Implement URL Forwarding via Nginx
Overview
Set up a URL forwarding server using Nginx's forwarding functionality to implement domain name redirection.
Requirement scenarios
Requirement scenario I: Explicit URL forwarding
This example uses the 301 redirect technology. The outcome is as follows: When you enter http://a.com in the browser's address bar and press Enter, the website displays the content of the target address http://cloud.baidu.com/, and the address bar updates to show http://cloud.baidu.com/.
Requirement scenario II: Implicit URL forwarding
Here, iframe technology and non-redirect methods are used. The outcome is as follows: When you enter http://a.com in the browser's address bar and press Enter, the website displays the content of the target address http://cloud.baidu.com/, but the address bar continues to show http://a.com.
Implementation overview
Currently, users must manually set up an Nginx server or cluster and configure the domain name's resolution IP at the registrar to point to the address of the custom-built Nginx server.
Nginx can redirect traffic to the target service through either the rewrite or proxy_pass functionalities.
- The rewrite feature enables explicit redirection. In this setup, when a user sends a request to Nginx, it responds with a redirected URL (either a 301 permanent redirect or a 302 temporary redirect), prompting the client to fetch the final server using the new URL. If a permanent redirect is configured, the browser will cache the address, allowing subsequent visits to bypass Nginx and directly connect to the final server.
- proxy_pass provides implicit forwarding. Here, the Nginx server acts as a proxy, receiving user traffic and forwarding it to the actual backend service.
Notes In general, implicit forwarding is not recommended, as traffic passing through the Nginx server poses challenges to operation and maintenance and load balancing.
Configuration steps
Explicit URL forwarding
1. Nginx installation
Install with root privileges
1#Download the installation package
2wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
3 #Unzip
4tar -zxvf nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
5cd nginx-1.18.0
6
