VPC网络SASL_PLAINTEXT方式生产和消费消息
更新时间:2025-08-21
在同 VPC 网络下访问,使用 SASL_PLAINTEXT 协议接入,接入点可以在 集群详情 页面查看。
环境准备
- 安装GCC
- 安装C++ 依赖库。
Shell
1yum install librdkafka-devel
2yum install cyrus-sasl
3yum install cyrus-sasl-scram集群准备
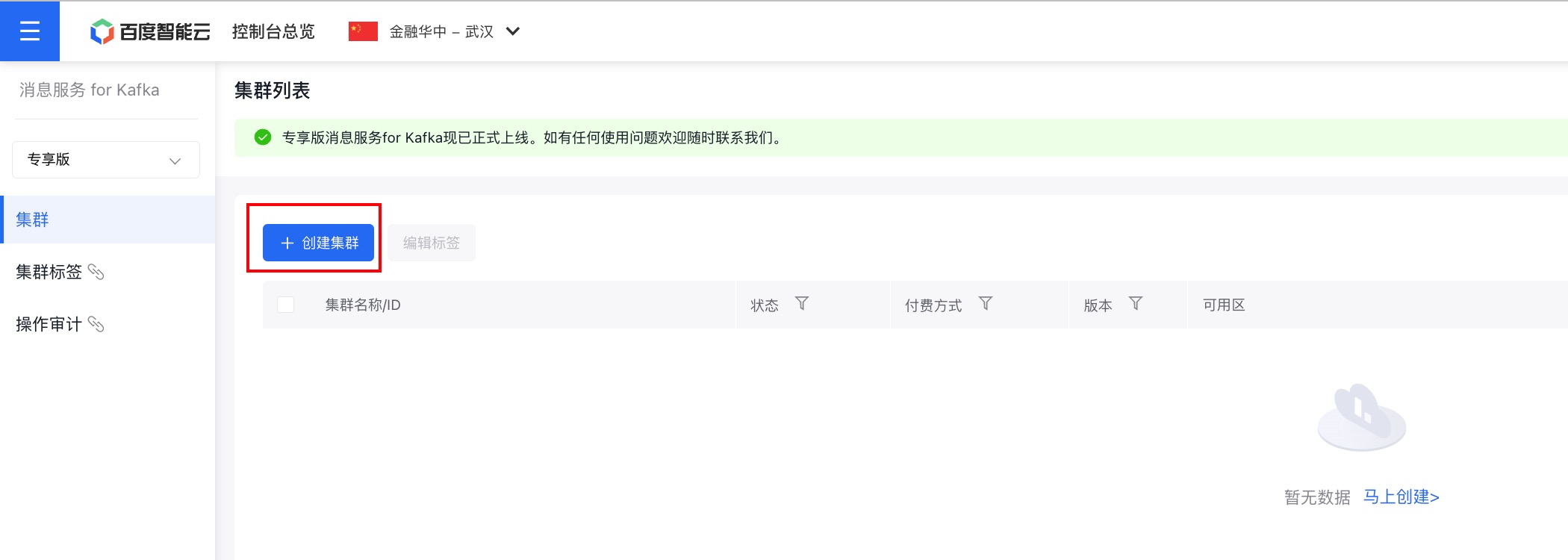
1. 购买专享版消息服务for Kafka集群
开通消息服务 for Kafka服务后,在控制台页面点击『创建集群』,即可进行购买。
2. 为购买的集群创建主题
在控制台页面点击集群名称,进入集群详情页面。
在左侧的边栏中点击『主题管理』,进入主题管理页面。
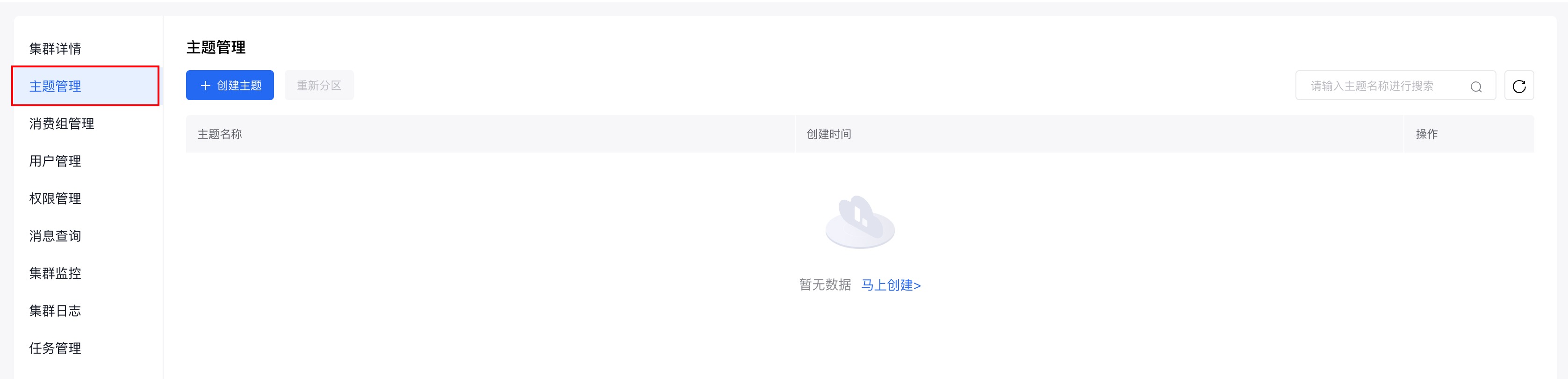
在主题管理页面点击『创建主题』,进行主题的创建。
使用步骤:
步骤一:获取集群接入点
具体请参考:接入点查看。
步骤二:编写测试代码
生产者代码示例
创建KafkaProducerDemo.c文件,具体代码示例如下:
Shell
1/*
2* librdkafka - Apache Kafka C library
3*
4* Copyright (c) 2017, Magnus Edenhill
5* All rights reserved.
6*
7* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
8* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
9*
10* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
11* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
12* 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
13* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
14* and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
15*
16* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
17* AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
18* IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
19* ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE
20* LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
21* CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
22* SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS
23* INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
24* CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)
25* ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
26* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
27 */
28
29/**
30* Simple Apache Kafka producer
31* using the Kafka driver from librdkafka
32* (https://github.com/edenhill/librdkafka)
33 */
34
35#include <stdio.h>
36#include <signal.h>
37#include <string.h>
38
39
40/* Typical include path would be <librdkafka/rdkafka.h>, but this program
41* is builtin from within the librdkafka source tree and thus differs. */
42 #include "librdkafka/rdkafka.h"
43
44
45static volatile sig_atomic_t run = 1;
46
47/**
48* @brief Signal termination of program
49 */
50 static void stop(int sig) {
51 run = 0;
52 fclose(stdin); /* abort fgets() */
53 }
54
55
56/**
57* @brief Message delivery report callback.
58*
59* This callback is called exactly once per message, indicating if
60* the message was succesfully delivered
61* (rkmessage->err == RD_KAFKA_RESP_ERR_NO_ERROR) or permanently
62* failed delivery (rkmessage->err != RD_KAFKA_RESP_ERR_NO_ERROR).
63*
64* The callback is triggered from rd_kafka_poll() and executes on
65* the application's thread.
