Local IDC Interconnection with Cloud DNS Service via Resolver
Overview
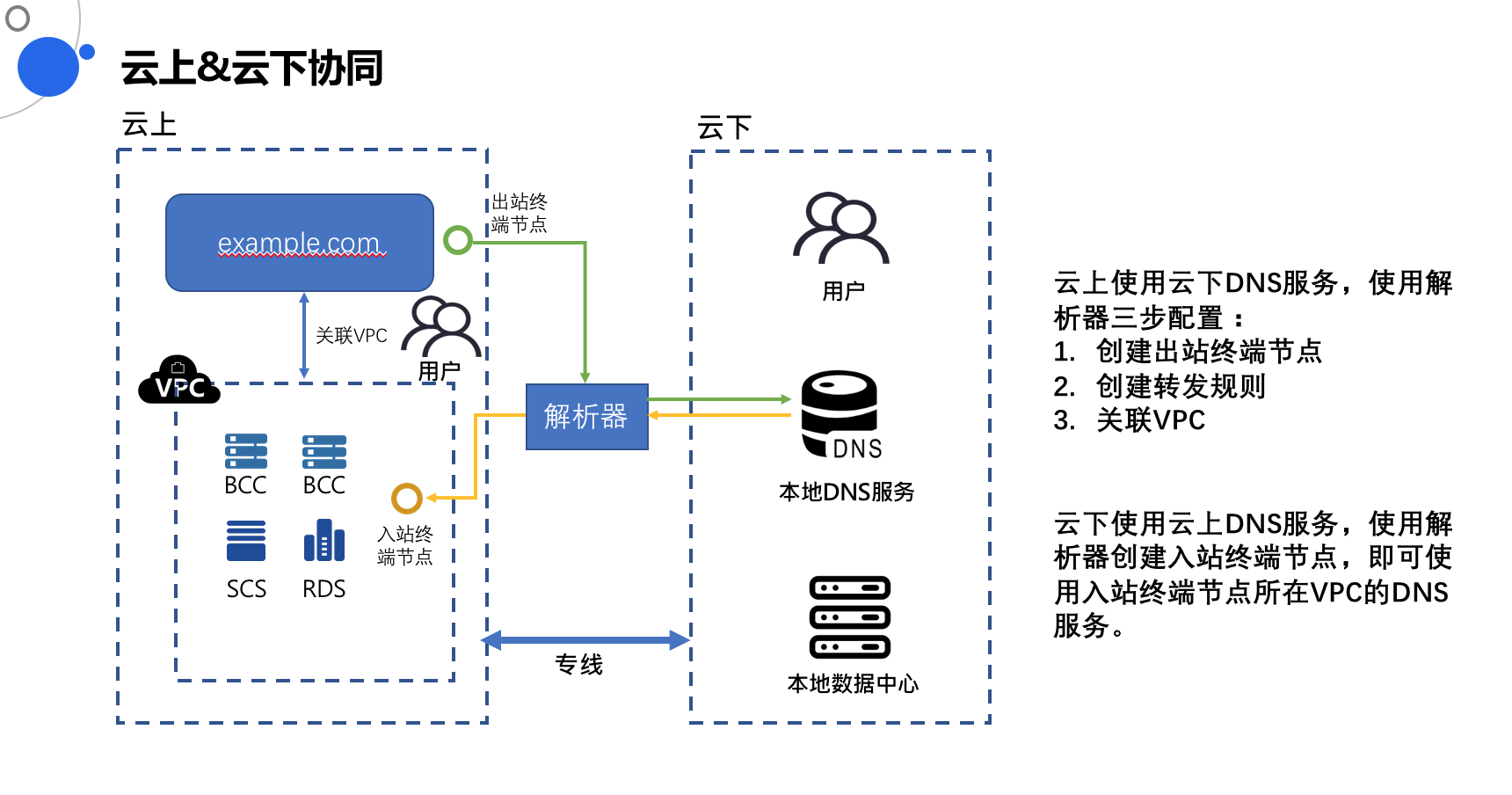
The prerequisite for using the resolver is that the cloud VPC and the user's IDC must be connected!
