Create Transmission Task
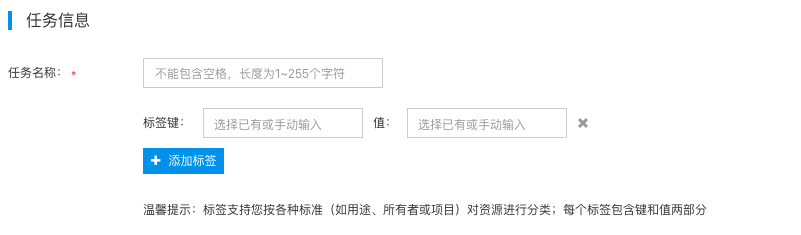
Task Information
- On the Log Service page, click Transmission Task to enter the Transmission Task List page, and then click Create Transmission Task to enter the Create Transmission Task page.
- In the Task Information section, enter the task name.
- Add tags to this task to facilitate category management and searching.
Destination location settings
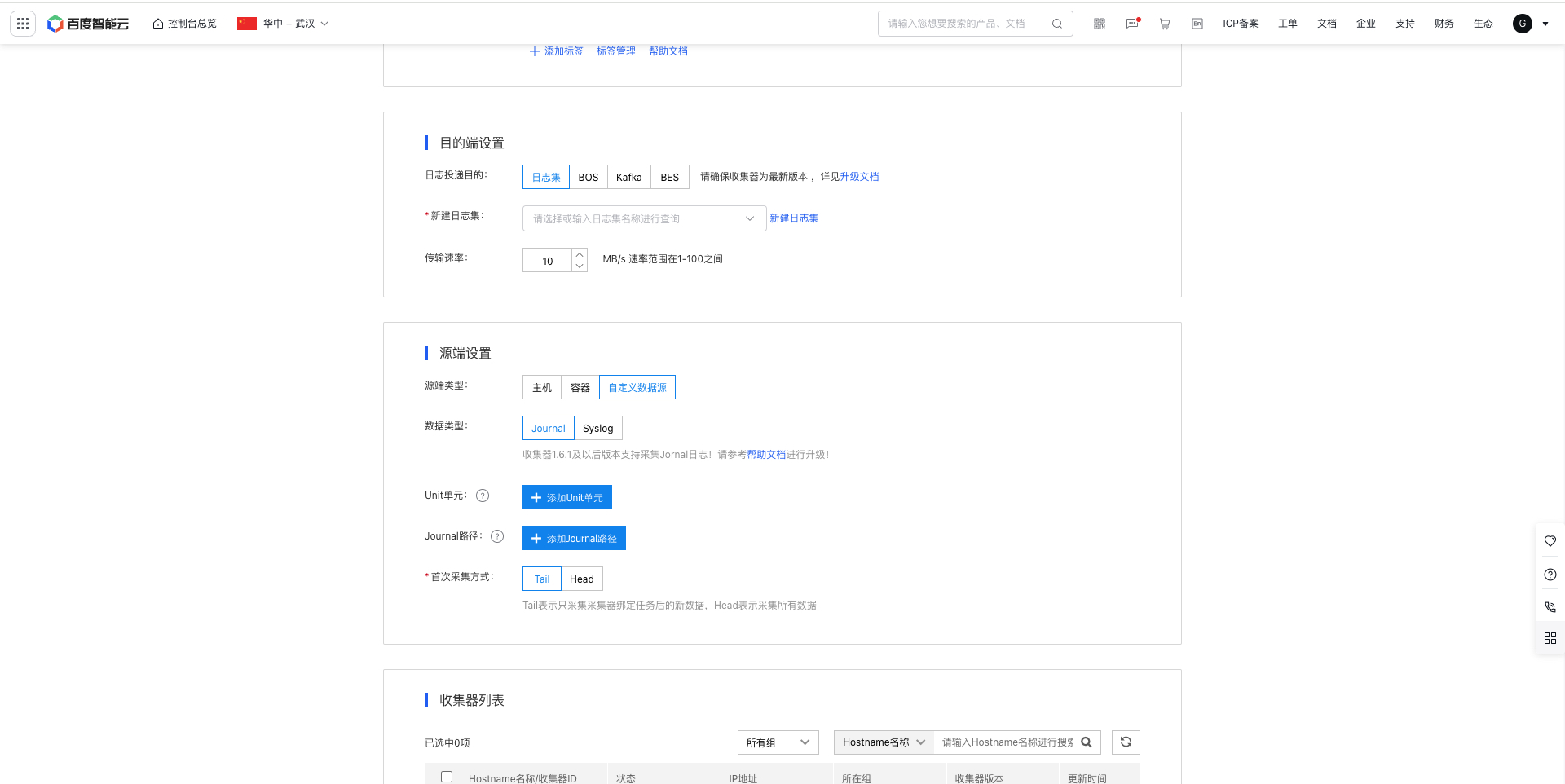
- Set log data delivery destination locations in Destination Location Settings. The product currently offers four destination locations: LogStore, KAFKA, BOS and BES. The specific parameters for each are configured as follows:
(1) LogStore as the destination location

- LogStore: Select an created LogStore; for LogStore function, please refer to LogStore
- Transmission rate: 10 MB/s by default, supported rate range: [1-100] MB/s.