66 */
67 static void dr_msg_cb(rd_kafka_t *rk, const rd_kafka_message_t *rkmessage, void *opaque) {
68 if (rkmessage->err) {
69 fprintf(stderr, "%% Message delivery failed: %s\n", rd_kafka_err2str(rkmessage->err));
70 } else {
71 fprintf(stderr, "%% Message delivered (%zd bytes, partition %" PRId32 ")\n", rkmessage->len, rkmessage->partition);
72 }
73
74 /* The rkmessage is destroyed automatically by librdkafka */
75 }
76
77
78
79int main(int argc, char **argv) {
80rd_kafka_t *rk; /* Producer instance handle */
81rd_kafka_conf_t *conf; /* Temporary configuration object */
82
83 char errstr[512]; /* librdkafka API error reporting buffer */
84 char buf[512]; /* Message value temporary buffer */
85
86 const char *brokers; /* Argument: broker list */
87 const char *topic; /* Argument: topic to produce to */
88 const char *username; /* Argument: sasl username */
89 const char *password; /* Argument: sasl password */
90
91 /*
92 * Argument validation
93 */
94
95 // 检查参数配置
96 if (argc != 5) {
97 fprintf(stderr, "%% Usage: %s <broker> <topic> <username> <password>\n", argv[0]);
98 return 1;
99 }
100
101 // 接入点信息
102 brokers = argv[1];
103 // 主题名称
104 topic = argv[2];
105 // 用户管理中创建的用户名称
106 username = argv[3];
107 // 用户管理中创建的用户密码
108 password = argv[4];
109
110
111 /*
112 * Create Kafka client configuration place-holder
113 */
114 conf = rd_kafka_conf_new();
115
116 /* Set bootstrap broker(s) as a comma-separated list of
117 * host or host:port (default port 9092).
118 * librdkafka will use the bootstrap brokers to acquire the full
119 * set of brokers from the cluster. */
120 if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "bootstrap.servers", brokers, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {
121 fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", errstr);
122 return 1;
123 }
124 // 认证机制支持PLAIN、SCRAM-SHA-512两种机制,根据集群所使用的认证方式进行选择
125 if (
126 rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "security.protocol", "sasl_plaintext", errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK
127 || rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "sasl.mechanism", "SCRAM-SHA-512", errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK
128 || rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "sasl.username", username, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK
129 || rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "sasl.password", password, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK
130 ) {
131 fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", errstr);
132 return -1;
133 }
134
135 /* Set the delivery report callback.
136 * This callback will be called once per message to inform
137 * the application if delivery succeeded or failed.
138 * See dr_msg_cb() above.
139 * The callback is only triggered from rd_kafka_poll() and
140 * rd_kafka_flush(). */
141 rd_kafka_conf_set_dr_msg_cb(conf, dr_msg_cb);
142
143 /*
144 * Create producer instance.
145 *
146 * NOTE: rd_kafka_new() takes ownership of the conf object
147 * and the application must not reference it again after
148 * this call.
149 */
150 rk = rd_kafka_new(RD_KAFKA_PRODUCER, conf, errstr, sizeof(errstr));
151 if (!rk) {
152 fprintf(stderr, "%% Failed to create new producer: %s\n", errstr);
153 return 1;
154 }
155
156 /* Signal handler for clean shutdown */
157 signal(SIGINT, stop);
158
159 fprintf(stderr,
160 "%% Type some text and hit enter to produce message\n"
161 "%% Or just hit enter to only serve delivery reports\n"
162 "%% Press Ctrl-C or Ctrl-D to exit\n");
163
164 while (run && fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin)) {
165 size_t len = strlen(buf);
166 rd_kafka_resp_err_t err;
167
168 /* Remove newline */
169 if (buf[len - 1] == '\n') {
170 buf[--len] = '\0';
171 }
172
173 /* Empty line: only serve delivery reports */
174 if (len == 0) {
175 rd_kafka_poll(rk, 0/*non-blocking */);
176 continue;
177 }
178
179 /*
180 * Send/Produce message.
181 * This is an asynchronous call, on success it will only
182 * enqueue the message on the internal producer queue.
183 * The actual delivery attempts to the broker are handled
184 * by background threads.
185 * The previously registered delivery report callback
186 * (dr_msg_cb) is used to signal back to the application
187 * when the message has been delivered (or failed).