7 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx # Replace with the actual desired installation path during configuration
8make && make install
9
10 #Verify whether the installation is successful after installation
11cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin
12./nginx -t
13 #The following content indicates successful installation
14nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx//conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
15nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx//conf/nginx.conf test is successful2. Nginx configuration
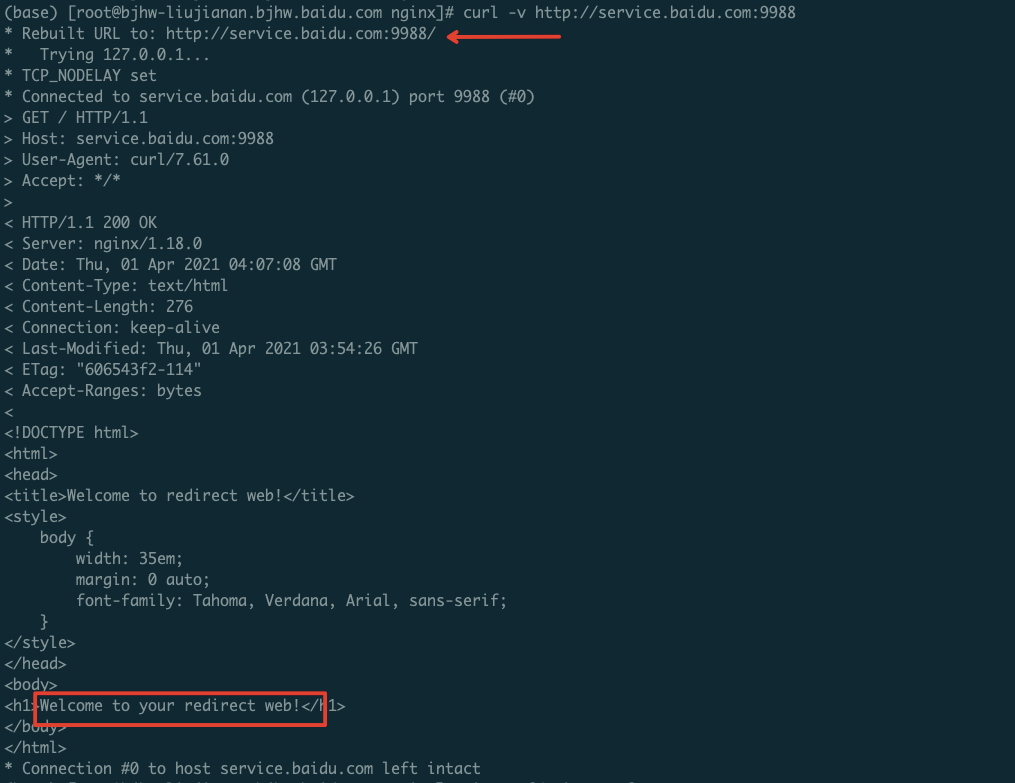
301 permanent redirect
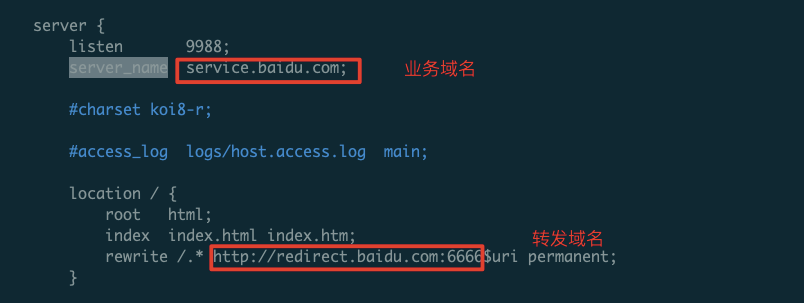
1server {
2 listen 80;
3 server_name $your_domain;
4 rewrite /.* http://$new_domain$uri permanent;
5}In this context, $uri refers to the redirected target address matched via a regular expression. For instance, visiting $your_domain/about will redirect to http://$new.domain/about.
302 temporary redirect
1server {
2 listen 80;
3 server_name $your_domain;
4 rewrite /.* http://$new_domain$uri redirect;
5}3. Restart Nginx
1cd /usr/local/nginx/ # Replace with the configuration path during installation
2./sbin/nginx -s reload4. Verify
Implicit URL forwarding
1. Nginx installation
Install with root privileges
1#Download the installation package
2wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
3 #Unzip
4tar -zxvf nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
5cd nginx-1.18.0
6
7 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx # Replace with the actual desired installation path during configuration
8make && make install
9
10 #Verify whether the installation is successful after installation
11cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin
12./nginx -t
13 #The following content indicates successful installation
14nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx//conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
15nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx//conf/nginx.conf test is successful2. Nginx configuration
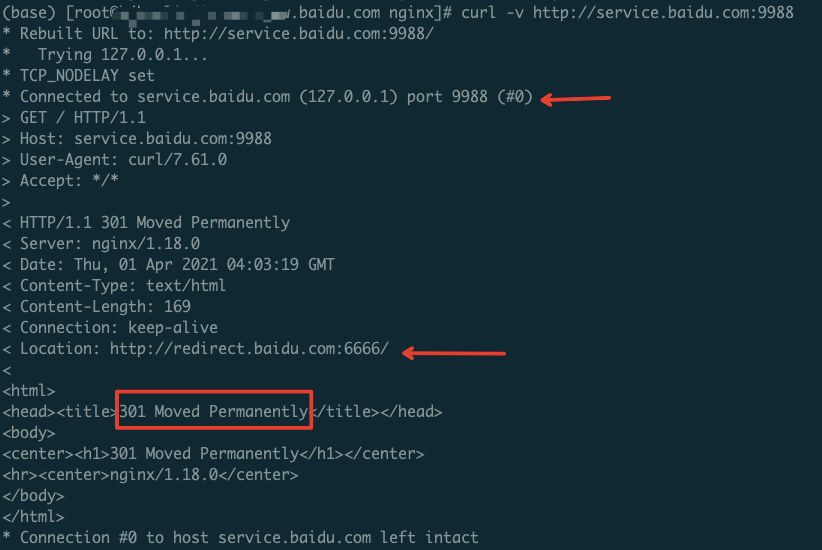
We proxy traffic accessing service.baidu.com:9988 to redirect.baidu.com:6666.
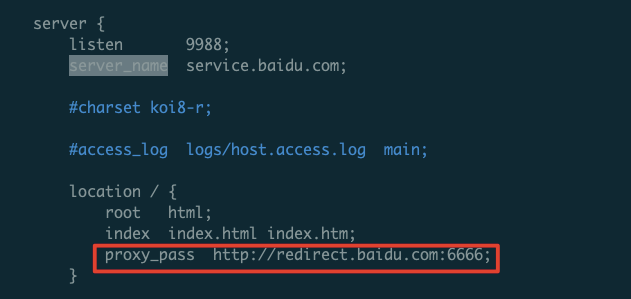
3. Verify Traffic