(2) BOS as the destination location

Select BOS as the log delivery destination, do not support log content resolution Note: When the source location is offline files, each file is uploaded as a BOS object. When the source location is real-time files, the collection interval can be customized, and the collected content is generated as a BOS object. Please configure the following parameters:
- BOS path: Choose a BOS path as the destination for storing logs.
-
Log aggregation: Decide whether to aggregate logs in directories based on “time” or “host” configurations. Multiple options can be selected simultaneously.
- Time-based aggregation: Choose the time format included in the source log filenames (e.g., “yyyy-MM-dd”) and select one of the following aggregation methods: daily, hourly, or custom aggregation. If "Custom Aggregation" is selected, configure the date wildcards according to the provided prompts. The system will organize logs in the specified BOS path using the defined date wildcards.
- Host-based aggregation: Aggregate logs by host IPs or hostnames.
- Transmission rate: 10 MB/s by default, supported rate range: [1-100] MB/s.
-
Data compression: Choose whether to enable the function of compressing log files before transmission. It is disabled by default. If it is enabled, select a compression algorithm. The characteristics of each algorithm are as follows:
- Gzip: Offers a high compression ratio that effectively saves space but has slower compression speeds and higher CPU usage when compared to Snappy and Lzop.
- Snappy: Provides faster compression speeds but a lower compression ratio than Gzip.
- Lzop: Delivers fast compression speed, slightly slower than Snappy, but provides a better compression ratio than Snappy.
- Bzip2: Operates at a slow compression speed.
- Real-time file processing policy: For real-time file collection, the Log service allows configurable collection intervals to reduce the creation of many small files in BOS. This policy does not apply to offline files, which will always be collected in real time.
- Transmission notification: The transmission notification feature can only be used during time aggregation for offline log sources. It is off by default. When enabled, the system creates an empty file with a “.done” suffix in the BOS destination directory after each file transmission, making it easier for downstream services to begin processing based on the markers. Details are as follows:
(3) KAFKA as the destination location

Support transmitting logs to dedicated Kafka. For dedicated Kafka usage, refer to Dedicated Kafka.
- Cluster: Choose an existing Kafka cluster.
- Topic: Select an existing Kafka topic.
- Authentication protocol: Select the correct protocol provided by the Kafka cluster based on your agent and cluster network environment. Refer to Cluster Endpoints for details
- Connection address: Choose an address compatible with the certification protocol.
- SASL mechanism: Choose the SASL mechanism compatible with the certification protocol.
- Username: Please input the certified username to access the cluster.
- Password: Please input the certified user's password to access the cluster.
- Data discard: Disabled by default. When enabled, messages larger than 10 MB will be discarded.
-
Data compression: Choose whether to enable the function of compressing log files before transmission. It is disabled by default. If it is enabled, select a compression algorithm. The characteristics of each algorithm are as follows:
- Gzip: Offers a high compression ratio that effectively saves space, but has slower compression speeds and higher CPU usage compared to Snappy and Lz4.
- Snappy: Provides faster compression speeds but a lower compression ratio than Gzip.
- LZ4: Offers high compression speed, slightly slower than Snappy, but with a slightly better compression ratio than Snappy.