188 */
189 retry:
190 err = rd_kafka_producev(
191 /* Producer handle */
192 rk,
193 /* Topic name */
194 RD_KAFKA_V_TOPIC(topic),
195 /* Make a copy of the payload. */
196 RD_KAFKA_V_MSGFLAGS(RD_KAFKA_MSG_F_COPY),
197 /* Message value and length */
198 RD_KAFKA_V_VALUE(buf, len),
199 /* Per-Message opaque, provided in
200 * delivery report callback as
201 * msg_opaque. */
202 RD_KAFKA_V_OPAQUE(NULL),
203 /* End sentinel */
204 RD_KAFKA_V_END
205 );
206
207 if (err) {
208 /*
209 * Failed to *enqueue* message for producing.
210 */
211 fprintf(stderr,
212 "%% Failed to produce to topic %s: %s\n", topic,
213 rd_kafka_err2str(err));
214
215 if (err == RD_KAFKA_RESP_ERR__QUEUE_FULL) {
216 /* If the internal queue is full, wait for
217 * messages to be delivered and then retry.
218 * The internal queue represents both
219 * messages to be sent and messages that have
220 * been sent or failed, awaiting their
221 * delivery report callback to be called.
222 *
223 * The internal queue is limited by the
224 * configuration property
225 * queue.buffering.max.messages */
226 rd_kafka_poll(rk, 1000 /*block for max 1000ms*/);
227 goto retry;
228 }
229 } else {
230 fprintf(stderr, "%% Enqueued message (%zd bytes) "
231 "for topic %s\n",
232 len, topic);
233 }
234
235
236 /* A producer application should continually serve
237 * the delivery report queue by calling rd_kafka_poll()
238 * at frequent intervals.
239 * Either put the poll call in your main loop, or in a
240 * dedicated thread, or call it after every
241 * rd_kafka_produce() call.
242 * Just make sure that rd_kafka_poll() is still called
243 * during periods where you are not producing any messages
244 * to make sure previously produced messages have their
245 * delivery report callback served (and any other callbacks
246 * you register). */
247 rd_kafka_poll(rk, 0 /*non-blocking*/);
248 }
249
250
251 /* Wait for final messages to be delivered or fail.
252 * rd_kafka_flush() is an abstraction over rd_kafka_poll() which
253 * waits for all messages to be delivered. */
254 fprintf(stderr, "%% Flushing final messages..\n");
255 rd_kafka_flush(rk, 10 * 1000 /* wait for max 10 seconds */);
256
257 /* If the output queue is still not empty there is an issue
258 * with producing messages to the clusters. */
259 if (rd_kafka_outq_len(rk) > 0) {
260 fprintf(stderr, "%% %d message(s) were not delivered\n", rd_kafka_outq_len(rk));
261 }
262
263 /* Destroy the producer instance */
264 rd_kafka_destroy(rk);
265
266 return 0;
267}消费者代码示例
创建KafkaConsumerDemo.c文件,具体代码示例如下:
Shell
1/*
2* librdkafka - Apache Kafka C library
3*
4* Copyright (c) 2019, Magnus Edenhill
5* All rights reserved.
6*
7* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
8* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
9*
10* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
11* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
12* 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
13* this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
14* and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
15*
16* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
17* AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
18* IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
19* ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE
20* LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
21* CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
22* SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS
23* INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
24* CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)
25* ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
26* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
27 */
28
29/**
30* Simple high-level balanced Apache Kafka consumer
31* using the Kafka driver from librdkafka
32* (https://github.com/edenhill/librdkafka)
33 */
34
35#include <stdio.h>
36#include <signal.h>
37#include <string.h>
38#include <ctype.h>
39
40
41/* Typical include path would be <librdkafka/rdkafka.h>, but this program
42* is builtin from within the librdkafka source tree and thus differs. */
43 //#include <librdkafka/rdkafka.h>
44 #include "librdkafka/rdkafka.h"
45
46
47static volatile sig_atomic_t run = 1;
48
49/**
50* @brief Signal termination of program
51 */
52 static void stop(int sig) {
53 run = 0;
54 }
55
56
57
58/**
59* @returns 1 if all bytes are printable, else 0.