- The user's local IDC resolves records in the cloud DNS-Server (such as Service Network Interface Card (SNIC) domain name resolution) — ingress resolver
- Machines in the cloud VPC resolve records in the user's local IDC DNS-Server — egress resolver
Ingress resolver
Typical application scenario: Off-cloud IDC requests a Service Network Interface Card (SNIC)
Step I: Associate the Service Network Interface Card (SNIC) to create cloud resolution records
First, there is an existing Service Network Interface Card (SNIC), and a domain name resolution service has been associated and created
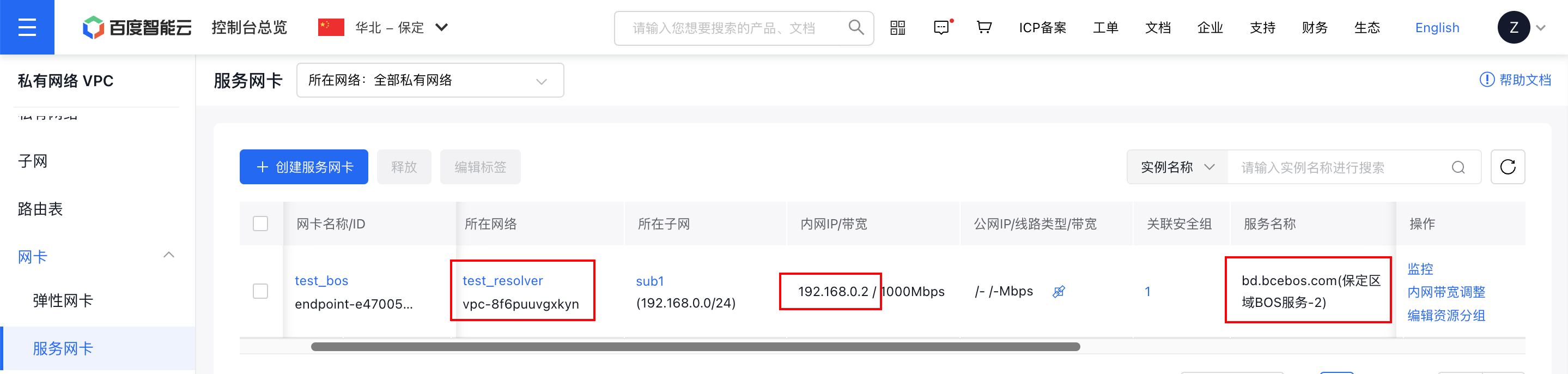
In the bcebos.com zone of the Intelligent Cloud DNS private zone product, a wildcard resolution *bd.bcebos.com -> 192.168.0.2 has been added for the Service Network Interface Card (SNIC)
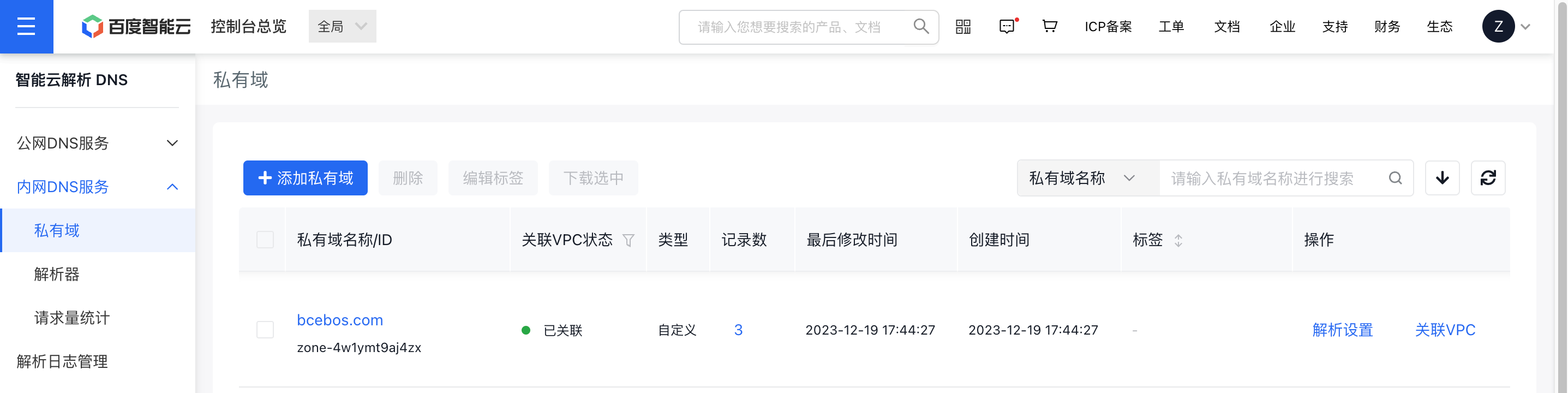
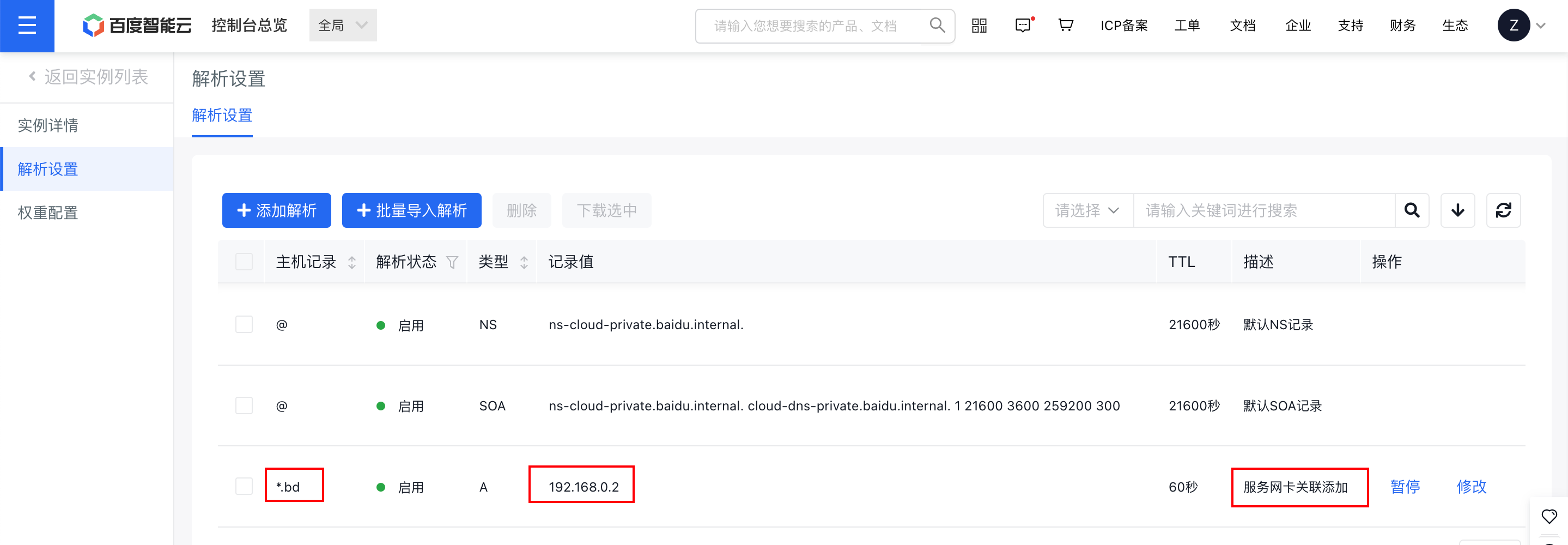
Step II: Create an ingress resolver in the console
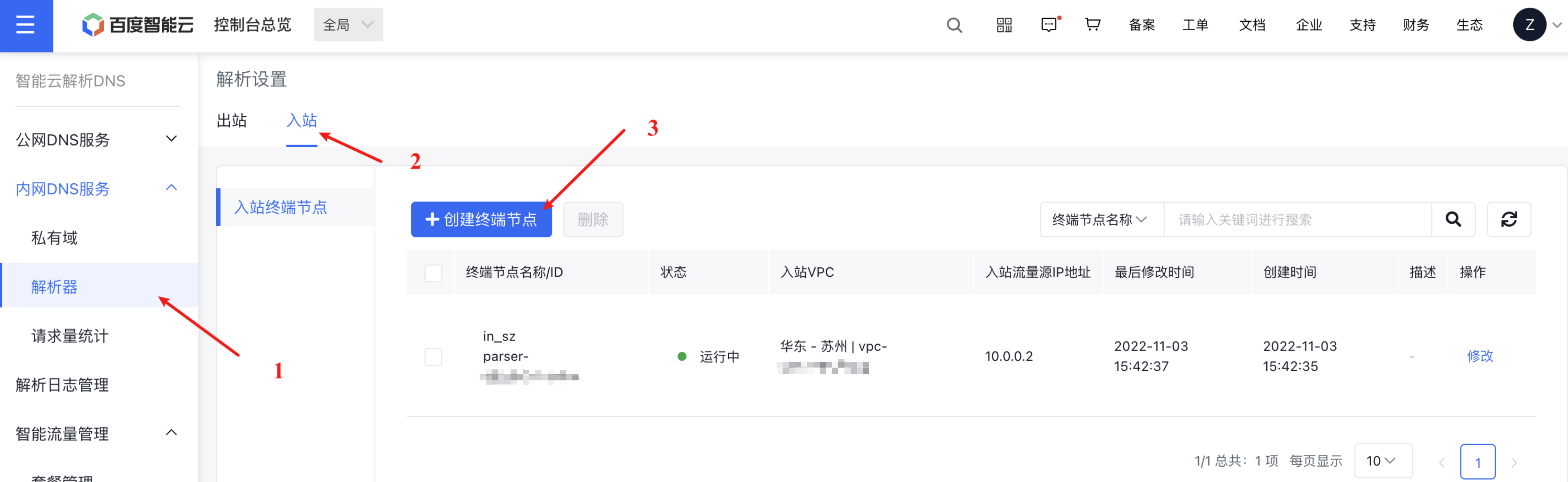
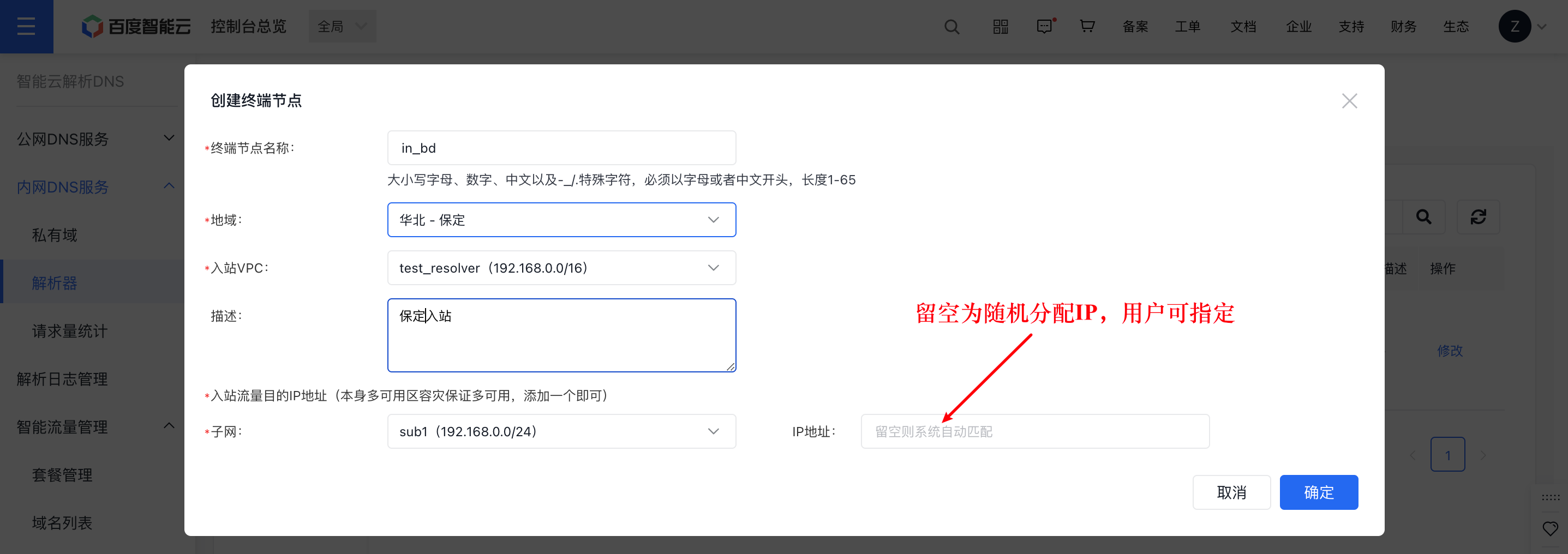