- Partitioner type: Default is set to Random; Hash by Value can be selected for message deduplication.
- Message key: Default is set to None. It can be modified to options like Source Location Host HostName or Source Location Host IP.
- Transmission rate: With data compression enabled, the data transmission rate limit is 1 MB/s; with data compression disabled, the limit is 10 MB/s.
(4) BES as the destination location

Select BES as the logshipper destination to transmit real-time logs. Configure the following parameters:
- Select ES cluster: Choose the BES cluster currently available in the current region.
- Username: Enter the login username for the selected BES cluster
- Password: Enter the login password for the selected BES cluster
- Connectivity Test: Verify the connection to the selected BES cluster. Transmission tasks won't function properly if the connection fails.
- Index Prefix: The index prefix is user-defined. If index rolling is enabled, the index name in the BES cluster will be “index prefix + collection date”; if disabled, the index name will only comprise the index prefix. The collection date refers to the date when data is written to BES, formatted as YYYY-MM-DD.
- Index Rolling: Set how often the BES cluster will generate a new index automatically. By default, it is disabled. When enabled, a new index will be created at the configured frequency, and incoming log data will be written to the new index.
Source location settings
- Add the source location settings. The product offers three types of source locations: “Host”, “Container”, and “Custom Data Source”:
- Host: Suitable for collecting both real-time and offline log files.
- Container: Suitable for collecting text logs and stdout logs generated within containers.
- Custom data source: It supports journal log collection and syslog log collection
The detailed configuration process is as follows.
(1) Configuration with “host” as the source location

When the source location type is “Host”, the following special configuration items apply:
- Source log directory: Enter the source directory for log collection. Directories support golang Glob pattern matching. For details, see Directory Rules.
- File matching rule: Enter a regular expression. Files matching with the regular expression will be monitored and collected. Common regular expression syntax and writing examples are as follows:
| Symbols | Description |
|---|---|
| . | Match any character except line breaks |
| \w | Match letters, numbers, or underscores |
| \s | Match any blank character |
| \d | Match numbers |
| \b | Match the prefix or suffix of a word |
| ^ | Match the prefix of a string |
| $ | Match the suffix of a string |
| * | Repeat zero or more times |
| + | Repeat once or more times |
| ? | Repeat zero or once |
| {n} | Repeat n times |
| {n,} | Repeat n or more times |
| {n,m} | Repeat n to m times |
| [^a] | Match any character except a |
| [^abc] | Match any character except abc |
| (?!abc) | Deny the prefix to exclude the abc string |
| \D | Match any non-numeric character |
| \S | Match any non-blank character |
1Example:
21.Match all files ending with .log: .*.log$
32.Match specific file like service1.log: ^service1.log$
43.Match multiple log files like service1 or service2: ^(service1|service2).log$
54.Match all log files except service3: ^(?!service3.log$).*.log$
65. Match files like service.log.2016-01-01_123 with date and incremental suffix numbers: ^\w*.log.\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}_\d*$- Exclusion File Rules: Enter a regular expression. Files matching the pattern will not be monitored or collected. Files actively being written can be excluded to prevent transmission errors. Refer to the file matching rules above for specific rule examples.
- Metadata collection: Add metadata uploaded along with logs. Hosts support custom environment variables, displays them in the @tag_Metadata format in LogStore logs and displays in JSON format in Kafka and BES!
- Directory Recursion: Disabled by default. When enabled, up to 5 active files that match the file rules within the specified directory (including subdirectories) can be transmitted concurrently. Note: Enabling directory recursion increases CPU usage.
- Valid File Period: The range is 1–90 days, with a default of 3 days. By default, files created or modified within 3 days before task creation and afterward are collected. The maximum retroactive period is 90 days.
