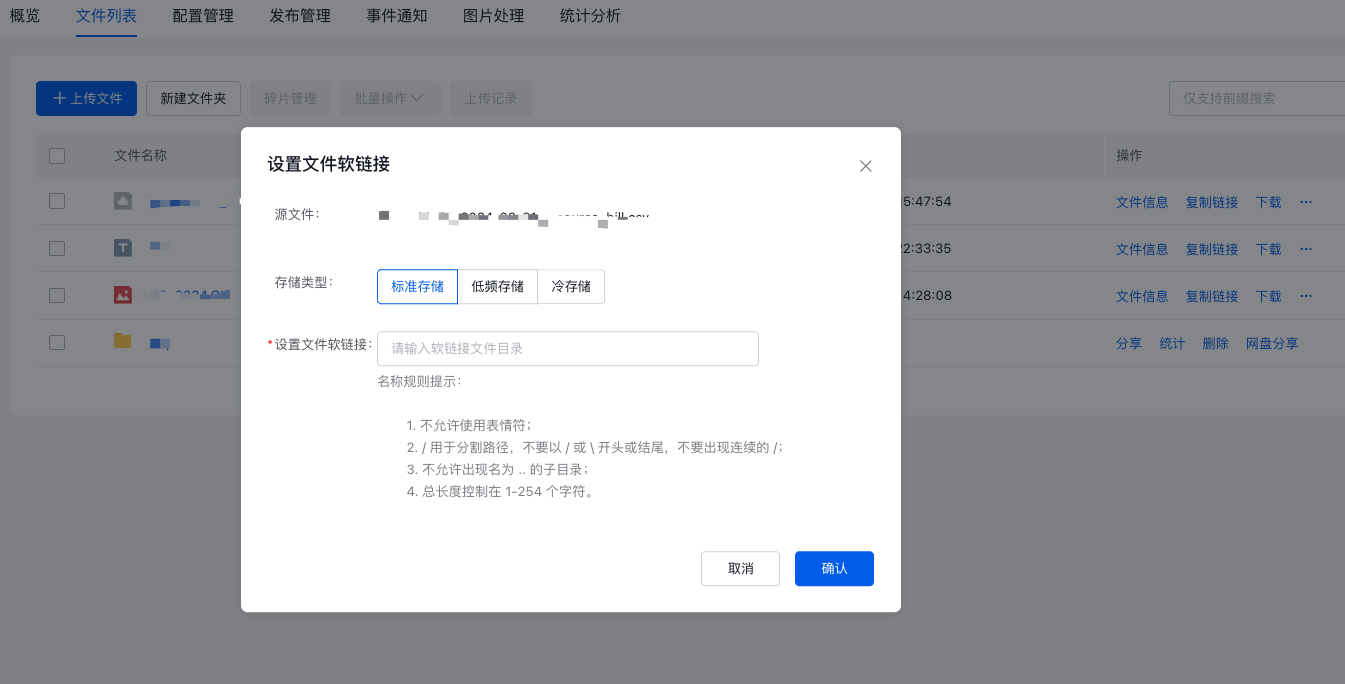
Description:
- If you don’t want to keep the created symlink files, you can delete them. Removing a symlink file does not impact the source file.
- Renaming a symlink file or changing its storage class will not affect the attributes of the source file;
- If the source file is deleted, the created symlink files won’t be removed automatically. However, accessing these symlinks may fail afterward. If you delete the source file, please ensure to manually delete the corresponding symlink file.
- You can perform operations on symlink files using the API in the same manner as regular files, including deletion and renaming.
Related APIs
- PutSymlink API: Use PutSymlink API to configure file symlinks.
- GetSymlink API: Use GetSymlink API to read and access symlink files.