60 */
61 static int is_printable(const char *buf, size_t size) {
62 size_t i;
63
64 for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
65 if (!isprint((int)buf[i])) {
66 return 0;
67 }
68 }
69
70 return 1;
71 }
72
73
74int main(int argc, char **argv) {
75rd_kafka_t *rk; /* Consumer instance handle */
76rd_kafka_conf_t *conf; /* Temporary configuration object */
77rd_kafka_resp_err_t err; /* librdkafka API error code */
78
79 char errstr[512]; /* librdkafka API error reporting buffer */
80
81 const char *brokers; /* Argument: broker list */
82 const char *groupid; /* Argument: Consumer group id */
83 const char *username; /* Argument: sasl username */
84 const char *password; /* Argument: sasl password */
85 char **topics; /* Argument: list of topics to subscribe to */
86
87 int topic_cnt; /* Number of topics to subscribe to */
88 rd_kafka_topic_partition_list_t *subscription; /* Subscribed topics */
89 int i;
90
91 /*
92 * Argument validation
93 */
94
95 // 检查参数配置
96 if (argc < 6) {
97 fprintf(stderr, "%% Usage: %s <broker> <group.id> <username> <password> <topic1> <topic2>..\n", argv[0]);
98 return 1;
99 }
100
101 // 接入点信息
102 brokers = argv[1];
103 // 消费组 id
104 groupid = argv[2];
105 // 用户管理中创建的用户名称
106 username = argv[3];
107 // 用户管理中创建的用户密码
108 password = argv[4];
109 // 主题名称
110 topics = &argv[5];
111
112 topic_cnt = argc - 5;
113
114
115 /*
116 * Create Kafka client configuration place-holder
117 */
118 conf = rd_kafka_conf_new();
119
120 /* Set bootstrap broker(s) as a comma-separated list of
121 * host or host:port (default port 9092).
122 * librdkafka will use the bootstrap brokers to acquire the full
123 * set of brokers from the cluster. */
124 if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "bootstrap.servers", brokers, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {
125 fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", errstr);
126 rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);
127 return 1;
128 }
129 // 认证机制支持PLAIN、SCRAM-SHA-512两种机制,根据集群所使用的认证方式进行选择
130 if (
131 rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "security.protocol", "sasl_plaintext", errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK
132 || rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "sasl.mechanism", "SCRAM-SHA-512", errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK
133 || rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "sasl.username", username, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK
134 || rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "sasl.password", password, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK
135 ) {
136 fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", errstr);
137 return -1;
138 }
139
140 /* Set the consumer group id.
141 * All consumers sharing the same group id will join the same
142 * group, and the subscribed topic' partitions will be assigned
143 * according to the partition.assignment.strategy
144 * (consumer config property) to the consumers in the group. */
145 if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "group.id", groupid, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {
146 fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", errstr);
147 rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);
148 return 1;
149 }
150
151 /* If there is no previously committed offset for a partition
152 * the auto.offset.reset strategy will be used to decide where
153 * in the partition to start fetching messages.
154 * By setting this to earliest the consumer will read all messages
155 * in the partition if there was no previously committed offset. */
156 if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "auto.offset.reset", "earliest", errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {
157 fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", errstr);
158 rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);
159 return 1;
160 }
161
162 /*
163 * Create consumer instance.
164 *
165 * NOTE: rd_kafka_new() takes ownership of the conf object
166 * and the application must not reference it again after
167 * this call.
168 */
169 rk = rd_kafka_new(RD_KAFKA_CONSUMER, conf, errstr, sizeof(errstr));
170 if (!rk) {
171 fprintf(stderr, "%% Failed to create new consumer: %s\n", errstr);
172 return 1;
173 }
174
175 conf = NULL; /* Configuration object is now owned, and freed,
176 * by the rd_kafka_t instance. */
177
178
179 /* Redirect all messages from per-partition queues to
180 * the main queue so that messages can be consumed with one
181 * call from all assigned partitions.