(2) Configuration with “container” as the source location
When the source location type is “Container”, both stdout and internal logs of containers can be collected. Specific configuration items are as follows:
(2.1) Log type is stdout logs

-
Metadata collection: Support fixed metadata, custom Labels, and custom environment variable collection
Note:
When the destination location is a logStore: Fixed metadata of the container in agent version 1.6.1 and above supports custom configurations, with added custom Label configurations. Versions prior to 1.6.1 collect fixed metadata by default and do not support custom Labels - modified two items will not take effect. To utilize new capabilities, please refer to Help Document to upgrade the corresponding agent version
When the destination location is Kafka or ES: Fixed metadata of the container in agent version 1.6.1 and above supports automatic enabling or disabling, and custom Label configurations are added. For agent versions prior to 1.6.1, if custom environment variables are added, container fixed Labels are automatically collected, but container fixed metadata and custom Label configurations do not take effect. To use new capabilities, refer to Help Document to upgrade the corresponding agent version
- Label Allow List: To configure the allow list, click "Add Allow List" and input both LabelKey and LabelValue (both are mandatory). LabelValue allows the use of regular expressions to match all target containers intended for collection.
-
Label Blacklist: To configure the blacklist, click "Add Blacklist" and input both LabelKey and LabelValue (both are mandatory). LabelValue allows the use of regular expressions to exclude specified target containers.
Note: >- Multiple key value pairs in Label allow list maintain logical relationships of “AND” >- Multiple key value pairs in Label blacklist maintain logical relationships of “OR” >- In the Label allow list and Label blacklist, Labelkey values must be unique, and LabelValue values cannot be empty
- Environment Variable Allow List: To define an environment variable allow list, click "Add Allow List" and input both EnvKey and EnvValue (both are mandatory). EnvValue supports regular expressions to match all target containers for collection.
-
Environment Variable Blacklist: To define an environment variable blacklist, click "Add Blacklist" and input both EnvKey and EnvValue (both are mandatory). EnvValue supports regular expressions to exclude specified target containers.
Note: >- Multiple key value pairs in environment variable allow list maintain logical relationships of “AND” >- Multiple key value pairs in environment variable blacklist maintain logical relationships of “OR” >- EnvKey value in environment variable allow list and blacklist must be unique; EnvValues cannot be empty
- Valid File Period: The range is 1–90 days, with a default of 3 days. By default, files created or modified within 3 days before task creation and afterward are collected. The maximum retroactive period is 90 days.
(2.2) Log type is internal logs of the container

- Source log directory: Enter the source directory for log collection. Directories support golang Glob pattern matching. For details, see Directory Rules. Note: The path within the container shall be filled in the directory here, but be not mounted to the host. Additionally, any parent path of the internal log file of the container must be mounted to the host.
- File matching rule: Enter a regular expression. Files matching with the regular expression will be monitored and collected. Common regular expression syntax and writing examples are as follows:
| Symbols | Description |
|---|---|
| . | Match any character except line breaks |
| \w | Match letters, numbers, or underscores |
| \s | Match any blank character |
| \d | Match numbers |
| \b | Match the prefix or suffix of a word |
| ^ | Match the prefix of a string |
| $ | Match the suffix of a string |
| * | Repeat zero or more times |
| + | Repeat once or more times |
| ? | Repeat zero or once |
| {n} | Repeat n times |
| {n,} | Repeat n or more times |
| {n,m} | Repeat n to m times |
| [^a] | Match any character except a |
| [^abc] | Match any character except abc |
| (?!abc) | Deny the prefix to exclude the abc string |
| \D | Match any non-numeric character |
| \S | Match any non-blank character |
1Example:
21.Match all files ending with .log: .*.log$
32.Match specific file like service1.log: ^service1.log$
43.Match multiple log files like service1 or service2: ^(service1|service2).log$
54.Match all log files except service3: ^(?!service3.log$).*.log$
65. Match files like service.log.2016-01-01_123 with date and incremental suffix numbers: ^\w*.log.\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}_\d*$- Exclusion File Rules: Enter a regular expression. Files matching the pattern will not be monitored or collected. Files actively being written can be excluded to avoid transmission errors. Refer to the file matching rules above for specific examples.
