Using File Systems Across Regions Or Accounts
Problem background
In some scenarios, users may need to use file systems across different accounts and regions. Typical cases include the following:
- A user has multiple Baidu AI Cloud accounts, and one account has purchased CFS and wants to share it with another account;
- A user who has purchased a file system in one region and wants to access it from another region.
This usage method is generally not recommended due to the reliance on connecting networks across accounts or regions to address such needs. While this enables file system usage, it may pose data security risks and impact access performance. If this requirement is necessary, follow the steps outlined in this document.
Basic principles
The method introduced in this document uses the “VPC Peering Connection” feature of VPC. For detailed introductions to this feature, please refer to Document 1 and Document 2.
Steps for using file systems across regions
For example, suppose cross-region access to a file system is needed between "North China - Beijing" and "South China - Guangzhou." The file system is created in "South China - Guangzhou," and the VPCs requiring connection are named "test_vpc_bj" (Beijing) and "test_vpc_gz" (Guangzhou).
Select either the North China - Beijing or South China - Guangzhou region, and create a peering connection for the VPC
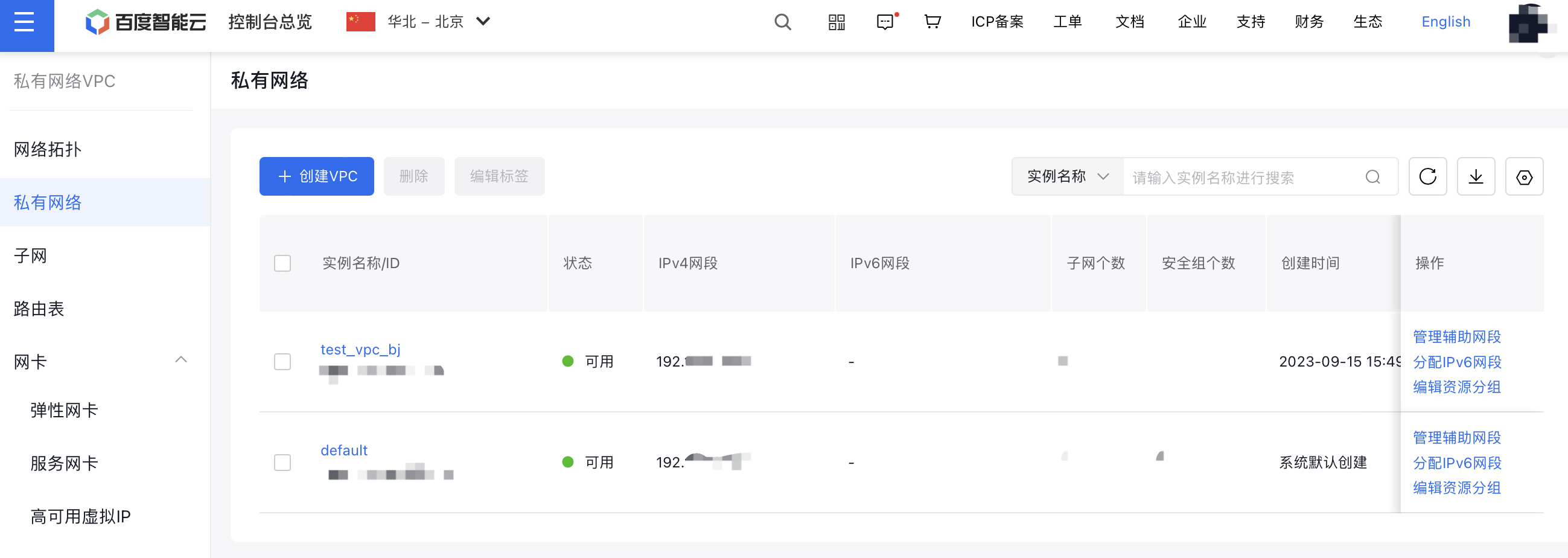
- Access the VPC instance management interface and select test_vpc_bj:
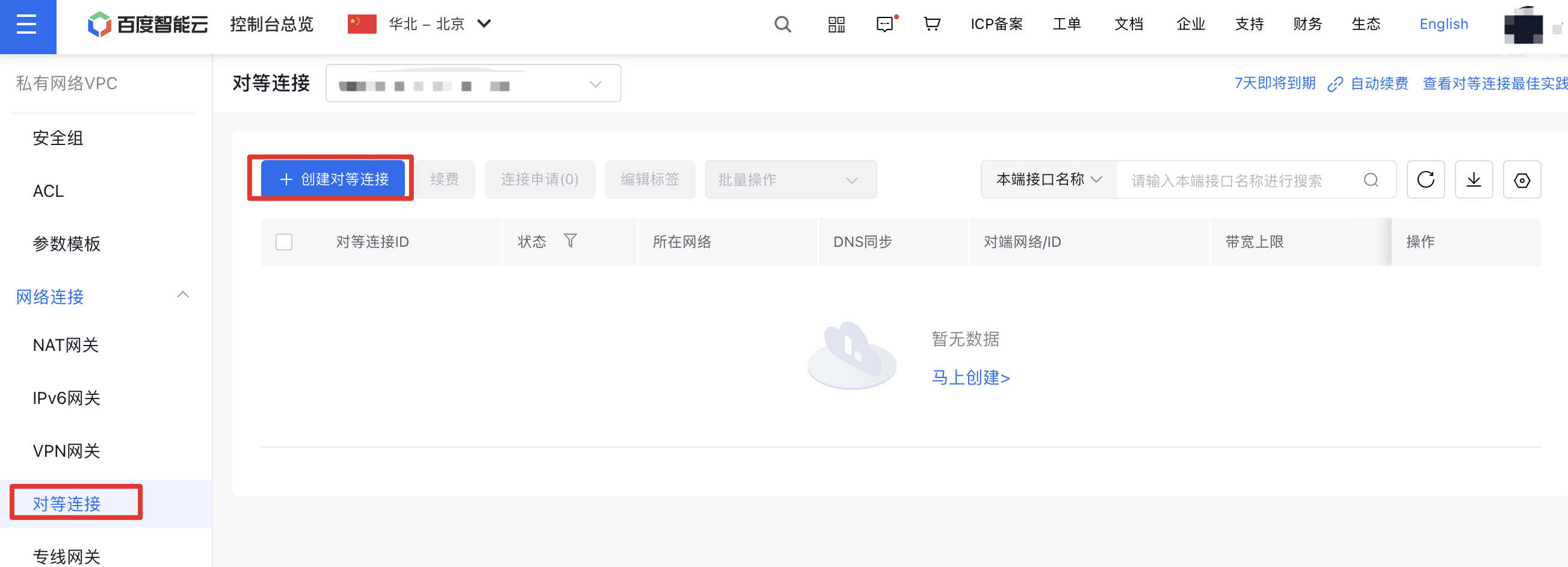
- On the Peering Connections page, click Create Peering Connection:
