HAVIP Combined with Keepalived to Achieve Master-Backup Multi-Machine High Availability
Overview
Using a high-availability virtual IP address with Keepalived enables a primary-backup cluster setup. By default, the primary cluster handles client traffic. If the primary cluster fails, the standby cluster seamlessly takes over, ensuring high service availability.
Solution overview
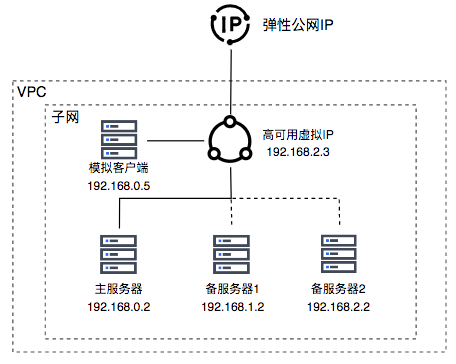
This document presents the following scenario: creating four BCC instances with private IPs 192.168.0.2, 192.168.1.2, 192.168.2.2, and 192.168.0.5, along with one HAVIP (192.168.2.3). Using Keepalived, 192.168.0.2 acts as the active server, while 192.168.1.2 and 192.168.2.2 serve as backup servers. A simulated client (192.168.0.5) accesses the HAVIP (192.168.2.3).
Configuration steps
Step 1: Create HAVIP
- Navigate to Products & Services - Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and select Network Interface Card - High-Availability Virtual IP Address from the left navigation bar.
- Click Create Virtual IP to open the virtual IP creation dialog, and fill in the required configuration information.
| ConfigMap | Description |
|---|---|
| Virtual IP name | User-defined HAVIP name |
| Network | Select the virtual private cloud where the HAVIP is to be created |
| Subnet belonged | HAVIP has subnet attributes. Please select the subnet under the current VPC from the dropdown |
| IP address | By default, automatic IP address assignment is selected. Specifying a custom IP is supported, provided that the IP is unoccupied |
| Description | Edit HAVIP description |
- Click OK to create the high-availability virtual IP address.

Step 2: Install Keepalived on the active and standby servers
- Sign in to the BCC console, navigate to the instance page, click Create Instance, and complete the BCC creation by filling in the configuration details. For detailed steps, refer to Instance Creation Guide.
- Sign in to the Baidu Cloud Compute instance. For specific operations, refer to Login Method Overview.
-
Install Keepalived on the active and standby servers by using the yum method to set it up.
yum install keepalived -y
Step 3: Configure Keepalived to bind the HAVIP to the active and backup servers
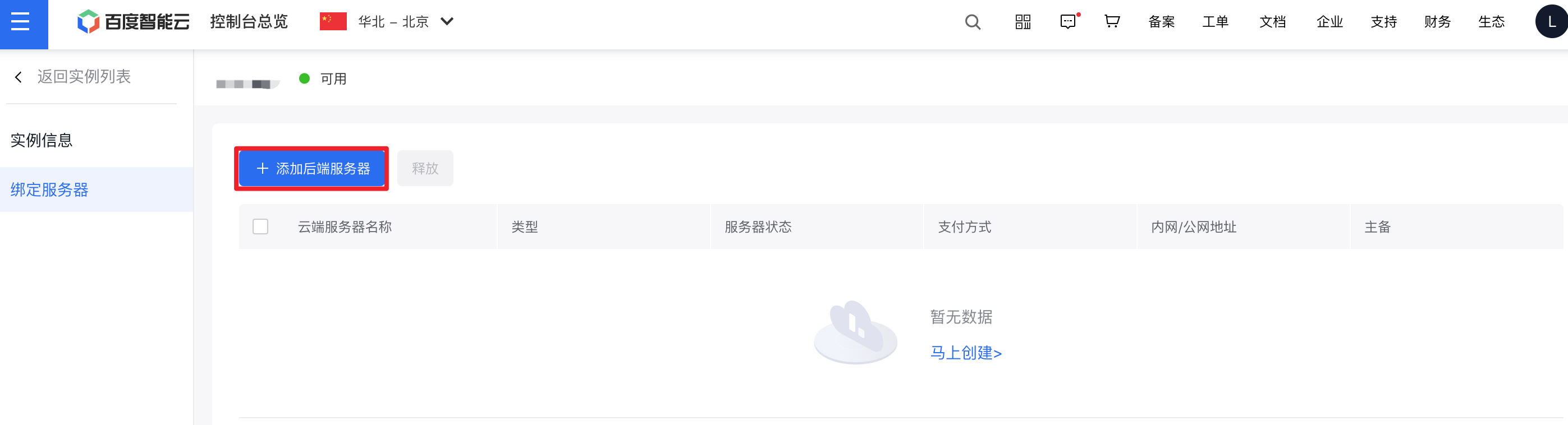
- Sign in to the High-availability Virtual IP Address console, click the instance name to enter the details page, select Bind Server from the left navigation bar to access the backend server list, and click Add Real Server to select the Baidu Cloud Compute instance to be bound.