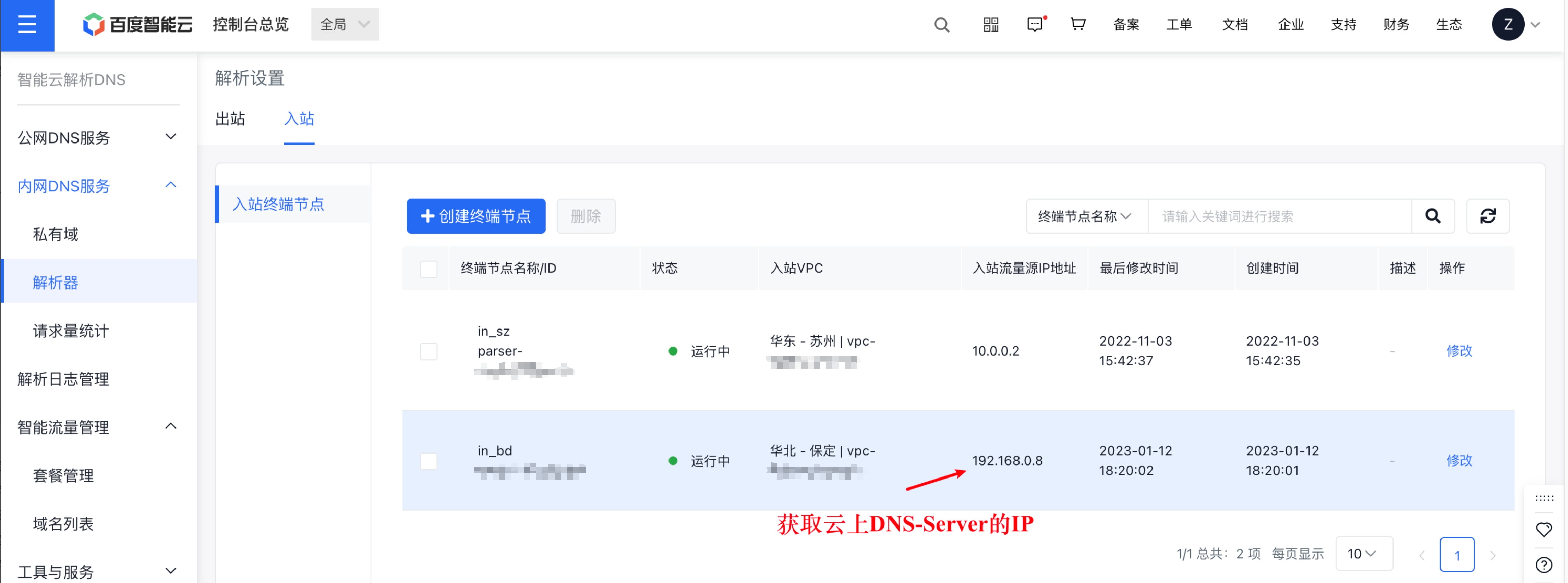
Step III: Obtain the DNS-Server IP of the cloud ingress VPC
Step IV: Configure forwarding rules for the local IDC DNS-Server according to requirements (taking bind9 as an example)
For a simplest configuration of DNS-server (bind9), set it to forward all domain names under the bd.bcebos.com domain to the DNS-Server of the VPC on Baidu AI Cloud:
1# /etc/named.conf
2options {
3 listen-on port 53 { any; };
4 listen-on-v6 port 53 { any; };
5 directory "/var/named";
6 allow-query { any; };
7 ...
8};
9...
10zone "bcebos.com" {
11 type forward;
12 forward only;
13 forwarders { 192.168.0.8; };
14};
15include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";Users can configure custom forwarding policies on their local IDC DNS server as needed.
Notes:
- forward first (default): First use the forwarder's DNS servers for domain name resolution; if the query fails, switch to the local DNS server for resolution.
- forward only: Use only the forwarder's DNS servers for domain name resolution; if the query fails, return a DNS client query failure. It is recommended to use forward only. Baidu AI Cloud DNS also provides recursive public network capabilities.
Step V: Allow IP addresses through routing
Besides interconnecting the local IDC and cloud VPC, users must configure bidirectional routes. This includes allowing access for the ingress resolver and the IDC DNS server's IP accessing the ingress resolver. Additionally, if the local IDC DNS server has security measures like firewalls, traffic from the ingress source IP must be permitted.
Take dedicated line as an example:
When connecting a local IDC and cloud VPC through a dedicated line, users must set up bidirectional routes. This enables communication between the ingress resolver's IP (e.g., 192.168.0.8) obtained in Step 2 and the IDC DNS server's IP accessing the ingress resolver. Typically, if the dedicated line route covers the current VPC/Subnet and the IDC CIDR, no additional action is required. Furthermore, firewalls and other security measures must permit traffic from these IPs.