182 *
183 * The alternative is to poll the main queue (for events)
184 * and each partition queue separately, which requires setting
185 * up a rebalance callback and keeping track of the assignment:
186 * but that is more complex and typically not recommended. */
187 rd_kafka_poll_set_consumer(rk);
188
189
190 /* Convert the list of topics to a format suitable for librdkafka */
191 subscription = rd_kafka_topic_partition_list_new(topic_cnt);
192 for (i = 0; i < topic_cnt; i++) {
193 rd_kafka_topic_partition_list_add(
194 subscription,
195 topics[i],
196 /* the partition is ignored
197 * by subscribe() */
198 RD_KAFKA_PARTITION_UA
199 );
200 }
201
202 /* Subscribe to the list of topics */
203 err = rd_kafka_subscribe(rk, subscription);
204 if (err) {
205 fprintf(stderr, "%% Failed to subscribe to %d topics: %s\n", subscription->cnt, rd_kafka_err2str(err));
206 rd_kafka_topic_partition_list_destroy(subscription);
207 rd_kafka_destroy(rk);
208 return 1;
209 }
210
211 fprintf(stderr,
212 "%% Subscribed to %d topic(s), "
213 "waiting for rebalance and messages...\n",
214 subscription->cnt);
215
216 rd_kafka_topic_partition_list_destroy(subscription);
217
218
219 /* Signal handler for clean shutdown */
220 signal(SIGINT, stop);
221
222 /* Subscribing to topics will trigger a group rebalance
223 * which may take some time to finish, but there is no need
224 * for the application to handle this idle period in a special way
225 * since a rebalance may happen at any time.
226 * Start polling for messages. */
227
228 while (run) {
229 rd_kafka_message_t *rkm;
230
231 rkm = rd_kafka_consumer_poll(rk, 100);
232 if (!rkm) {
233 continue; /* Timeout: no message within 100ms,
234 * try again. This short timeout allows
235 * checking for `run` at frequent intervals.
236 */
237 }
238
239 /* consumer_poll() will return either a proper message
240 * or a consumer error (rkm->err is set). */
241 if (rkm->err) {
242 /* Consumer errors are generally to be considered
243 * informational as the consumer will automatically
244 * try to recover from all types of errors. */
245 fprintf(stderr, "%% Consumer error: %s\n", rd_kafka_message_errstr(rkm));
246 rd_kafka_message_destroy(rkm);
247 continue;
248 }
249
250 /* Proper message. */
251 printf("Message on %s [%" PRId32 "] at offset %" PRId64 ":\n",
252 rd_kafka_topic_name(rkm->rkt), rkm->partition,
253 rkm->offset);
254
255 /* Print the message key. */
256 if (rkm->key && is_printable(rkm->key, rkm->key_len)) {
257 printf(" Key: %.*s\n", (int)rkm->key_len, (const char *)rkm->key);
258 } else if (rkm->key) {
259 printf(" Key: (%d bytes)\n", (int)rkm->key_len);
260 }
261
262 /* Print the message value/payload. */
263 if (rkm->payload && is_printable(rkm->payload, rkm->len)) {
264 printf(" Value: %.*s\n", (int)rkm->len, (const char *)rkm->payload);
265 } else if (rkm->payload) {
266 printf(" Value: (%d bytes)\n", (int)rkm->len);
267 }
268
269 rd_kafka_message_destroy(rkm);
270 }
271
272
273 /* Close the consumer: commit final offsets and leave the group. */
274 fprintf(stderr, "%% Closing consumer\n");
275 rd_kafka_consumer_close(rk);
276
277
278 /* Destroy the consumer */
279 rd_kafka_destroy(rk);
280
281 return 0;
282}步骤三:编译并运行
编译并运行上述两个代码文件。
Bash
1# 启动消费者
2gcc -lrdkafka ./consumer.c -o consumer
3./consumer <broker> <group.id> <username> <password> <topic1> <topic2>..