-
Metadata collection: Support fixed metadata, custom Labels, and custom environment variable collection
Note:
When the destination location is a logStore: Fixed metadata of the container in agent version 1.6.1 and above supports custom configurations, with added custom Label configurations. Versions prior to 1.6.1 collect fixed metadata by default and do not support custom Labels - modified two items will not take effect. To utilize new capabilities, please refer to Help Document to upgrade the corresponding agent version
When the destination location is Kafka or ES: Fixed metadata of the container in agent version 1.6.1 and above supports automatic enabling or disabling, and custom Label configurations are added. For agent versions prior to 1.6.1, if custom environment variables are added, container fixed Labels are automatically collected, but container fixed metadata and custom Label configurations do not take effect. To use new capabilities, refer to Help Document to upgrade the corresponding agent version
- Label Allow List: To configure the allow list, click "Add Allow List" and input both LabelKey and LabelValue (both are mandatory). LabelValue allows the use of regular expressions to match all target containers intended for collection.
-
Label Blacklist: To configure the blacklist, click "Add Blacklist" and input both LabelKey and LabelValue (both are mandatory). LabelValue allows the use of regular expressions to exclude specified target containers.
Note: >- Multiple key value pairs in Label allow list maintain logical relationships of “AND” >- Multiple key value pairs in Label blacklist maintain logical relationships of “OR” >- In the Label allow list and Label blacklist, Labelkey values must be unique, and LabelValue values cannot be empty
- Environment Variable Allow List: To define an environment variable allow list, click "Add Allow List" and input both EnvKey and EnvValue (both are mandatory). EnvValue supports regular expressions to match all target containers for collection.
-
Environment Variable Blacklist: To define an environment variable blacklist, click "Add Blacklist" and input both EnvKey and EnvValue (both are mandatory). EnvValue supports regular expressions to exclude specified target containers.
Note: >- Multiple key value pairs in environment variable allow list maintain logical relationships of “AND” >- Multiple key value pairs in environment variable blacklist maintain logical relationships of “OR” >- EnvKey value in environment variable allow list and blacklist must be unique; EnvValues cannot be empty
- Valid File Period: The range is 1–90 days, with a default of 3 days. By default, files created or modified within 3 days before task creation and afterward are collected. The maximum retroactive period is 90 days.
(3) Custom data source configuration
(3.1) Journal logs

- Data source: Journal logs
- Unit: It is empty by default, indicating data from all Units will be collected. Support custom additions and support adding multiple Units
- Journal path: It is empty by default, indicating journal memory data will be collected. Adding a specific journal path indicates that collecting journal persistent data, such as /var/log/journal. Support adding multiple paths
- Initial collection method: Tail is set by defaults, Tail indicates that only new data after a task is bound to the agent is collected. Head indicates that all data is collected. Prompt contents are displayed below the button
(3.2) Syslog logs

- Data type: syslog logs
- Output Source: Required. Default value: tcp://127.0.0.1:9999, indicating only locally forwarded logs can be received. Support custom modifications, format: [tcp/udp]://[ip]:[port].
- Log resolution protocol type:
- Specify the protocol for log resolution (default: no resolution). Support selecting alternative resolution types
- fc3164: Specify protocol for log resolution by using RFC3164
- rfc5424: Specify protocol for log resolution by using RFC5424
- auto: Specify resolution protocol selected automatically by Logtail based on log contents
Processing configuration
- Logs can be further resolved and processed through processing configuration.
(1) Host and container processing configuration
- Sample logs: Optional, but recommended to fill in
- Multi-Line Mode: Enable this setting for multi-line logs and configure a regular expression for the first line. The system will use this regular expression as an identifier for log segmentation.
-
Data processing plugin: None by default, supporting multiple processing plugins to be added, moved up or down, or deleted, and serial processing in sequence.
Note: The combination configuration of data processing plugins requires upgrading to Version 1.6.8 or higher. Older versions support as follows:
- Older versions only support configuring one of the following resolution rules: Json resolution, KV resolution, regular expression resolution or delimiter resolution. Configuring multiple rules will not take effect.
- Older versions support time resolution configuration and filter processing plugins, but they must be placed after Json resolution, KV resolution, regular expression resolution or delimiter resolution to take effect.