- Select Same Account as the connection type, then choose the peer region and VPC, and set the maximum bandwidth:
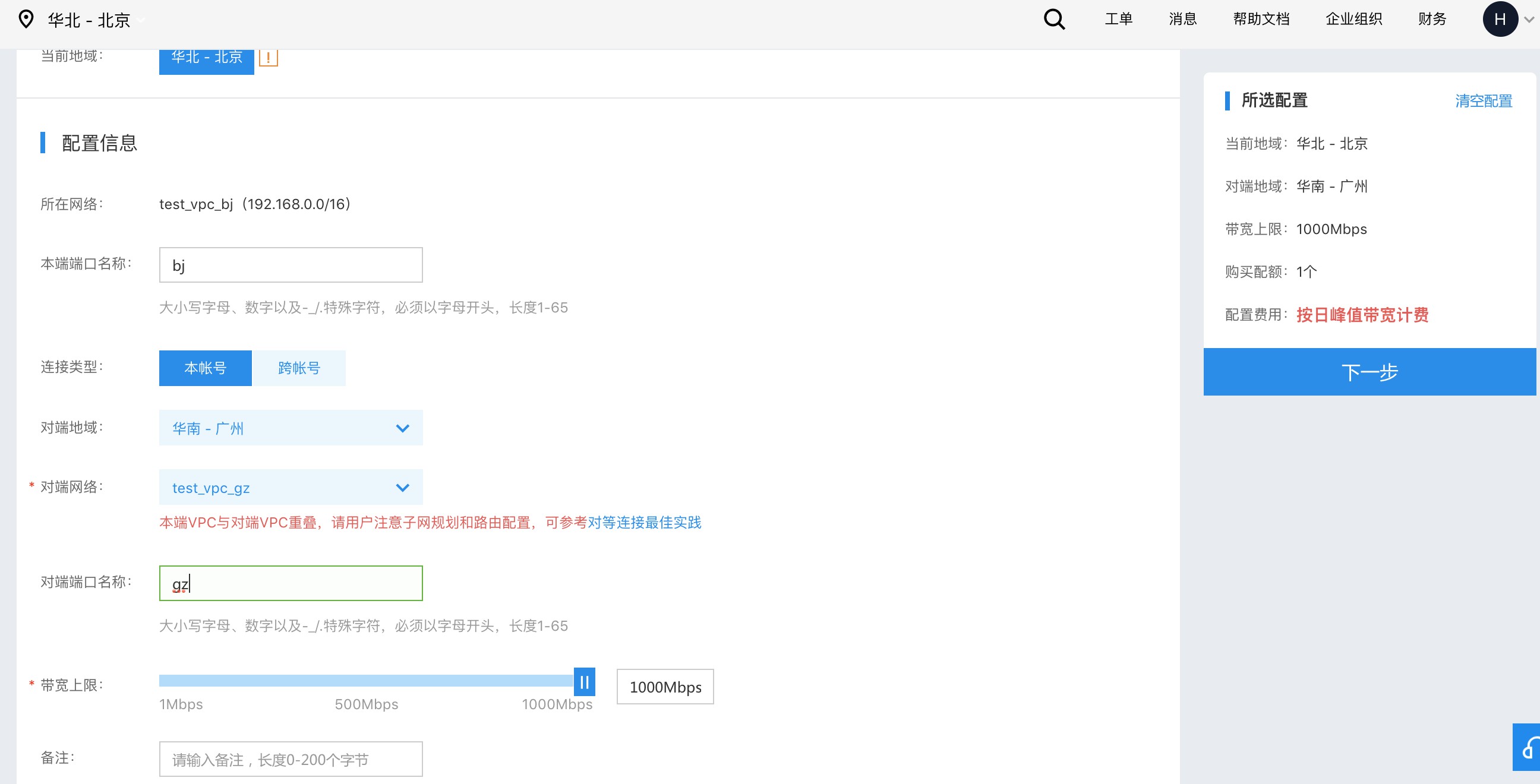
Note: If the CIDR blocks of the local VPC and the peer VPC overlap, ensure that the subnet segments of the virtual machines do not overlap, as this will lead to network conflicts.
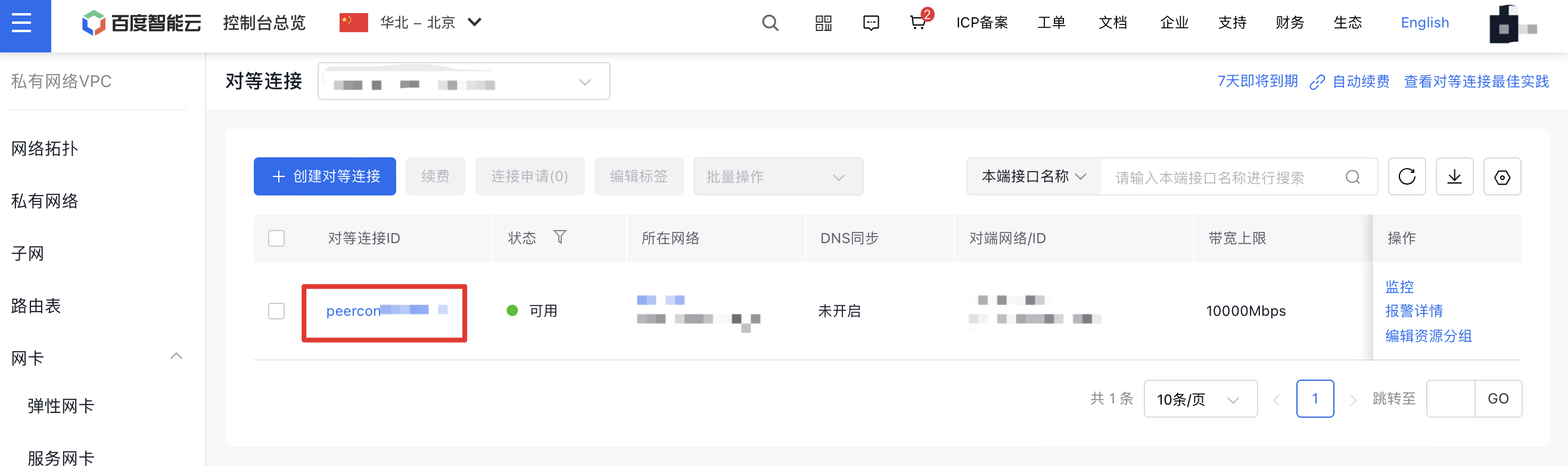
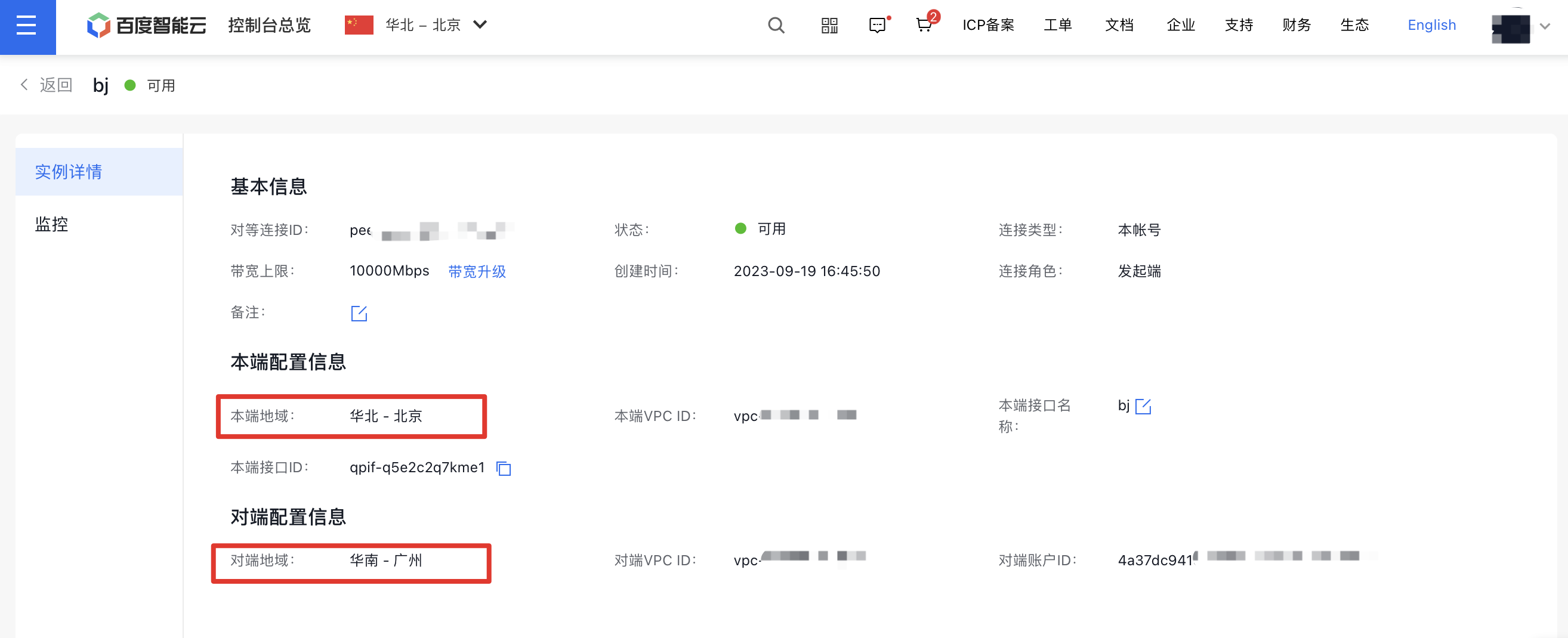
- After successful creation, click the peering connection ID to access the details page, where you can view information such as the local region and the peer region.