Egress resolver
Typical application scenario: Cloud virtual machine requests a user IDC domain name such as idc.test.com
Step I: Create an egress endpoint for the egress resolver in the console
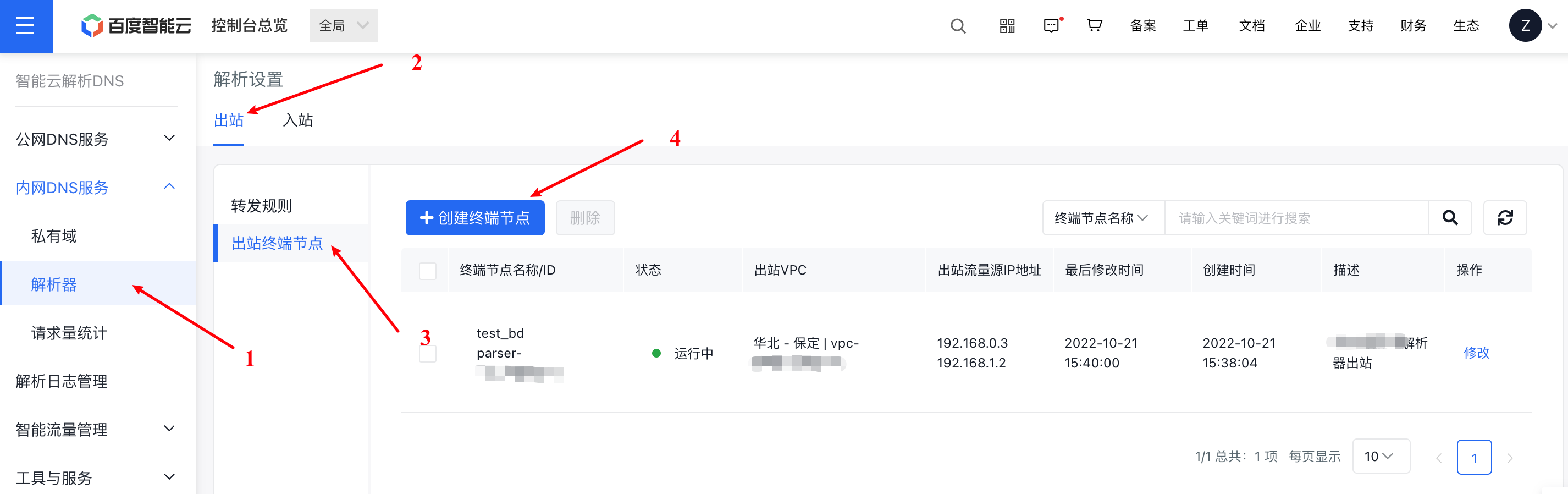
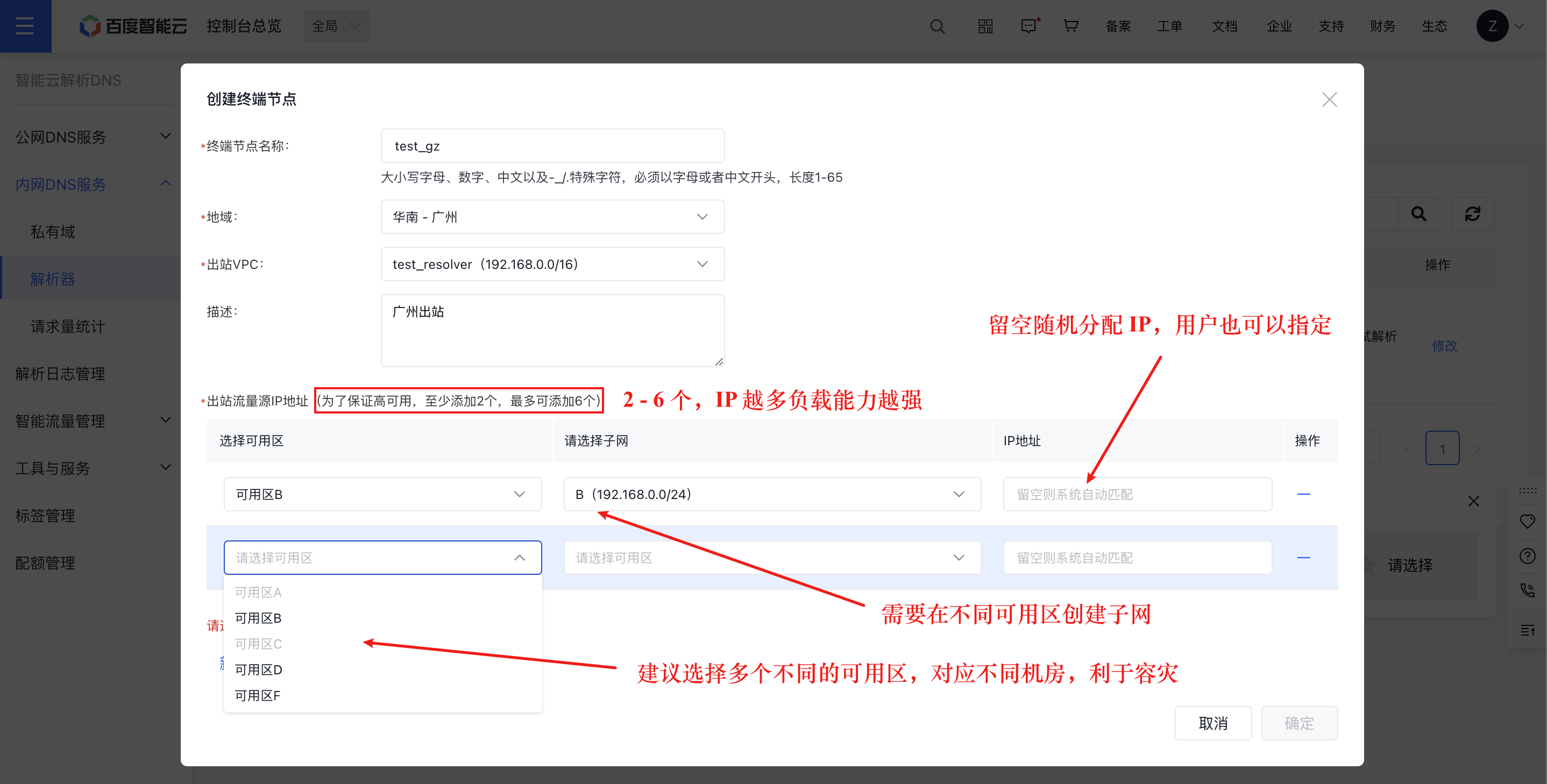
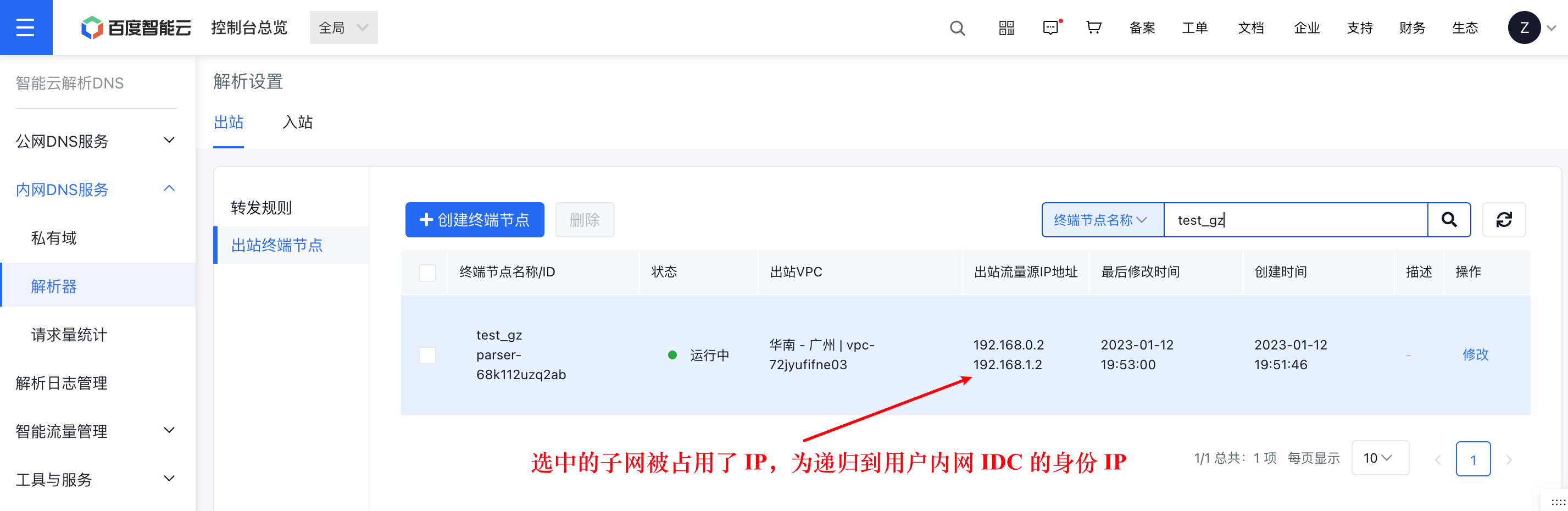
Step II: Obtain multiple Forward IPs of the cloud egress VPC
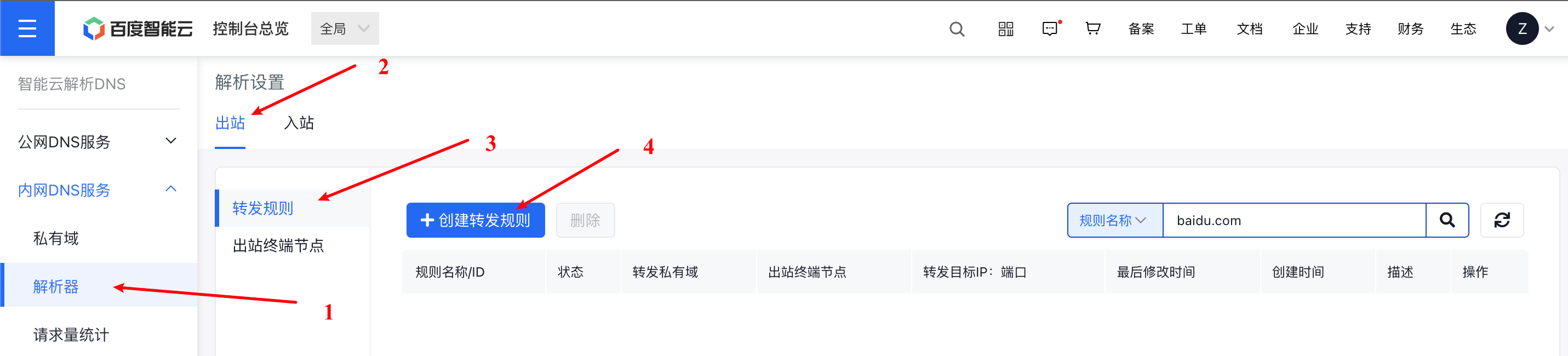
Step III: Create forwarding rules for the egress resolver in the console
For example, set the domain names under the test.com domain to be forwarded to the user's local IDC for resolution:
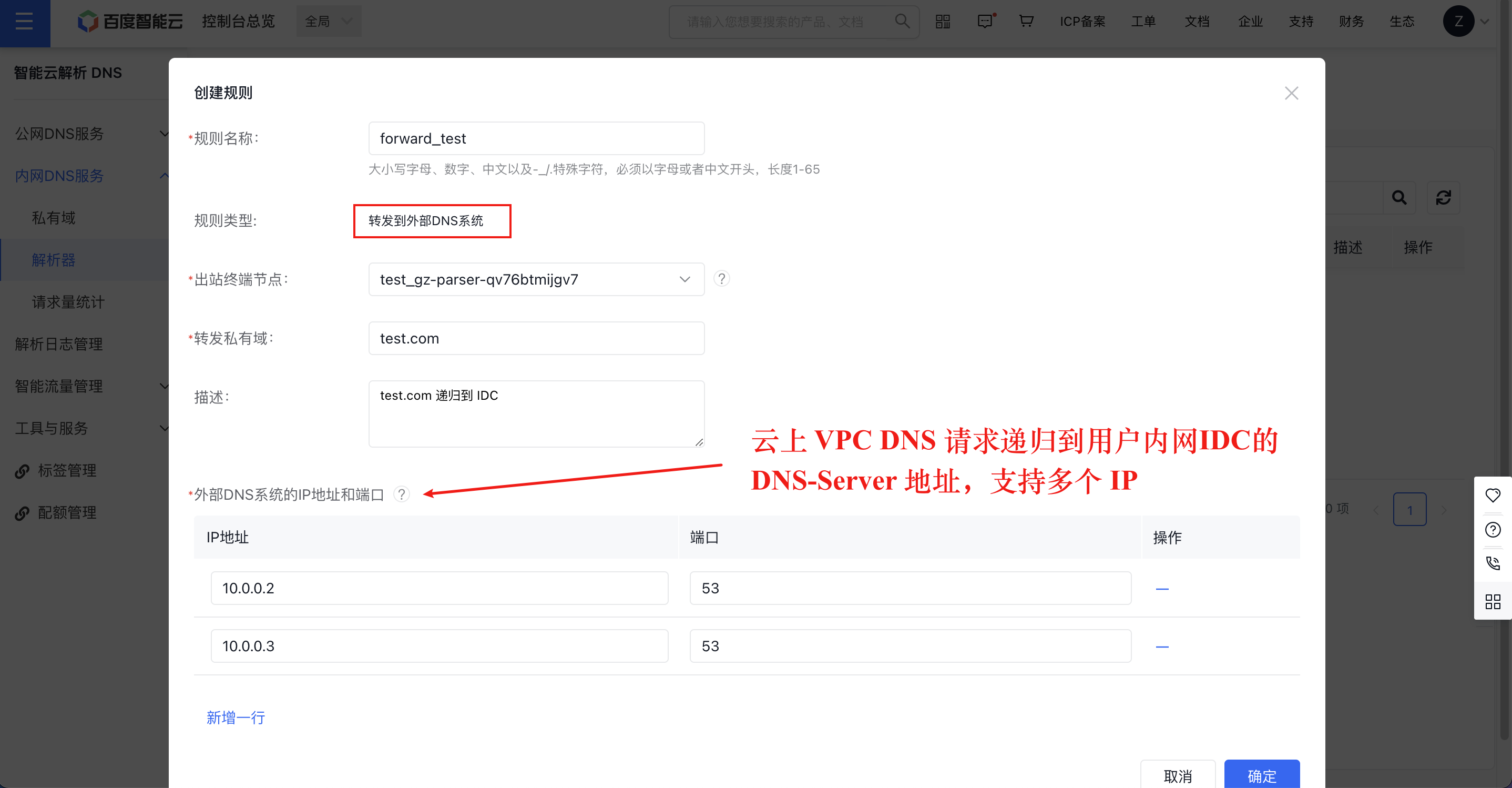
Note that the priority of private zones on Baidu AI Cloud is higher than the forwarding rules of the egress resolver. For example, the actual matching principle for the test.com domain is domain names in the private zone test.com
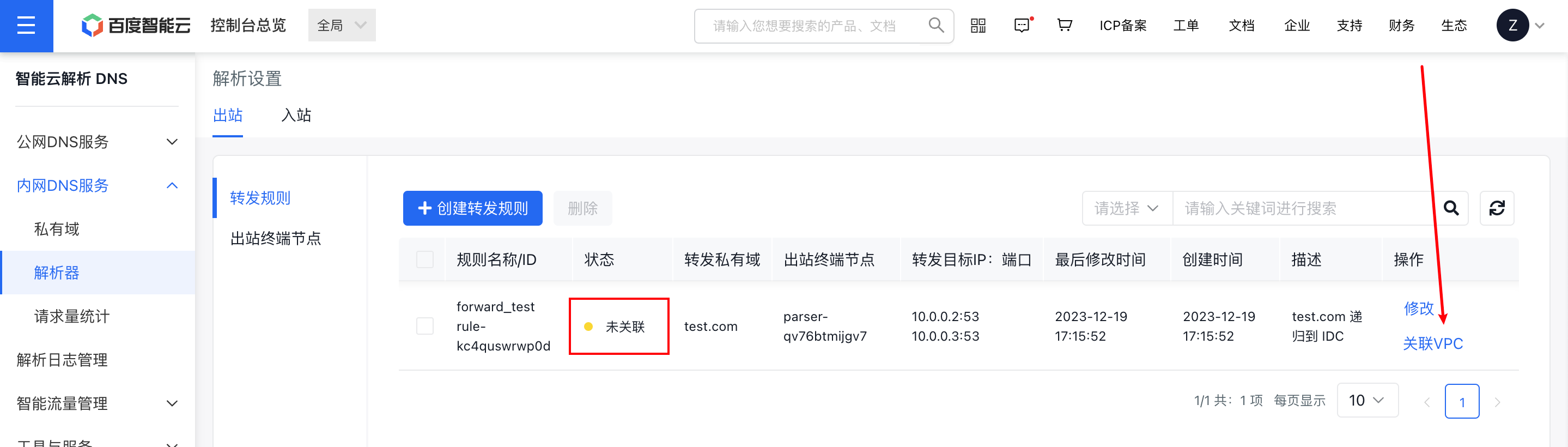
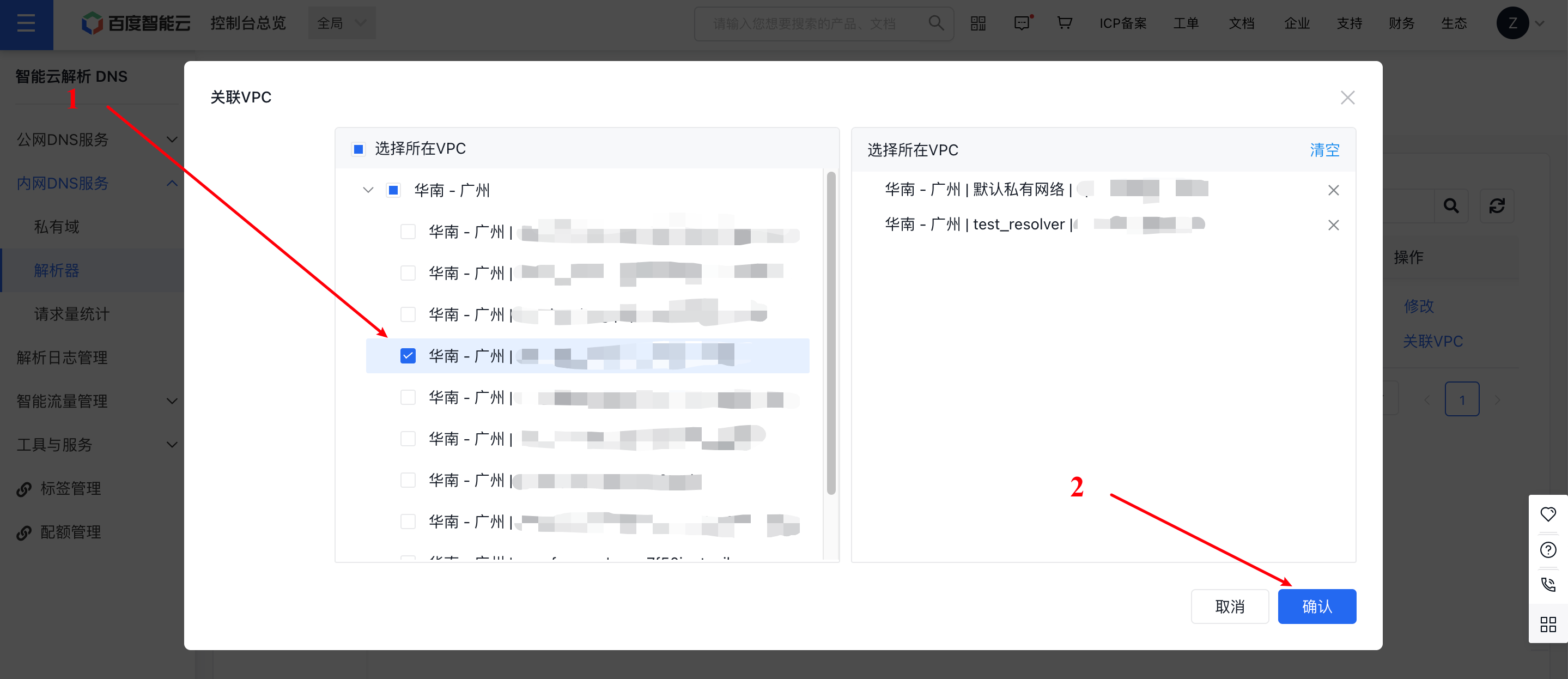
Step IV: Bind the VPC to the forwarding rules in the console
A resolver located in a VPC only consumes its resources, but this does not imply that the