- Older versions do not support the field addition and discard plugins.
| Types | Description |
|---|---|
| JSON resolution | Logs in Json format can be resolved  Original field: Default system field @raw, customizable modificationDiscard logs that fail in resolution: When enabled, log data that fails in resolution will be automatically discarded; when disabled, original logs will be uploaded if log resolution fails. Original field: Default system field @raw, customizable modificationDiscard logs that fail in resolution: When enabled, log data that fails in resolution will be automatically discarded; when disabled, original logs will be uploaded if log resolution fails. |
| KV resolution | Extract log fields through KV and resolve logs into key-value pairs  Original field: Default system field @raw, customizable modification Sample logs: Inherit from the external source by defaultRegular expression: Enter regular expression. For the method of configuring regular expression, refer to Syslog log processing configuration belowLog extraction field: Support resolution from sample logs based on resolution rules. Users need to input custom keys and types of value, or add custom fields (resolution is supported when sample log is present in the first position; otherwise, only custom addition is allowed) Discard logs that fail in resolution: When enabled, log data that fails in resolution will be automatically discarded; when disabled, original logs will be uploaded if log resolution fails.Retain original fields: When enabled, the original fields of the logs before resolution will be retained. Original field: Default system field @raw, customizable modification Sample logs: Inherit from the external source by defaultRegular expression: Enter regular expression. For the method of configuring regular expression, refer to Syslog log processing configuration belowLog extraction field: Support resolution from sample logs based on resolution rules. Users need to input custom keys and types of value, or add custom fields (resolution is supported when sample log is present in the first position; otherwise, only custom addition is allowed) Discard logs that fail in resolution: When enabled, log data that fails in resolution will be automatically discarded; when disabled, original logs will be uploaded if log resolution fails.Retain original fields: When enabled, the original fields of the logs before resolution will be retained. |
| Regular expression resolution | Extract log fields through regular expression and resolve logs into key-value pairs  Original field: Default system field @raw, customizable modification Sample log: Inherit from the external source by defaultRegular expression: Enter regular expression. For the method of configuring regular expression, refer to Syslog log processing configuration belowLog extraction field: Support resolution from sample logs based on resolution rules. Users need to input custom keys and types of value, or add custom fields (resolution is supported when sample log is present in the first position; otherwise, only custom addition is allowed) Discard logs that fail in resolution: When enabled, log data that fails in resolution will be automatically discarded; when disabled, original logs will be uploaded if log resolution fails.Retain original fields: When enabled, the original fields of the logs before resolution will be retained. Original field: Default system field @raw, customizable modification Sample log: Inherit from the external source by defaultRegular expression: Enter regular expression. For the method of configuring regular expression, refer to Syslog log processing configuration belowLog extraction field: Support resolution from sample logs based on resolution rules. Users need to input custom keys and types of value, or add custom fields (resolution is supported when sample log is present in the first position; otherwise, only custom addition is allowed) Discard logs that fail in resolution: When enabled, log data that fails in resolution will be automatically discarded; when disabled, original logs will be uploaded if log resolution fails.Retain original fields: When enabled, the original fields of the logs before resolution will be retained. |
| Delimiter resolution | Structure log contents through delimiters and resolve them into multiple key-value pairs  Original field: Default system field @raw, customizable modification Sample log: Inherit from the external source by defaultDelimiter: Choose to separate by spaces, vertical bars, commas or other delimiters, and support custom delimiters Quote: Disabled by default. Choose to use single quotes, double quotes or other quotesLog extraction field: Support resolution from sample logs based on resolution rules. Users need to input custom keys and types of value, or add custom fields (resolution is supported when sample log is present in the first position; otherwise, only custom addition is allowed) Discard logs that fail in resolution: When enabled, log data that fails in resolution will be automatically discarded; when disabled, original logs will be uploaded if log resolution fails.Retain original fields:** When enabled, the original fields of the logs before resolution will be retained. Original field: Default system field @raw, customizable modification Sample log: Inherit from the external source by defaultDelimiter: Choose to separate by spaces, vertical bars, commas or other delimiters, and support custom delimiters Quote: Disabled by default. Choose to use single quotes, double quotes or other quotesLog extraction field: Support resolution from sample logs based on resolution rules. Users need to input custom keys and types of value, or add custom fields (resolution is supported when sample log is present in the first position; otherwise, only custom addition is allowed) Discard logs that fail in resolution: When enabled, log data that fails in resolution will be automatically discarded; when disabled, original logs will be uploaded if log resolution fails.Retain original fields:** When enabled, the original fields of the logs before resolution will be retained. |
