Identity and access management
Introduction
Identity and Access Management helps users manage resource access permissions within cloud accounts. It caters to various enterprise roles by granting different staff levels access to specific product permissions. For enterprises requiring multi-user collaboration for resource operations, using Identity and Access Management is recommended.
It is applicable to the following usage scenarios:
- For medium and large enterprise customers: Efficiently manage authorizations for multiple employees in the organization.
- For technology-driven vendors or SaaS platform providers: Manage resources and permissions for proxy client accounts.
- For small and medium-sized developers or small enterprises: Add team members or collaborators to streamline resource management.
Create User
-
After logging into the root account, select Identity and Access Management from the console to access the user management page.

- Click on User Management in the left navigation bar, then click New User on the IAM User Management List page.
- In the New User dialog box that appears, enter the username, confirm the details, and return to the IAM User Management List to view the newly created IAM user.
Configuration Policy
ET supports both system policies and custom policies, providing product-level and instance-level permission control for ET.
- System policy: A pre-defined set of permissions provided by the Baidu AI Cloud system for resource management. These can be directly assigned to IAM users, but users cannot modify them.
- Custom policy: A user-created, more granular set of permissions for resource management, allowing specific permissions to be configured for single instances. This provides flexibility to address the unique permission management needs of different users.
Description:
- Permissions for ET can be categorized into three types: read-only, O&M, and administration;
- For all products, O&M permissions include all read-only permissions. Administration permissions cover both read-only and O&M permissions. The table below only highlights instances where higher-level permissions differ from lower-level permissions.
- Custom policies apply to specific individual instances and only take effect for those instances. As a result, they do not include permissions for instance creation.
System Policy