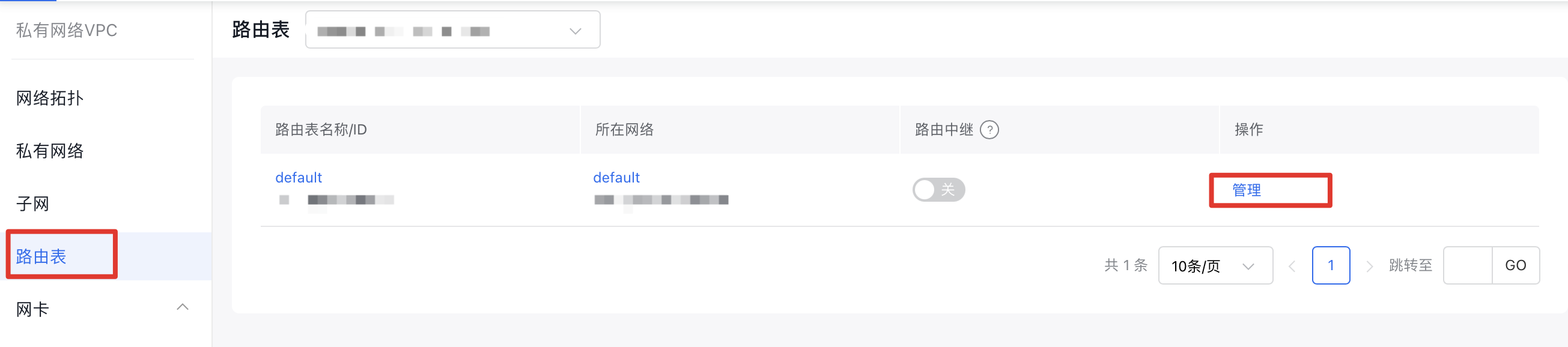
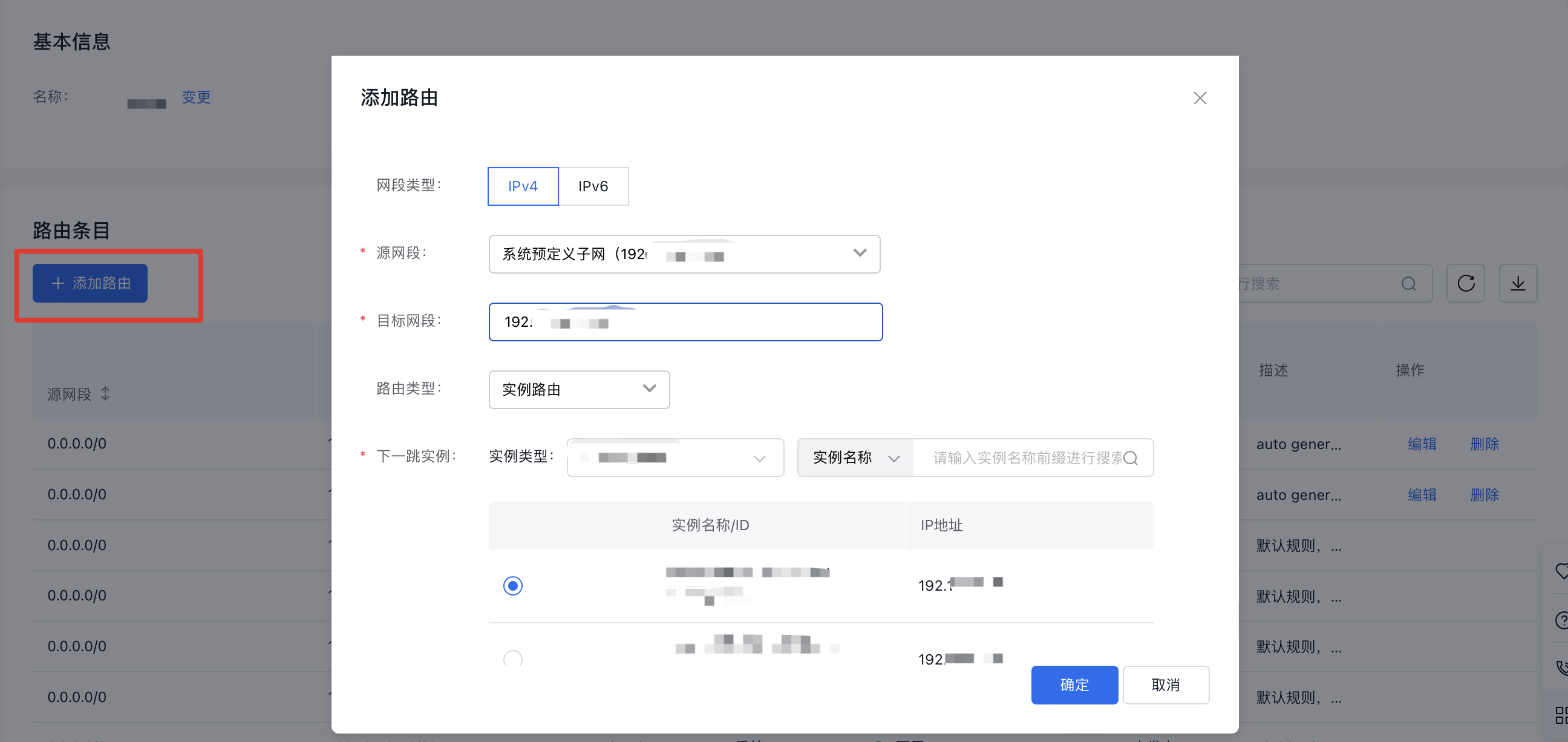
- Add routing rules for the VPCs in the two regions. The destination of each rule should be the peer VPC segment or subnet segment:
- Once the peering connection is established, you can ping the private IP address of a VM in the peer region's VPC from a VM in the local region's VPC to verify network connectivity. If the connection fails, review the security group rules.