VPC inherently has DNS egress capabilities. You must bind the configured forwarding rules to the specified VPC. Additionally, multiple VPCs can share a single resolver egress endpoint.
Step V: Allow IP addresses through routing
Users must configure bidirectional routes to connect the local IDC with the cloud VPC. Additionally, if the user's local IDC DNS-Server has security measures like firewalls, it needs to allow traffic from the egress source IP.
Take dedicated line as an example:
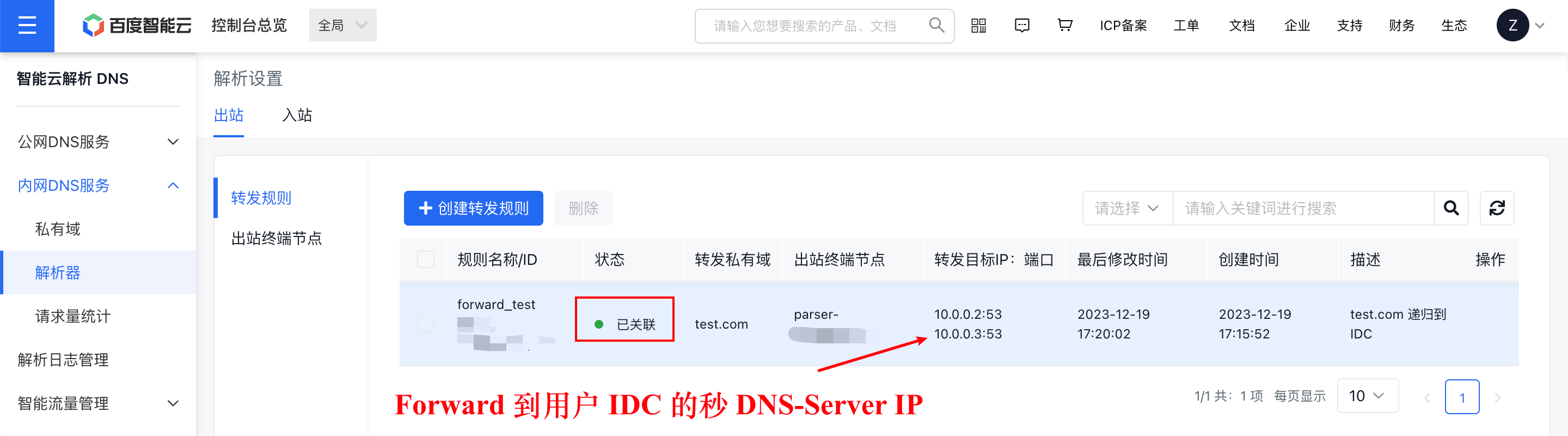
When connecting the local IDC and cloud VPC via a dedicated line, users must configure bidirectional routes for the dedicated line to allow traffic from the egress resolver IPs obtained in Step 2 (e.g., 192.168.0.2, 192.168.1.2) and the target DNS-Server IPs within the user's IDC that the egress resolver forwards traffic to (e.g., 10.0.0.2, 10.0.0.3). Generally, if the route for the dedicated line includes the current VPC/Subnet and the user's IDC CIDR, no further action is required. At the same time, firewalls and other security measures must permit access from these IPs.