| Time resolution | Resolve the log time field. If unresolved, the system time will be used by default  Original field: Default system field @raw, customizable modification Sample log: Inherit from the external source by defaultTime resolution format: If a time resolution format is configured, a specified field in the resolution result will be used as the time field. You need to provide the time resolution format for this field. The system will resolve the log time according to this format. If resolution fails, the system time will be used as the log time. For format writing, refer to this link: SimpleDateFormat. Original field: Default system field @raw, customizable modification Sample log: Inherit from the external source by defaultTime resolution format: If a time resolution format is configured, a specified field in the resolution result will be used as the time field. You need to provide the time resolution format for this field. The system will resolve the log time according to this format. If resolution fails, the system time will be used as the log time. For format writing, refer to this link: SimpleDateFormat.  | | |
| Filter processing | Filter log contents through data expression, only collecting log data that meets the expression requirements  Data expression: Configure data expression, only collecting log data that meets the expression requirements. The syntax supported by expression is as follows: Data expression: Configure data expression, only collecting log data that meets the expression requirements. The syntax supported by expression is as follows:  | | |
| Add field | Customize adding fields and field values in logs  Add field: Customize adding field names and values to each log Add field: Customize adding field names and values to each log |
| Discard field | Configurable discard fields. Fields in the original logs will be discarded  Discard field: Customize discard fields. The configured fields will be discarded. Discard field: Customize discard fields. The configured fields will be discarded. |
(2) Processing configuration of custom data source Syslog
The custom data source Syslog allows further processing configuration for the content field. The specific resolution and processing methods are as follows:
- Resolution failure upload:
- Log resolution type is displayed when a specific log resolution protocol type is selected
- If the Resolution Failure Upload switch is turned on, failed logs will be uploaded by default to the content field upon resolution failure. If it is disabled, logs will be discarded upon resolution failure
-
Content field resolution modes: No Resolution, JSON Resolution, Delimiter Resolution, Full Regular Expression Resolution, and KV Resolution
- No Resolution: Used to collect and transmit raw log data without parsing.
- JSON Mode: Designed for collecting log data in JSON format; supports the resolution of nested JSON structures.
- Delimiter Mode: Converts data into JSON format using specific delimiters. Supports spaces, tabs, vertical bars, and commas as delimiters, along with custom delimiters in any format. The resolved data is displayed as Values in the “Resolution Result” section, requiring users to input Keys corresponding to these Values.
- Full Regular Expression Mode: Input a log data sample and a corresponding regular expression, then click the "Resolution" button. The log data sample will be parsed based on the provided regular expression, and the resolved data will be displayed as Values in the Resolution Results. Users are required to assign custom Keys to these Values.
- The full regular expression mode is generally highly flexible and can be used to resolve and extract some scenarios where log printing is not very standardized. However, it may impact log resolution performance, especially with highly complex regular expressions. This approach should be used with caution in scenarios with extremely large log volume to avoid data delivery delays due to insufficient resolution performance. Below is a specific resolution example to illustrate the usage of full regular expression mode

1Original log in the above context:
22023-08-23T05:54:55,305 [WARN ][com.baidu.bls.Test.java] [12345678-192.168.0.1] took[15.9ms],source[{"size":1000,"query":{"bool":{"must":[{"term":{"deleted":{"value":false,"boost":1.0}}}],"adjust_pure_negative":true,"boost":1.0}}}],id[]
3 Regular expression:
4(\S+)\s\[([A-Z]+\s+)\]\[(\S+)\]\s+\[(\d+)-(\d+.\d+.\d+.\d+)\]\s+took\[(\d+\.*\d*)ms\],source(.*)
5 The matching process is as follows:
6 1. (\S+) matches non-blank strings as the first capturing group and will match the time field 2023-08-23T05:54:55,305
7 in the original text 2. \s\[ matches a blank character and a [ square bracket
8 3. ([A-Z]+\s+) represents the second capturing group for capturing words consisting of capital letters, and will match the WARN
9 in the level field in the original text. 4. \]\[ matches ] and [
10 5. (\S+) matches non-blank strings as the 3rd capture group, which will match the source field com.baidu.bls.Test.java
11 in the original text 6. )\]\s+\[ matches ] and [ along with any possible multiple blank characters in the middle
12 7. (\d+) is the 4th capture group for capturing 1 or more numbers, and will match 12345678
13 of field app_id in the original text 8. - is the delimiter matching between the app_id field and host_ip field
14 9. (\d+.\d+.\d+.\d+) is the 5th capture group, and the IPv4 address corresponds to the host_ip field in the original text
15 10. \]\S+took\[ matches ], multiple blank characters, a word took, and [
16 11. (\d+\.*\d*)ms represents the 6th capture group, and will match the millisecond time consumption in the original text. However, remove the unit to facilitate float value analysis
17 12. \],source matches ], source section
18 13. (.*) is the 7th capture group, and will match 0 or more characters except line breaks as the detail field
19 After matching mentioned in 13 steps above, irregularly formatted log field information can be extracted from the original text- Log Time: Choose between “Use Log Time” or “Use System Time.” If “Use Log Time” is selected, the system will extract time information from the logs and use it. If “Use System Time” is selected, the system will use the time when the logs are uploaded as the log time.
