Access Logs
Updated at:2025-10-16
BLB supports Layer 7 (HTTP/HTTPS) access log collection. Access logs can help you understand client requests, analyze user behavior, and assist in troubleshooting. After enabling the Log Service, we will push your original access logs to the Baidu AI Cloud Object Storage (BOS) bucket you selected. BOS ensures permanent log retention and facilitates log management, download and analysis. Before configuring access logs, you need to ensure the following:
- A Layer 7 load balancer has been successfully created.
- The BOS service has been successfully activated.
Cost description: Regarding the billing for the access log feature, the load balancer side does not charge currently, while BOS charges according to BOS Billing Rules.
Configure access logs
- Log in to Baidu AI Cloud Platform, navigate to Products & Services > Baidu Load Balance (BLB), and click on the BLB instance name to access the BLB Instance Details page.
- In the left navigation bar, click on Logs to open the Log Configuration page.
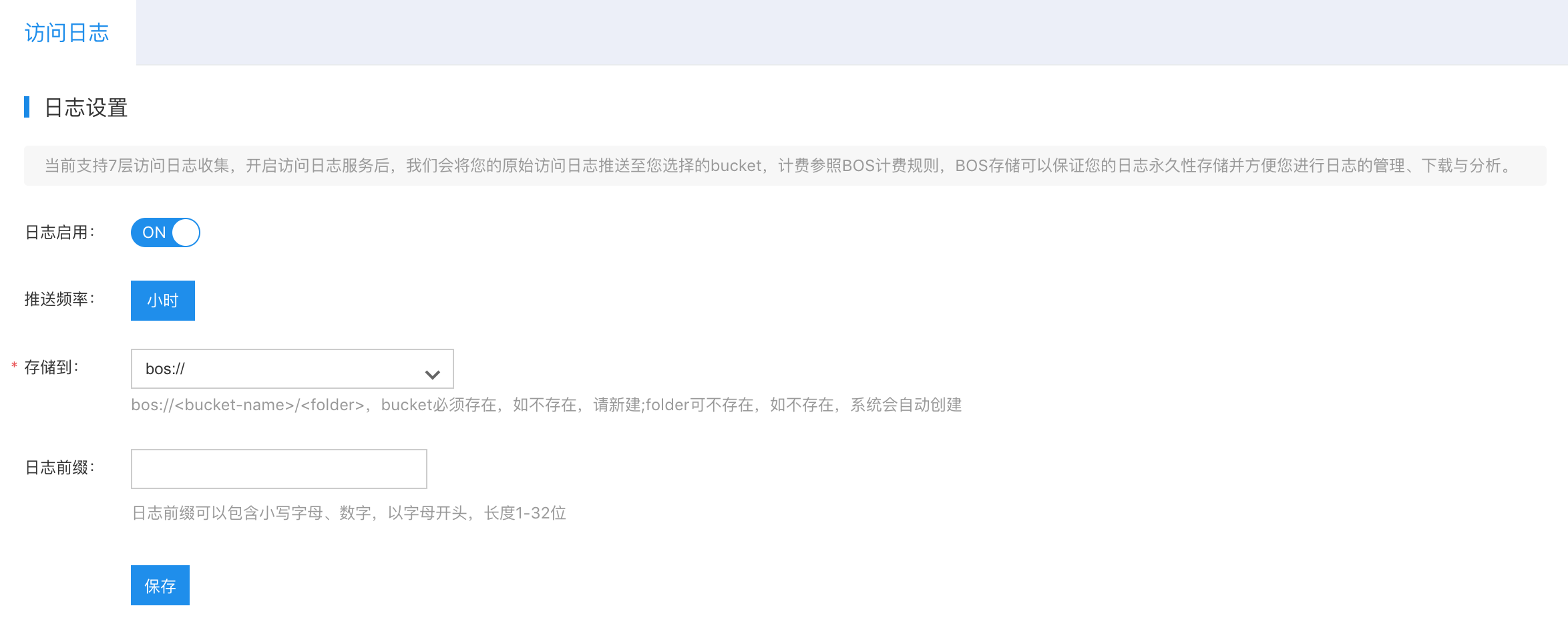
- Fill in the following configuration information:
| ConfigMap | Description |
|---|---|
| Store to | Required. The bucket must exist; if not, create a new one. The folder may not exist; if it does not exist, the system will automatically create it |
| Log prefix | Optional. The log prefix is customizable. |
- Click Save to finalize the log configuration.
- Once the load balancer access logs are configured, you can download and view them in BOS.
| Field | Types | Description |
|---|---|---|
| time_local | string | Record the time of access logs |
| vip | string | BLB IP |
| vport | int | BLB listener port |
| response_status | int | Status code of BLB response message |
| vdum_ups_id | string | ID of server group accessed by traffic |
| upstream_addr | string | Address of real server accessed by traffic |
| upstream_status | string | Response code of real server accessed by traffic |
| remote_addr | string | The remote client IP establishing connection with the BLB. If BGW does not enable cip_forward, it will be the BGW BIP. |
| cip | string | The remote client IP establishing connection with BLB |
| cport | int | The remote client port establishing connection with BLB |
| server_addr | string | Virtual server IP of the accessed BLB |
| server_port | int | Virtual server port of the accessed BLB |
| scheme | string | Protocol type (HTTP/HTTPS) |
| host | string | Domain name |
| request | string | Request line information |
| request_length | int | Request length |
| body_bytes_sent | int | Bytes of sent responses |
| http_referer | string | The refer header content in the request message received by the BLB |
| http_user_agent | string | The user-agent header content in the request message received by the BLB |
| http_x_forwarded_for | string | The x-forward-for content in the request message received by the BLB |
| upstream_connect_time | float | Connection establishment time between BLB and real servers |
| upstream_response_time | float | The time taken by BLB to forward a request to the real server and receive a response from the real server |
| request_time | float | The time taken by BLB to receive a request from the client and return a response to the client |
| ssl_handshake_time | float | SSL handshake time |
| ssl_session_reused | string | Indicate whether SSL session is reused. r means reuse, and . means no reuse. |
| vdum_rs_proto | string | Real server protocol type |
| upstream_local_addr | string | BLB service nodes use internal IPs, which require no attention from users |
| dylimit_id | string | BLB instance ID |
| dylimit_status | string | The rate limiting status of a BLB instance. 0 indicates no rate limiting, and 1 indicates rate limiting. |
| dylimit_raw_qps | long | The QPS of the BLB instance at the current service node. It is displayed as 0 when no rate limiting is applied. |
| dylimit_token | long | Count of QPS tokens of the BLB instance at the current service node. It is displayed as 0 when no rate limiting is applied. |