(Recommended) Enable DNS Synchronization, and use the mount target address to mount the file system across regions
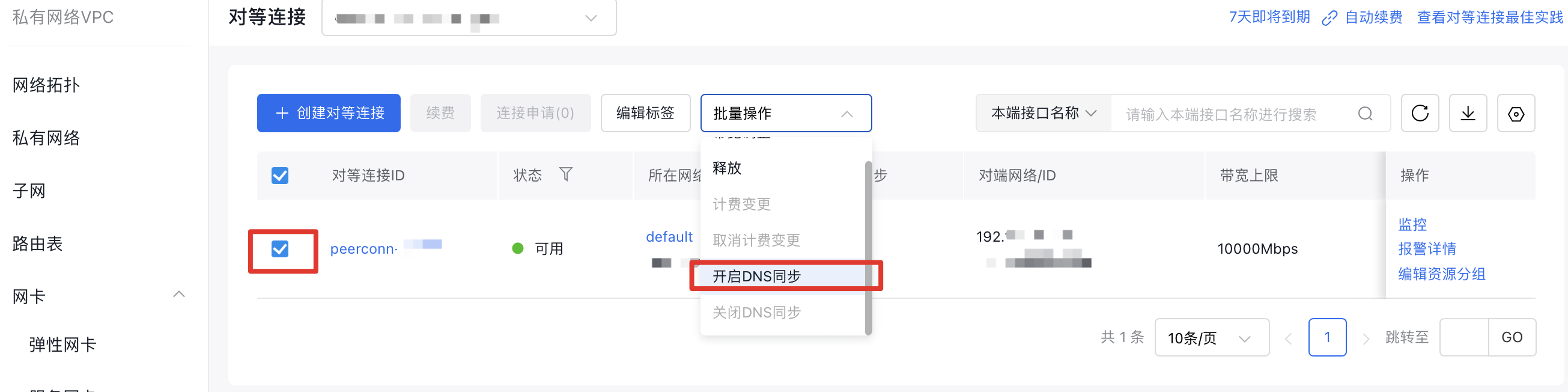
- Enable DNS Synchronization for the peering connection:
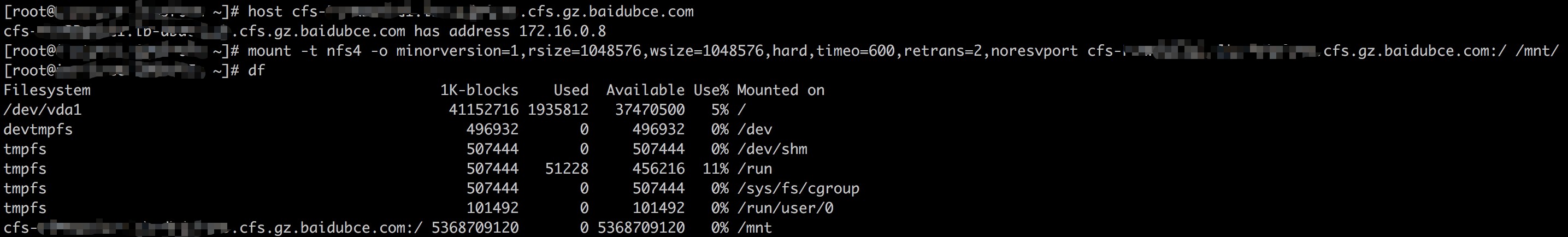
- After confirming that the mount target address is reachable from the VM, mount the file system:
(Optional) Disable DNS Synchronization, and use the mount target address to mount the file system across regions
If you cannot enable DNS Synchronization for the peering connection due to special reasons, you can mount the file system directly using the IP address.The risk of this method is that after a mount target is deleted, its IP address may be occupied by other newly created mount targets or services. This could lead to accessing the wrong file system or service, so use it with caution.
- On a VM in the region where the file system is located, use the
hostcommand to resolve the IP address corresponding to the mount target address:

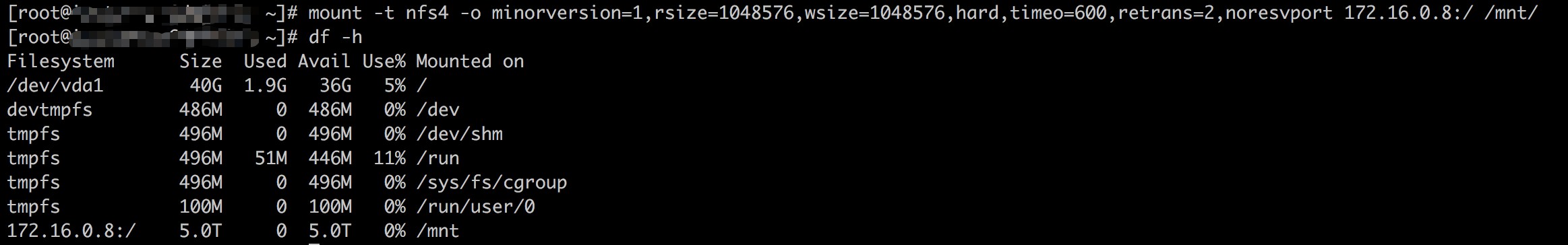
- On a VM in the other region, mount the file system using the resolved IP address:
Steps for using file systems across users
The process for using a file system across accounts is almost identical to the steps for cross-region mounting, except for the establishment of a "Peering Connection.\
On the Create Peering Connection page, select Cross-Account as the type, then provide the Peer User ID and Peer Network (e.g., VPC ID).