4# 启动生产者
5gcc -lrdkafka ./producer.c -o producer
6./producer <broker> <topic> <username> <password>步骤四:查看集群监控
查看消息是否发送成功或消费成功有两种方式:
- 在服务器端/控制台查看日志。
- 在专享版消息服务 for Kafka控制台查看集群监控,获取集群生产、消息情况。
推荐使用第二种方式,下面介绍如何查看集群监控。
(1)在专享版消息服务 for Kafka的控制台页面找到需要连接的集群,点击集群名称进入『集群详情』页面。
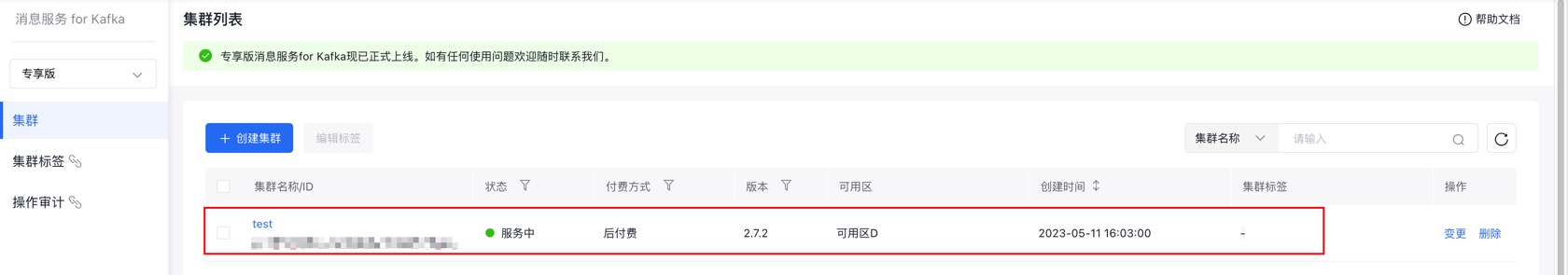
(2)页面跳转后,进入左侧边中的『集群详情』页面。
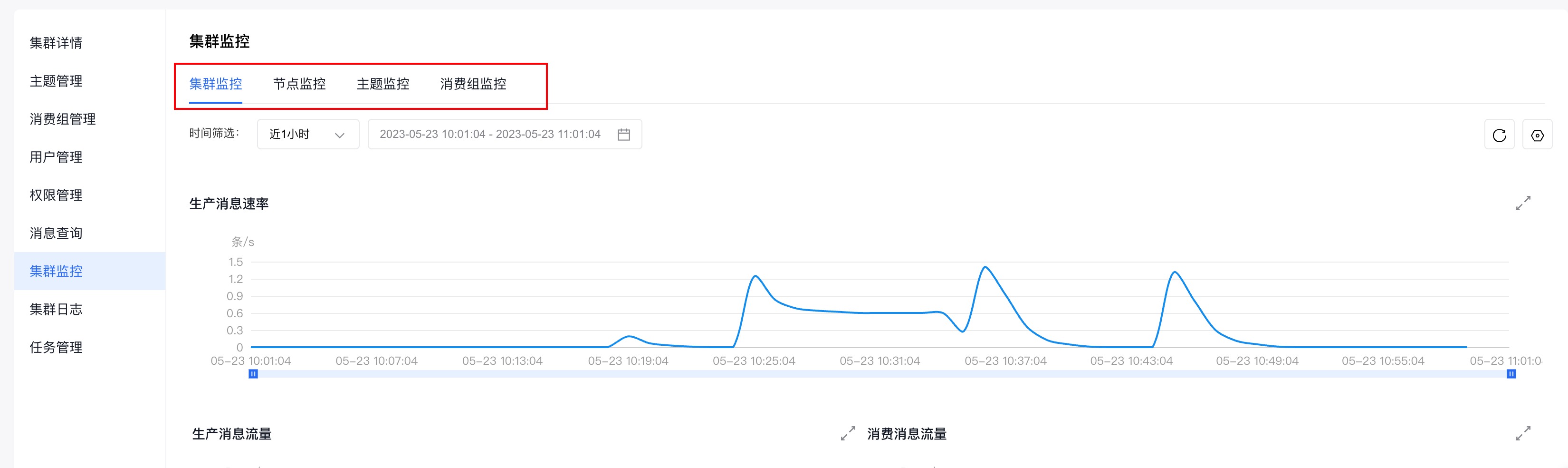
(3)点击左侧边栏中的『集群监控』,进入『集群监控』页面。
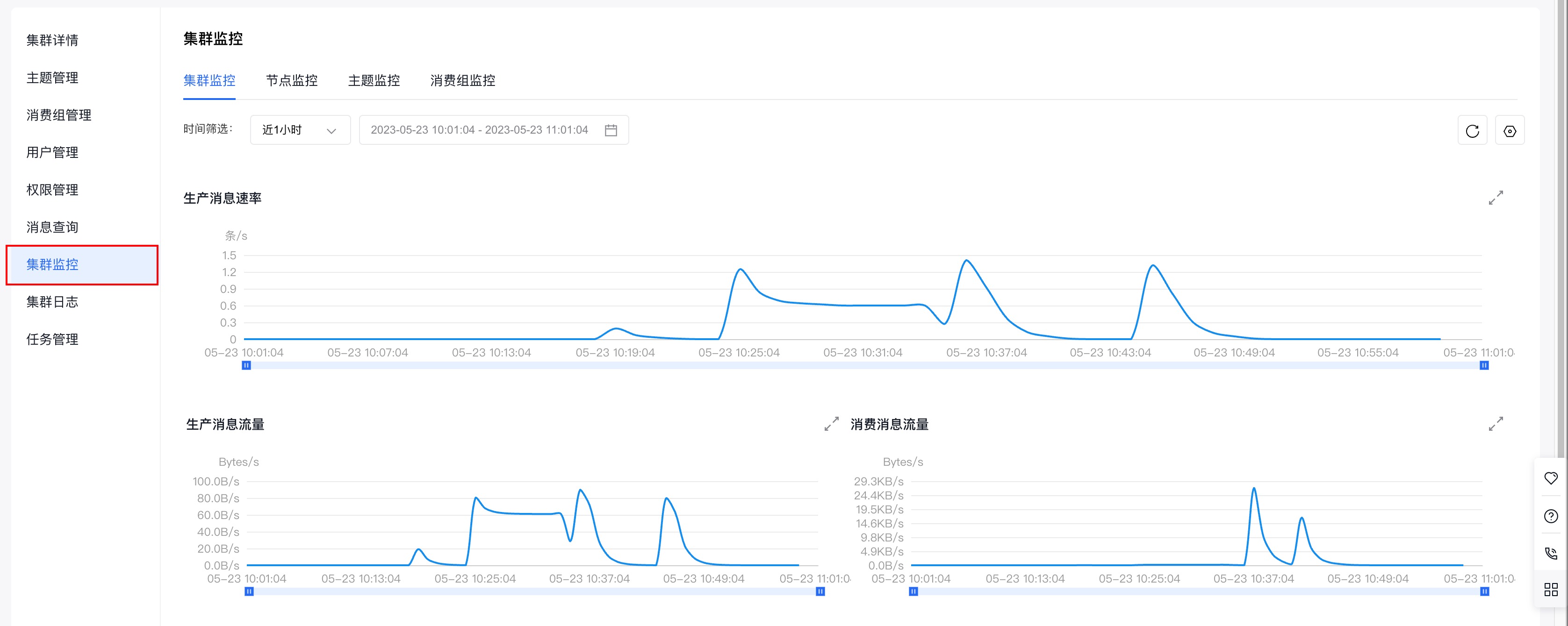
(4)通过查看『集群监控』页面,提供的不同纬度的监控信息(集群监控、节点监控、主题监控、消费组监控),即可获知集群的生产和消费情况。
集群监控的具体使用请参考:集群监控