- Specify Time Field Key Name: If “Use Log Time” is chosen above, specify a field from the resolved data to act as the time field. If not, the system time will be used.
- Time resolution format: If “Use Log Time” is selected above and a field from the resolution result is designated as the time field, you must provide the time resolution format for that field. The system will resolve the log time according to this format. If resolution fails, the system time will be used as the log time. For format writing, refer to this link: SimpleDateFormat. Below are several common time resolution formats:
| Time sample | Resolution format |
|---|---|
| 2021-07-04 08:56:50 | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss |
| 2021-07-04 08:56:50.123 | yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS |
| 2001-07-04T12:08:56.235-07:00 | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX |
| 2001-07-04T12:08:56.235-0700 | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ |
| 010704120856-0700 | yyMMddHHmmssZ |
| Wed, 4 Jul 2001 12:08:56 -0700 | EEE, d MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss Z |
- Discard Logs with Resolution Failure: When enabled, logs with resolution issues will be discarded automatically. If disabled, unresolved logs will be passed downstream. This option is not available in “No Resolution” mode.
- Retain the original text: When it is enabled, the original log content before resolution will be retained in the @raw field
-
Data Matching Expression: Leaving this blank means all data will be collected. If filled, only logs meeting the expression criteria will be collected. The supported expression syntax is as follows:
- Field Key is represented by $key
- In logical operators, string fields support = and !=; numeric fields support =, !=, >, <, >=, and <=; boolean fields support !; and &&, ||, (, and ) can be applied between fields
- If operators, brackets, $, or other special characters appear in the regular expression, they must be enclosed in double quotes “”
Example: ($level = "^ERROR|WARN$" || $ip != 10.25.) && (($status>=400) || !$flag) && $user.name = ^B.
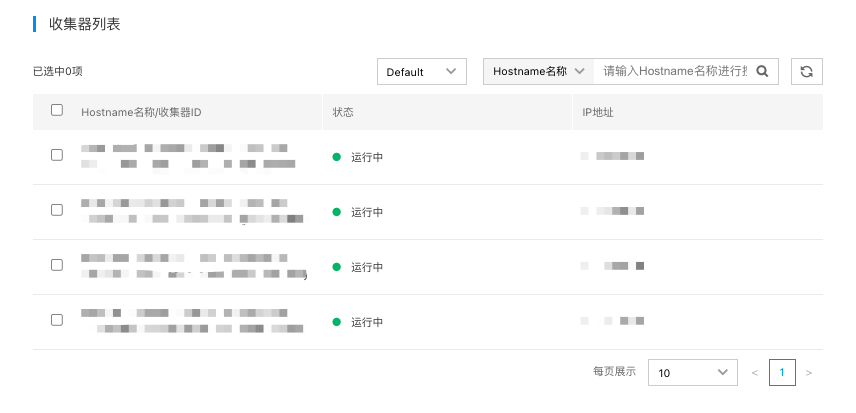
Select the agent
- Select the agents installed on the host. The agent Server will deploy transmission tasks to the selected hosts. As shown below, the list displays hosts in the current Region have installed the collector and are not in a "lost" status.
- Click “Save” to finalize and create the transmission task. The task will become effective approximately 1 minute later.