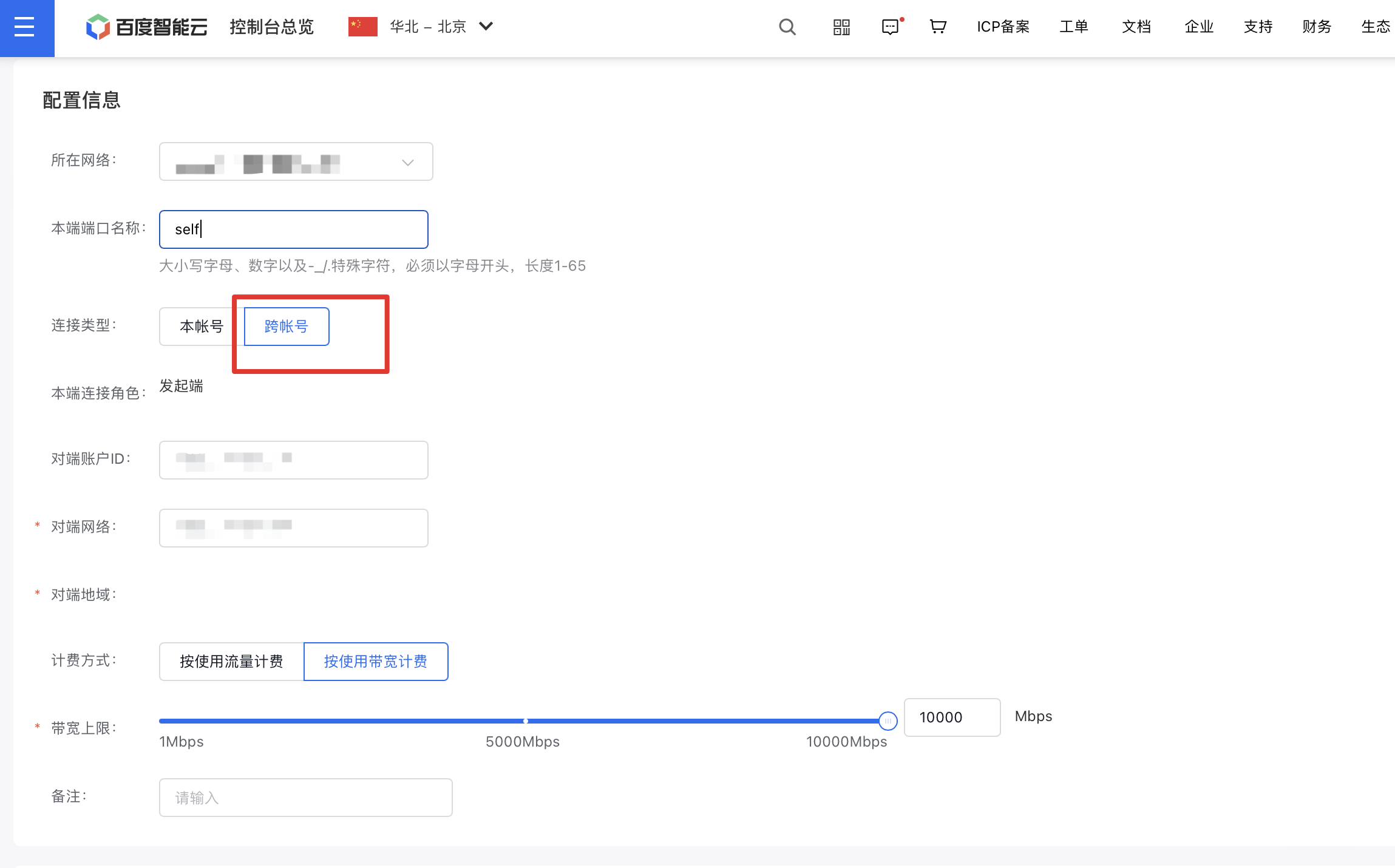
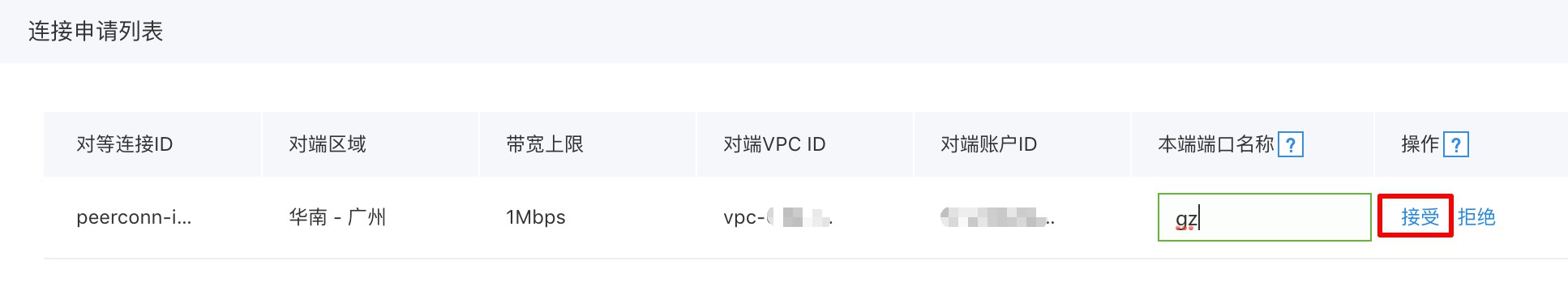
After creating the peering connection, sign in to the other user’s account. On the Peering Connections management page