Mount and Unmount SMB Protocol CFS on Single BCC
When you create a CFS SMB file system, you must mount it on Baidu Cloud Compute (BCC) to provide shared access across multiple BCC instances. This document details the process for mounting a CFS SMB file system using a Linux BCC instance.
Prerequisites
- The target BCC instance (Linux) has been created for mounting the CFS file system. For BCC creation methods, refer to: Quick Configuration of Linux Cloud Servers.
- An SMB file system has been created with a mount target added. For detailed steps, refer to: Create File System, Add Mount Target.
Mounting steps
Step I: Obtain domain name of a mount target
Once the mount target has been created, you can start using the file system. Click the Manage button in the operation toolbar of the file system list to access the mount target information page, as demonstrated below:
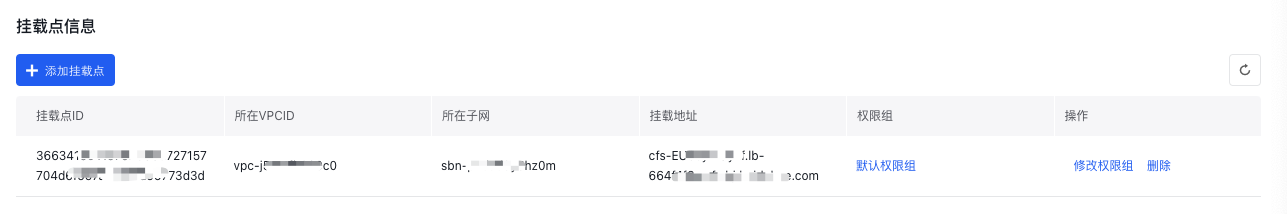
After logging into the virtual machine or container, use the mount target’s domain name to perform file system operations.
Step II: Install SMB client
Most Linux operating systems do not include an SMB client by default, so you need to manually install the SMB client before mounting the file system. Log in to Baidu Cloud Compute (BCC) and execute the command to install the SMB client.
- For CentOS/RHEL OS, run the following command:
1yum install cifs-utils- For Ubuntu/Debian OS, run the following command:
1apt-get install cifs-utilsStep III: Mount SMB file system
Execute the following command to mount an SMB file system:
1mount -t cifs -o vers=3.0,guest,mfsymlinks,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,cache=strict
2 //<Domain name of a mount target>/cfs <client local path>Description:
- <Domain name of a mount target> is available in the file system’s mount target list (refer to Step I).
- <Client local path> refers to the client’s local path for mounting. It must be an absolute path beginning with / (e.g., /mnt/cfs) and must already exist prior to mounting.
Parameters in the command are explained in the table below:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| vers | The SMB protocol supports major versions including 1.0, 2.0, 2.1, and 3.0. Because some advanced SMB versions are not fully supported by the Linux kernel, version 3.0 is recommended (and is used by default when the "vers" option is not specified). |
| rsize | Specify the maximum byte size a client’s file read request can retrieve. Setting this value too low will reduce read throughput. Recommended value: 1048576. |
| wsize | Specify the maximum byte size a client’s file write request can transmit. If this value is too low, write throughput will be negatively affected. Recommended value: 1048576. |
| guest | SMB now supports guest mounting for identity authentication and file access. |
| mfsymlinks | Symbolic link functionality is supported. |
| cache | Configure whether to use the SMB client cache, with options: strict and none. If not configured, the default value is strict, meaning the client cache will be used. |
Example:
1mount -t cifs -o vers=3.0,guest,mfsymlinks,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,cache=strict
2//cfs-***.lb-b768ef66.cfs.bj.baidubce.com/cfs /mnt/smb_dirStep IV: View mounted SMB file systems
After mounting, use the following command to view mounted file systems:
1cat /proc/mountsTo view the file system capacity information, use the following command:
1df -hUnmounting steps
- Sign in to the Baidu Cloud Compute (BCC) where the CFS file system is mounted.
- Use the "umount" command to detach the file system.
1umount <target path>
2 ## Among them, <target path> refers to the local path of the CFS file system to be unmounted- Execute the
mount -lcommand to check the unmounting result. If the mounted CFS file system information is not found in the echo, it means the file system's mount directory has been successfully unmounted.