-
Log into the active server, execute
vim /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf, and update the necessary configuration.Plain Text1 global_defs { 2 notification_email { 3 acassen@firewall.loc 4 failover@firewall.loc 5 sysadmin@firewall.loc 6 } 7 notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc 8 smtp_server 192.168.200.1 9 smtp_connect_timeout 30 10 router_id LVS_DEVEL 11 vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr 12 vrrp_garp_interval 0 13 vrrp_gna_interval 0 14 } 15 vrrp_script checkService 16 {script "/etc/keepalived/check_status.sh” # Check whether the business process is running normally. The "check_status.sh" file is a user-defined business process detection script. Execute it according to business needs, and replace "check_status.sh" with the actual script name during execution. interval 1 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state MASTER # Set the initial status to "MASTER” interface eth0 # Set the network interface card bound to the VIP, e.g., eth0 virtual_router_id 51 # Configure the cluster's virtual_router_id value nopreempt # Set non-preemptive mode, priority 100 # Higher values indicate higher priority (range: 1-254) advert_int 1 # #Advertisement interval, default is 1. authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } unicast_src_ip 192.168.0.2 # Set the local intranet IP address unicast_peer { 192.168.1.2
192.168.2.2 # Intranet IP address of other peer devices bound to the high-availability virtual IP address } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.2.3 # Configure high-availability virtual IP address } notify_master "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh MASTER" notify_backup "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh BACKUP" notify_fault "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh FAULT" notify_stop "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh STOP" garp_master_refresh 5 # Set the interval for the master node to send ARP messages garp_master_delay 1 # Sets the delay for updating ARP cache after switching to master status track_interface { eth0 # Use the network interface card bound to VIP, e.g., eth0 } track_script { checkService } } -
Log into standby server 1, execute
vim /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf, and update the necessary configuration.Plain Text1 global_defs { 2 notification_email { 3 acassen@firewall.loc 4 failover@firewall.loc 5 sysadmin@firewall.loc 6 } 7 notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc 8 smtp_server 192.168.200.1 9 smtp_connect_timeout 30 10 router_id LVS_DEVEL 11 vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr 12 vrrp_garp_interval 0 13 vrrp_gna_interval 0 14 } 15 vrrp_script checkService 16 {script "/etc/keepalived/check_status.sh” # Check whether the business process is running normally. The "check_status.sh" file is a user-defined business process detection script. Execute it according to business needs, and replace "check_status.sh" with the actual script name during execution. interval 1 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state BACKUP # Set the initial status to "BACKUP” interface eth0 # Set the network interface card bound to the VIP, e.g., eth0 virtual_router_id 51 # Configure the cluster's virtual_router_id value nopreempt # Set non-preemptive mode, priority 100 # Higher values indicate higher priority (range: 1-254) advert_int 1 # #Advertisement interval, default is 1. authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } unicast_src_ip 192.168.1.2 # Set the local intranet IP address unicast_peer { 192.168.0.2 192.168.2.2 # Intranet IP address of other peer devices bound to the high-availability virtual IP address } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.2.3 # Configure high-availability virtual IP address } notify_master "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh MASTER" notify_backup "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh BACKUP" notify_fault "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh FAULT" notify_stop "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh STOP" garp_master_refresh 5 # Set the interval for the master node to send ARP messages garp_master_delay 1 # Sets the delay for updating ARP cache after switching to master status track_interface { eth0 # Use the network interface card bound to VIP, e.g., eth0 } track_script { checkService } }
-
Log into standby server 2, execute
vim /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf, and update the necessary configuration.Plain Text1 global_defs { 2 notification_email { 3 acassen@firewall.loc 4 failover@firewall.loc 5 sysadmin@firewall.loc 6 } 7 notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc 8 smtp_server 192.168.200.1 9 smtp_connect_timeout 30 10 router_id LVS_DEVEL 11 vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr 12 vrrp_garp_interval 0 13 vrrp_gna_interval 0 14 } 15 vrrp_script checkService 16 {script "/etc/keepalived/check_status.sh” # Check whether the business process is running normally. The "check_status.sh" file is a user-defined business process detection script. Execute it according to business needs, and replace "check_status.sh" with the actual script name during execution. interval 1 } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state BACKUP # Set the initial status to "BACKUP” interface eth0 # Set the network interface card bound to the VIP, e.g., eth0 virtual_router_id 51 # Configure the cluster's virtual_router_id value nopreempt # Set non-preemptive mode, priority 100 # Higher values indicate higher priority (range: 1-254) advert_int 1 # #Advertisement interval, default is 1. authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } unicast_src_ip 192.168.2.2 # Set the local intranet IP address unicast_peer { 192.168.0.2 192.168.1.2 # Intranet IP address of other peer devices bound to the high-availability virtual IP address } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.2.3 # Configure high-availability virtual IP address } notify_master "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh MASTER" notify_backup "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh BACKUP" notify_fault "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh FAULT" notify_stop "/etc/keepalived/notify_action.sh STOP" garp_master_refresh 5 # Set the interval for the master node to send ARP messages garp_master_delay 1 # Sets the delay for updating ARP cache after switching to master status track_interface { eth0 # Use the network interface card bound to VIP, e.g., eth0 } track_script { checkService } }
- Test the business script
check_status.sh.Customize the script content and path as required, then synchronize updates tokeepalived.conf. In this example, the existence of the/tmp/downfile determines the service status. If the file does not exist, the service is considered normal (returning 0); if it exists, the service is considered abnormal (returning 1), triggering Keepalived to switch to Master. The script and permissions (755 or higher) are as follows:

/etc/keepalived/check_status.sh
1#!/bin/sh
2if [ ! -f /tmp/down ]
3then
4 exit 0
5fi
6exit 1-
Restart the Keepalived process to apply the updated configurations.
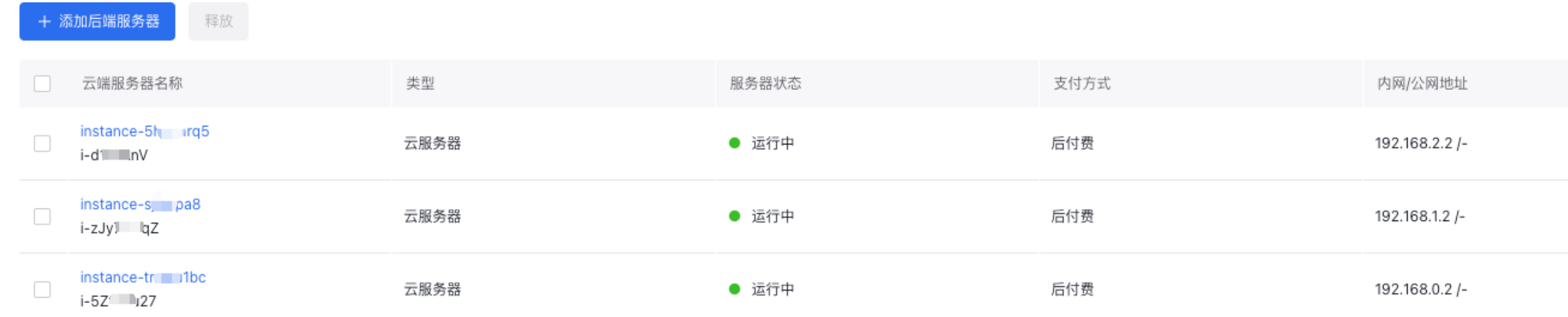
Plain Text1systemctl start keepalived 2systemctl restart keepalived 3systemctl status keepalived - Sign in to the high-availability virtual IP console to view the active server (192.168.0.2), standby server 1 (192.168.1.2), and standby server 2 (192.168.2.2) bound to the high-availability virtual IP address, as shown in the figure below.
Step 4: Bind the HAVIP to an EIP (optional)
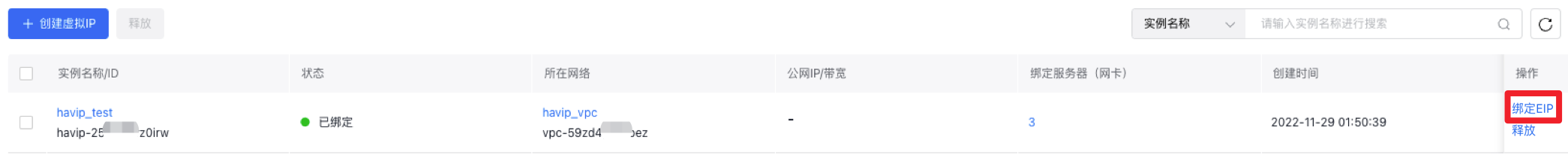
- Sign in to the high-availability virtual IP address console, click Bind in the operations for the HAVIP created in Step 1.
- In the EIP binding dialog, select the EIP to bind, then click OK. If no Public IP is available, click "Create Public IP" in the upper-right corner to apply for one.
Step 5: Testing and Verification
- After starting according to the Keepalived Configuration file, the server (192.168.0.2) becomes the master (state=MASTER, priority 100, with a 1-second Period for checking virtual machine status)
- Simulate client (192.168.0.5) continuously pinging HAVIP: ping 192.168.2.3 -i 0.001
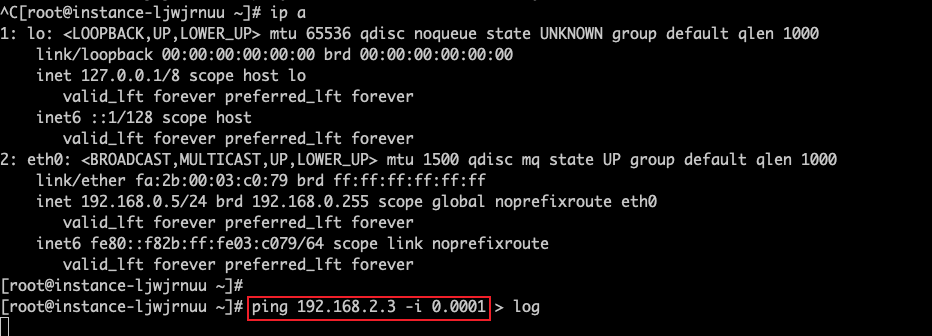
- On the master server (192.168.0.2), create a "down" file under /tmp directory. The Keepalived periodic task checks /tmp/down to simulate service failure and trigger HAVIP switchover
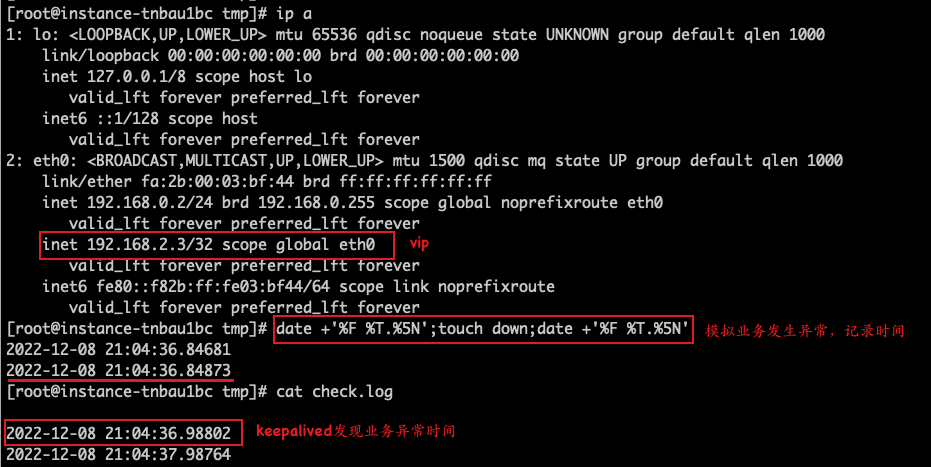
- Capture gratuitous ARP packets and ICMP packets for the HAVIP on Backup Server 1 (192.168.1.2) and Backup Server 2 (192.168.2.2).
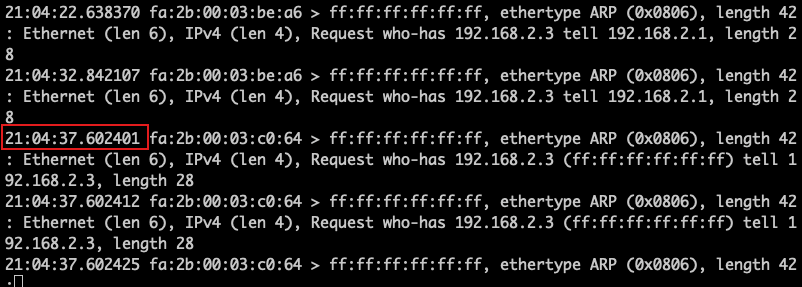
- When the server (192.168.2.2) switches to Master, observe the time when gratuitous ARP packets are sent.
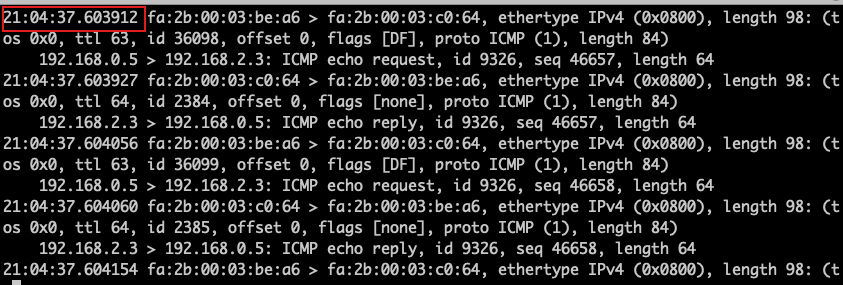
- Record the time when the server (192.168.2.2) completes traffic switching and starts receiving ICMP packets.
- Once the primary/standby switchover is complete, the bound host in the console will show as switched to the Baidu Cloud Compute instance (192.168.2.2).
Related products
Baidu Cloud Compute (BCC), Elastic Public IP, Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