The system policy includes 3 types of policies: management permission, operation and maintenance permission and read-only permission. The scope of permission is as follows:
| Policy name | Permission | Permission scope |
|---|---|---|
| ETFullControlPolicy | Full control permission for ET management | Query physical dedicated line list, view physical dedicated line details, query dedicated channel list, query dedicated channel details, query dedicated channel BFD, create dedicated channel, update dedicated channel, enable/disable IPv6, update channel associations, delete dedicated channel, resubmit channel for review, create dedicated channel BFD, modify dedicated channel BFD, delete dedicated channel BFD, update dedicated line information, create dedicated line, delete dedicated line |
| ETOperateAccessPolicy | ET operations permissions | Query physical dedicated line list, view physical dedicated line details, query dedicated channel list, query dedicated channel details, query dedicated channel BFD, create dedicated channel, update dedicated channel, enable/disable IPv6, update channel associations, delete dedicated channel, resubmit channel for review, create dedicated channel BFD, modify dedicated channel BFD, delete dedicated channel BFD, update dedicated line information |
| ETReadAccessPolicy | Permissions for read-only access to ET | Query physical dedicated line list, view physical dedicated line details, query dedicated channel list, query dedicated channel details, query dedicated channel BFD |
Custom Policy
Enable permission management for all ET resources and specific resources, with permission scope aligned to system policies
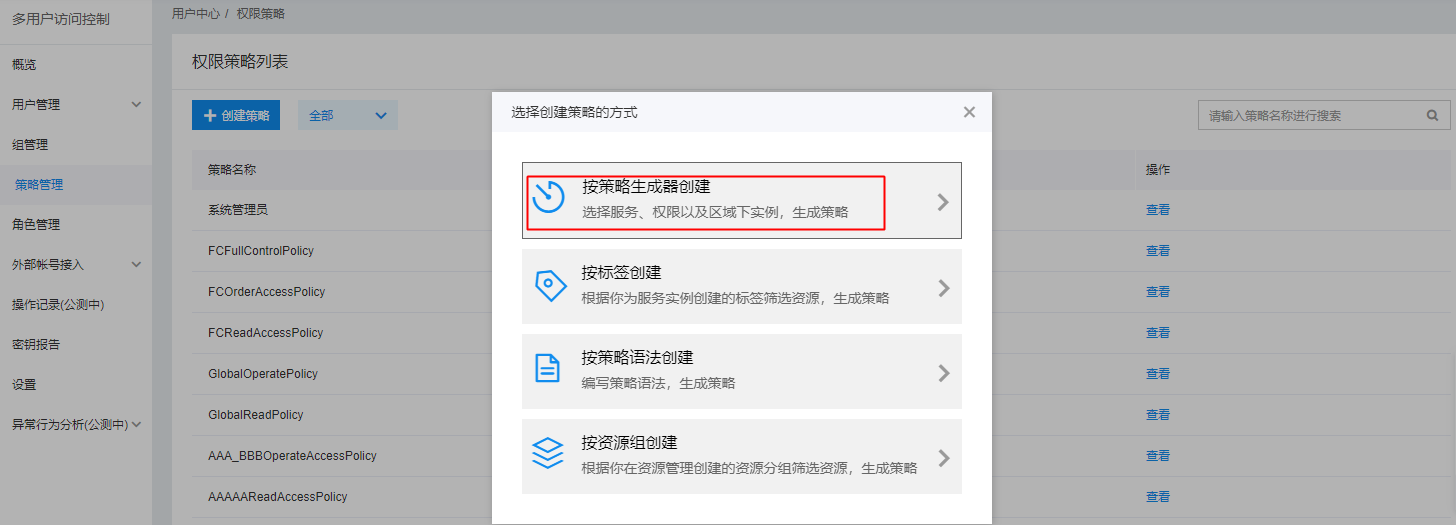
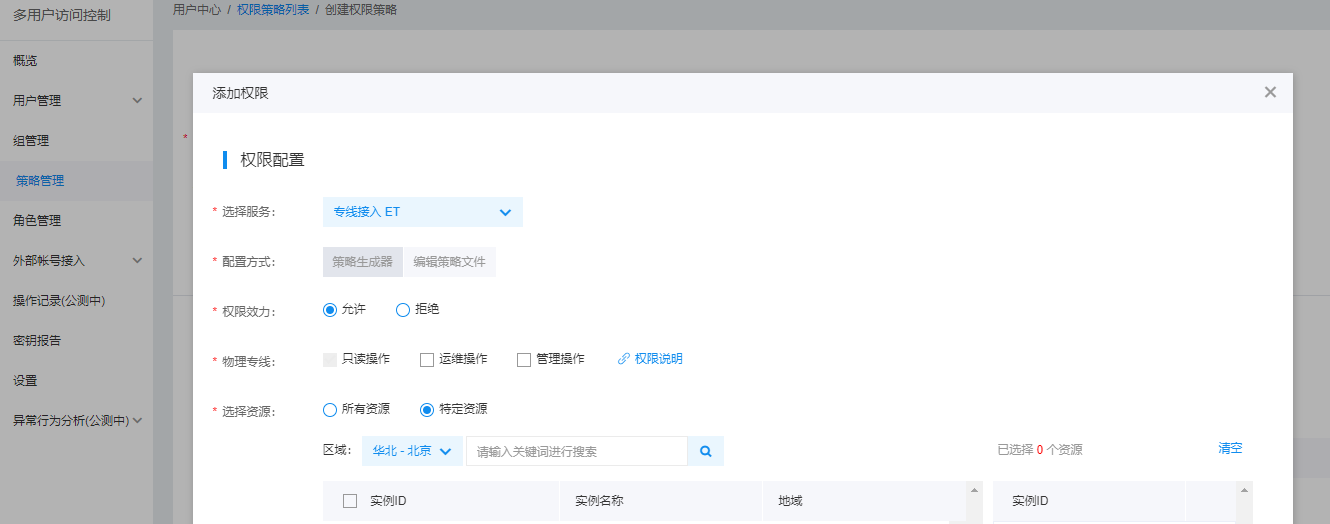
User Authorization
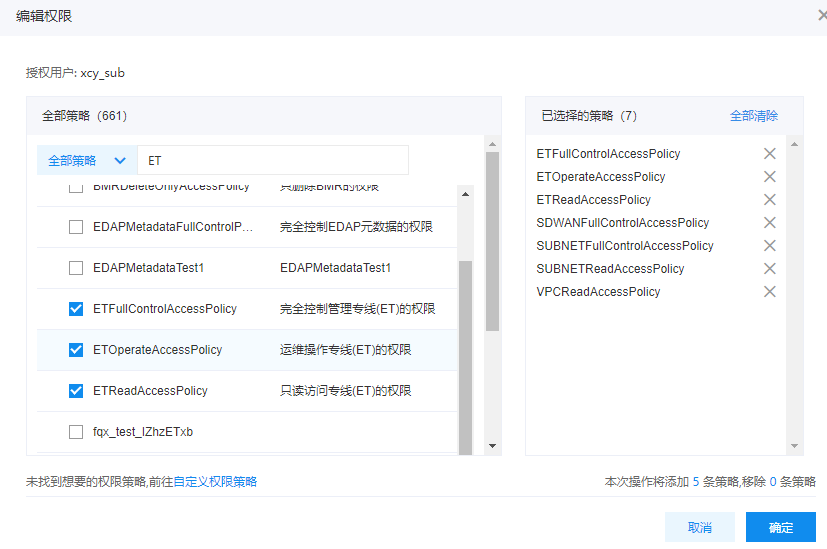
On the User Management -> IAM User management list page, find the desired IAM user and click Add Permission in the Operations column. Then, authorize the user using either a System Policy or a Custom Policy.
Sign in as IAM User
After the root account authorizes the IAM user, it can share the login link with the IAM user. The IAM user can then access the root account's management console via this link and operate or view the root account's resources based on the granted policies.

For other detailed operations, refer to: Identity and Access Management.