of the corresponding VPC, you will see a Connection Request:
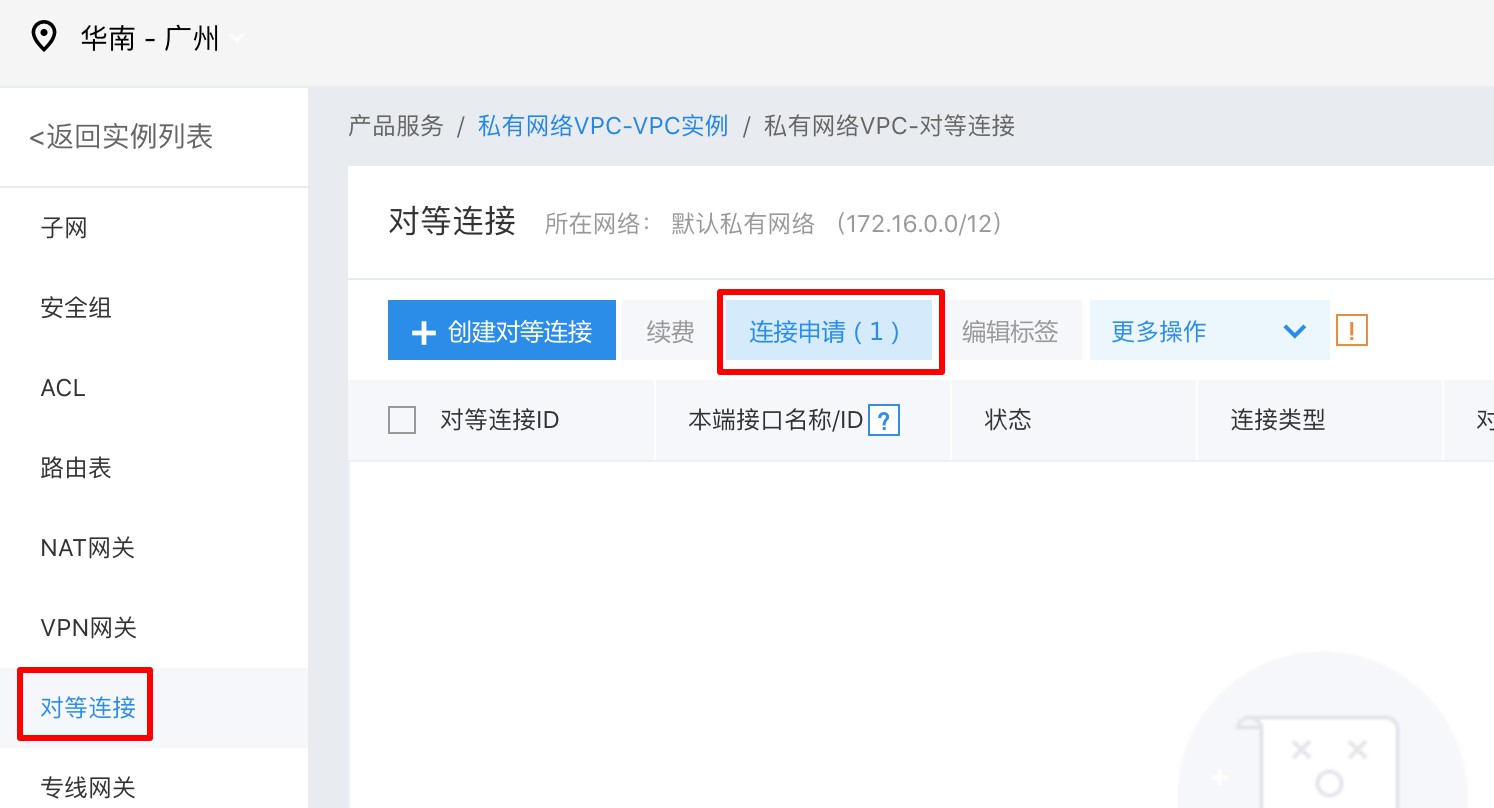
Accept the connection request. The remaining steps are the same as those for cross-region usage: